PHD - Staphylococci, Streptococci, and Enterococci (Steed) Flashcards
What is an advantage of having colonies of staph epidermidis on the skin?
Protection from staph aureus and staph pyogenes cutaneous infections
Keratinocytes that are infected with staph epidermidis produce anti-microbial peptides in response to infection. This prevents other staph from infecting the skin in that area.
What is rheumatic fever and how is it related to streptococcal infection?
Rheumatic Fever is characterized by immune-mediated damage to the heart muscle.
Streptococcal cell walls and myocardial cell surface antigens have similar proteins. Antibodies against Strep will cross-react with myocardial cells, causing heart damage.
This is a form of molecular mimicry

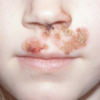
Which bacterium is always responsible for bullous impetigo?
Staph aureus
Bullous impetigo is a less contagious version of impetigo that tends to affect the face, axillae, trunk and perianal region. It may also involve mucous membranes.

Which patient population is recommended to get vaccinated with Prevnar?
Prevnar is recommended for infants as young as 2 months and for patients over 65.
This vaccine is also recommended for immunocompromised patients, patients with organ damage, and those who go to daycare.
What are the 4 major virulence factors of streptococcus pyogenes?
- M protein
- Streptolysins O and S
- Superantigenic exotoxins
- Hyaluronic capsule

Your patient is a 3-month-old infant who presents with a red rash and desquamation of the skin of the gluteal region, legs, and upper back. What is the mechanism that caused this disease process?
A. Biofilm formation
B. Enterotoxin-mediated superantigen activity
C. Exotoxin-mediated destruction of the stratum granulosum cell-cell cohesion
D. Leukocidin activity in combination with protein A activation of TNF
E. Superantigen-mediated cytokine production

C. Exotoxin-mediated destruction of the stratum granulosum cell-cell cohesion
This child has staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), which is caused by release of exfoliatins A and B. These exfoliatins interfere with cell-cell cohesion molecules in the upper layers of skin, causing desquamation and redness.
B would cause non-mentrual toxic shock syndrome and food poisoning
D is a virulence factor of Staph aureus
E would cause toxic-shock syndrome
What are the main stages of biofilm formation in Staph infections?
- Attachment of planktonic cells
- Multiplication and exodus - mediated by autolysin A
- Accumulation and formation of exopolysaccharide
- Formation of mature biofilm

What is vancomycin-intermediate staph aureus (VISA) and how is this form more difficult to treat?
VISA are staph bacteria that have an intermediate resistance to vancomycin.
Chromosomal mutations –> thicker cell wall –> traps vancomycin in cell wall and prevents it from reaching its target
What are the 4 requirements for the expression of Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1) that are provided by the use of highly absorbent tampons?
- Elevated protein
- Relatively neutral pH (6.5 to 8)
- Elevated pCO2
- Elevated pO2
1-3 are provided by the menstrual blood. 4 is caused by the tampon itself.
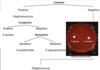
Which two Lancefield System groups contain beta-hemolytic streptococci?
A and B
A (S. pyogenes) and B (S. agalactiae) are both highly pathogenic and pyogenic.

What is the morphological difference between Staph and Strep on culture?
Staph grows in clusters
Strep grows in chains
Staphylo means cluster
Strepto means chain

What are the 3 types of carriers of staph aureus and how can this make it difficult to determine carrier status?
- Persistent carrier (~20%) - carry the same strain over time
- At increased risk of infection
- Intermittent carriers (~30%) - carry different strains over time
- Difficult to determine because there are times when this individual does not have staph present
- Non-carriers (50%)
True or False: Staphylococci are able to colonize on virtually all animals.
True
Which drugs are used to treat Staphylococcus agalactiae?
- High-dose parenteral penicillin
- Ampicillin
- Ceftriaxone

What type of hemolysis does Strep pneumoniae cause and how would this colony appear on a blood agar plate?
Alpha hemolysis
Remember that alpha hemolysis is characterized by oxidation of hemoglobin to form methemoglobin. Methemoglobin appears as green on the blood agar plate.

How is the SCCmec gene different between healthcare-associated vs. community-acquired MRSA?
- Healthcare-associated has a large SCCmec gene - means it is multi-antibiotic resistant bacteria
- Community-acquired has a small SCCmec gene - means it is resistant to only methicillin and erythromycin

What is the standard drug of choice to treat streptococcus pneumoniae? What about if the bacteria are tolerant to this drug of choice?
Penicillin
If the bacteria are tolerant or moderately resistant to Penicillin, a third-generation cephalosporin (eg ceftriaxone), should be given.
A 29-year-old male presents to the emergency department complaining of back pain. Upon physical examination, you notice facial edema and a BP of 150/95. He tells you that his urine has been a dark color recently ever since he got over a strep infection. What is this condition called and would you expect to see on a histologic section of the kidney?
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Histologic section would show immune complexes within the glomeruli. These immune complexes consist of anti-strep antibodies that cross-react with self-antigen or strep-antigen.

What are the invasive infections caused by Streptococcus agalactiae in adults?
- Pneumonia
- UTIs
- Skin/soft tissue infections (w/ or w/o osteomyelitis)
- Bacteremia (w/ or w/o endocarditis)
- Meningitis
What is one way to get around the action of bacterial beta-lactamases?
Clavulanic acid
Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Using this with penicillin or amoxicillin will help to prevent breakdown of the drug before it has a chance to work on the bacteria.
Augmentin = amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
Which specific part of the body do Staph aureus bacteria prefer to reside?
Anterior Nares
These bacteria also colonize the axillae and perineum
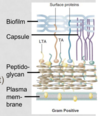
What are the 4 types of Microbial Surface Components Recognizing Adhesive Matrix Molecules (MSCRAMMs)?
- Protein A - binds Fc portion of IgG/IgM to inhibit opsonization and complement activation
- Clumping factor - binds fibrinogen and platelets
- Fibronectin-binding proteins
- Collagen-binding proteins
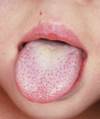
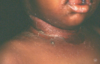
A 26-year-old female presents to you clinic complaining of pain with swallowing, a cough, and a runny nose. Upon examination, you notice that the tonsils are swollen and that there are red patches on the pharynx and uvula (seen below). What bacteria has infected your patient and what do you prescribe?

Streptococcus pyogenes
Treat with penicillin
Remember that strep. pyogenes presents as pharyngitis, skin infection, toxic shock syndrome, or necrotizing fasciitis.
What are staphylokinases and how do they contribute to staph infections?
Staphylokinases are enzymes used to break off staph cells from a cluster via fibrin lysis.
This allows single staph bacterial cells to travel and infect other parts of the body.
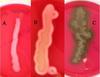
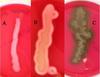
Based on the image below, which type of hemolysis is occurring in the sample labeled B?

Beta hemolysis
Notice the yellow colony growing with a clear space surrounding it. This clear space is where hemolysis of RBCs in the blood agar has occurred.

True or False: Strep viridans grows in 6.5% NaCl.
False.
Enterococcus sp. grow on 6.5% NaCl agar plates, but streptococci do not. This is a good way to differentiate between Strep and Enterococci.

What is erysipelas and which type of streptococcus causes it?
Erysipelas is a strep. pyogenes infection of the upper layers of the epidermis.
Patients will typically present with a bright red rash that has clearly demarcated lines.

How and when does late onset Strep. agalactiae present?
Within 7-90 days
Presents as meningitis and bacteremia
50% of meningitis survivors will have permanent neurologic sequelae.

You are working as a pathologist and receive a urine sample from a patient suspected of having a UTI. You begin to make bacterial cultures. You decide that you should do a blood agar and a 7.5% NaCl plate. What other type of agar should you use if you suspect that this bacteria is Staph?
Mannitol Salt Agar
Only few types of bacteria (staph and micrococcus) are able to grow in high concentrations of salt.
Mannitol and phenol red are also added to the agar. Mannitol-fermenting bacteria will produce acid upon fermentation of the sugar. Phenol Red dye change color from red to yellow in the presence of acid.

What drug is typically used to treat penicillin-resistant Staph aureus?
Vancomycin
Vancomycin generally works on all Staph. strains. However, resistance to vancomycin is becoming evident.
What are the 6 main types of invasice Staph aureus infection?
- Bacteremia/septic shock
- Endocarditis
- Osteomyelitis
- Septic arthritis
- Pneumona (often with abscess)
- Deep organ abscess

What is the basis of the Lancefield System of identification in Streptococci and Enterococci?
C-substance
The C-substance is the cell wall carbohydrate antigen
On what type of culture medium do Staphylococci typically grow best?
Blood agar with 7.5% NaCl
This type of bacteria grow best with blood agar, and will typically show up on the agar as “white streaks” because they break down blood (beta hemolytic). Some are gamma hemolytic, meaning they grow on blood agar, but don’t break down the blood.

How and when does early onset strep. agalactiae infection present?
Early onset presents within 6 days of birth
Typically presents as bacteremia and pneumonia
During vaginal delivery, Strep. agalactiae gets into the nasal, vaginal, and oral openings of the newborn.

What are superantigens and what are the two main types of superantigens involved with Staph?
Superantigens are non-antigen-specific molecules that activate T-cells and macrophages to release massive amounts of cytokines, leading to shock.
Two main types:
- Enterotoxins
- Toxic Shock Toxin-1 (TSST-1)
What is the major virulence factor of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Polysaccharide capsule
This capsule helps to evade phagocytosis by host immune cells.

Food poisoning caused by staphylococcal enterotoxins is unique and can be distinguished from a bacterial infection of the gut by what?
It does not produce fever
Staph bacteria produce enterotoxins (SEA, SEB, SEC), which cause the malaise, nausea, vomiting, and pain.
Fever is not caused because this is not technically a bacterial infection. Only toxin is involved in causing these symptoms.
What nutritional molecule is required for optimal aerobic growth of streptococci?
CO2
What are some ways to prevent the spread of MRSA?
- Handwashing
- Contact precautions - gloves, etc.
- Sparing use of antibiotics
- Detection of MRSA positive individuals
- Decolonization of carriers via mupirocin (intranasal) or chlorhexidine bathing
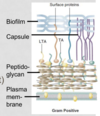
Are staphylococcus sp. gram positive or gram negative?
Gram positive
During lab analysis of a staph culture, you find that the organism is catalase positive, coagulase negative, and novobicin resistant. What specific type of Staph is this?
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
S. saprophyticus typically colonizes the rectum and urogenital tract in 5-10% of women. It is the second most common form of bacteria involved in UTI of young, sexually-active females.

What is the most common bacteria involved in urinary tract infections?
E. coli
What is the most common clinical manifestation of alpha-hemolytic streptococci (mutans, mitis, salivarius, and sanguis) in normal patients?
Dental caries
These bacteria are most commonly involved in the production of tooth decay because they form a biofilm over the teeth that leads to demineralization.

What are 2 methods of prevention that can decrease the risk of acquiring menstrual-associated toxic shock syndrome?
- Do not use hyperabsorbant tampons
- Prevent/eliminate S. aureus colonization in nares/wounds with mupirocin and/or clorhexidine bathing
What is pneumolysin, when is it released, and what does it do?
Pneumolysin is a pore-forming toxin that is released when pneumococci are lysed.
Main functions:
- Disrupts respiratory cilia
- Toxic to pulmonary endothelial cells and host phagocytes
- Damages endothelial cells along blood-brain barrier

What are the 2 main virulence factors of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
- Pneumolysin
- Neuraminidase

Why are Enterococci infections so difficult to treat?
Many types are resistant to penicillin and vancomycin.
Because these bacteria live in the GI tract, they are exposed to oral antibiotics over the lifespan of the individual. This increases the risk that these bacteria will be antibacterial resistant.
What is the importance of fibronectin-binding proteins for Staph infection of a host?
Staph bacteria use fibronectin to bind to endothelial cells. This allows them to adhere and replicate to further spread throughout the host.
What is Protein A and what is its mechanism of action?
Protein A is a PVL that activates the TNF receptor to increase cytokine release and attract WBCs.
When these cells are attracted to the area of Staph infection, the PVLs will destroy the WBCs.