Fetal physiology Flashcards
What type of blood to the umbilical veins and umbilical arteries carry?
Umbilical Arteries - deoxygenated blood
Umbilical Veins- oxygenated blood

How does O2 diffuse across the placenta?
Gas diffuses down partial pressure gradient
Maternal pO2 increases only marginally → in order for a gradient to establish fetal pO2 must be lower than maternal pO2
Progesterone causes a physiological hyperventilation causing respiratory alkalosis. This would normally increase maternal affinity for O2. How is this overcome?
Increased maternal production of 2,3 DPG shifts the Hb binding curve to the right

What is the structure of fetal Hb?
HbF has 2 alpha, 2 gamma subunits

Why does HbF have have greater affinity than HbA?
HbF does not bind 2,3 DPG as effectively as HbA
What is the double bohr effect seen in placental circulation?
The Double Bohr effect speeds up the process of O2 transfer
On the Maternal side: CO2 passes into intervillous blood, decreasing pH, shifting the Hb binding curve to the right. Reducing mothers affinity for O2
On the fetal side: loss of CO2 to the mother causes pH to rise shifting the fetal curve to the left. Increasing fetal affinity for O2

How is a CO2 concentration gradient established across the placenta
CO2 must move from the fetus to the mother across the placenta
Maternal hyperventilation lowers the PCO2 on the maternal side so CO2 moves from high to low concentration
What is the double Haldane effect seen in CO2 transfer across the placenta?
Maternal side: Maternal Hb gives up O2 and can accept CO2 from the placenta
Fetal side: As O2 is accepted by Hb, CO2 is given up
Which fetal shunts exists?
Ductus Venosus → bypasses blood from the liver from the placenta direct to IVC
Ductus Arteriosus → bypasses the lungs directing blood from pulmonary trunk to aorta
Foramen Ovale → bypasses the lungs from Right to Left Atrium
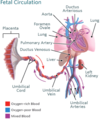
Why does blood need to bypass the liver in fetal circulation?
The liver is proportionally very large and could potetnially engulf the entire fetal circulation
Shunting blood away from the liver ensures lots of O2 in circulation for the rest of the fetal body
Explain how the shunt between right and left fetal atria creates 2 streams of blood flow?
The free border of the septum secundum forms a crest called crista dividens whic creates the 2 streams of flow
- Majority of blood flows through to the LA
- Minor flow to the RV as the muscle needs blood to push against and develop
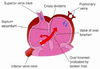
Where does the blood entering the left atrium come from?
- Majority from Right Atrium through foramen ovale
- Minority comes from pulmonary venous return (deoxygenated) → blood reaching Left Atrium is 60% saturated
What is the function of the ductus arteriosis?
Shunts blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta
Shunt joins distal to the branching that supplies the head and heart to minimise drop in O2 saturation

Explain how the fetus responds to hypoxia
- HbF increases
- Blood flow redistributed to protect the supply to the heart and brain
- Heart rate slows bradycardia to reduce O2 demand
- Fetal chemoreceptors detect decrease pO2/increased pCO2 → causes vagal stimulation leading to further bradycardia
What are the consequences of chronic hypoxia to the fetus?
- Growth restriction
- Behavioural Changes impacting development
Which hormones are necessery for fetal growth?
- Insulin
- IGF I and II
- IGF II nutrient dependent, dominant in 1st trimester
- IGF I nutrient dependent, dominant in T2 and T3
- Leptin (produced by placenta)
- EGF
- TGF alpha
With reference to cellular growth mechanisms, how does the fetus grow during pregnancy?

What is the difference between symmetrical and asymmetrical growth restriction and when in the pregnancy is the fetus susceptible to effects of malnutrition?
Symmetrical = the entire fetus is small affected by malnutrition early in the pregnancy
Asymmetrical = the head and brain grow more than the rest of the body affected by malnutriotion later in the pregnancy
How is amniotic fluid produced?
- Produced by recycling of fetal urine
- Fetus inhales amniotic fluid when practicing breathing movements
- Fetus swallows amniotic fluid
- Placenta and fetal membranes make a small volume before the kidneys are made
What is the composition of amniotic fluid?
- 98% water
- Electrolytes
- Creatinine
- Bile pigments
- Renin
- Glucose
- Hormones
- Fetal cells
- Lanugo
- Vernix Caseosa
What is meconium?
A green substance passed from the babies bowel after delivery made of debris that acculumates in the gut
If amniotic fluid appears green, what is this a sign of?
A sign of fetal distress as the meconium has been passed before delivery
What is amniocentesis?
A technique for sampling amniotic fluid that allows collection of fetal cells to use for karyotyping

Carries a minor risk of miscarriage so mothers must be warned of this
Why is physiological jaundice common in newborns?
- During gestation fetal bilirum is handled by the placenta
- Fetus cannot conjugate bilirubin
- At birth, immature liver and intestine for metabolism can lead to jaundice


