Perineum 2 of 2 Flashcards
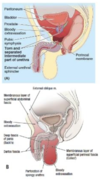
located betwen the pelvic diaphragm and theperineal membrane
- sking
- superficial fascia
- fatty layer
- membranous layer(colle’s fascia)
-
superficial perineal pouch
- located between colle’s fasica nad the perineal membrane
- anchors external genitalia
- perineal membrane
-
deep perineal pouch
- located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal menbrane
- includes external urethral sphincter
included in the external urethral sphincter
- sking
- superficial fascia
- fatty layer
- membranous layer(colle’s fascia)
-
superficial perineal pouch
- located between colle’s fasica nad the perineal membrane
- anchors external genitalia
- perineal membrane
-
deep perineal pouch
- located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal menbrane
- includes external urethral sphincter
located between the colles’ fascia and the perineal membrane
- sking
- superficial fascia
- fatty layer
- membranous layer(colle’s fascia)
-
superficial perineal pouch
- located between colle’s fasica nad the perineal membrane
- anchors external genitalia
- perineal membrane
-
deep perineal pouch
- located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal menbrane
- includes external urethral sphincter
anchors external genitalia
- sking
- superficial fascia
- fatty layer
- membranous layer(colle’s fascia)
-
superficial perineal pouch
- located between colle’s fasica nad the perineal membrane
- anchors external genitalia
- perineal membrane
-
deep perineal pouch
- located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal menbrane
- includes external urethral sphincter
indicate the layers of the urogenital trangle
- sking
- superficial fascia
- fatty layer
- membranous layer(colle’s fascia)
-
superficial perineal pouch
- located between colle’s fasica nad the perineal membrane
- anchors external genitalia
- perineal membrane
-
deep perineal pouch
- located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal menbrane
- includes external urethral sphincter
colle’s fascia
membranous layer of the superficial fascia
What innervates the scrotum
- scrotum
- 2 layer
- pigmented skin layer
- Dartos muscle/fascia
- continuous with scarpas fascia, fat free
- smooth muscle fibers allow for cremaster reflex
- adjacent to external spermatic fascia
- septum
- 2 internal compartments, each containing teste
- innervation
- iliolinguinal
- posterior scrotal
- vasculature
- cremaster artery
- internal and external pudendal
- 2 layer

what layer is continuous with the scarpas fascia and contains smoothe muscle allowing for the cremaster reflex
- scrotum
- 2 layer
- pigmented skin layer
- Dartos muscle/fascia
- continuous with scarpas fascia, fat free
- smooth muscle fibers allow for cremaster reflex
- adjacent to external spermatic fascia
- septum
- 2 internal compartments, each containing teste
- innervation
- iliolinguinal
- posterior scrotal
- vasculature
- cremaster artery
- internal and external pudendal
- 2 layer

describe the layers and contents of the scrotum
- scrotum
- 2 layer
- pigmented skin layer
- Dartos muscle/fascia
- continuous with scarpas fascia, fat free
- smooth muscle fibers allow for cremaster reflex
- adjacent to external spermatic fascia
- septum
- 2 internal compartments, each containing teste
- innervation
- iliolinguinal
- posterior scrotal
- vasculature
- cremaster artery
- internal and external pudendal
- 2 layer

abundant in the labia majora and mons pubis, but non in scrotum
- fatty layer
- just below skin
- continuous with camper’s fascia
- abundant in labia majora and mons pubis, non in scrotum
- colles’ fascia
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel
- not anal triangle
- continues to line scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia
- extends around penis (superficial penile fascia)
- continuous with Scarpas fascia of anterior abdominal wall
-
attaches to fascia lata of thighjust distal to inguinal ligament
- NO CONTINUATION WITH LOWER LIMB
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel

in the urogenital triangle but NONE IN THE anal triangle
- fatty layer
- just below skin
- continuous with camper’s fascia
- abundant in labia majora and mons pubis, non in scrotum
- colles’ fascia
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel
- not anal triangle
- continues to line scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia
- extends around penis (superficial penile fascia)
- continuous with Scarpas fascia of anterior abdominal wall
-
attaches to fascia lata of thighjust distal to inguinal ligament
- NO CONTINUATION WITH LOWER LIMB
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel

What lines the scrotum or labia?
- fatty layer
- just below skin
- continuous with camper’s fascia
- abundant in labia majora and mons pubis, non in scrotum
- colles’ fascia
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel
- not anal triangle
- continues to line scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia
- extends around penis (superficial penile fascia)
- continuous with Scarpas fascia of anterior abdominal wall
-
attaches to fascia lata of thighjust distal to inguinal ligament
- NO CONTINUATION WITH LOWER LIMB
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel

extends around scrotum, penis, and is continuous with scarpas fascia
- fatty layer
- just below skin
- continuous with camper’s fascia
- abundant in labia majora and mons pubis, non in scrotum
- colles’ fascia
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel
- not anal triangle
- continues to line scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia
- extends around penis (superficial penile fascia)
- continuous with Scarpas fascia of anterior abdominal wall
-
attaches to fascia lata of thighjust distal to inguinal ligament
- NO CONTINUATION WITH LOWER LIMB
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel

not continuous with the lower limb.
- fatty layer
- just below skin
- continuous with camper’s fascia
- abundant in labia majora and mons pubis, non in scrotum
- colles’ fascia
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel
- not anal triangle
- continues to line scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia
- extends around penis (superficial penile fascia)
- continuous with Scarpas fascia of anterior abdominal wall
-
attaches to fascia lata of thighjust distal to inguinal ligament
- NO CONTINUATION WITH LOWER LIMB
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel

Just below the skin of the urogenital triangle, continuous with the campers fascia
- fatty layer
- just below skin
- continuous with camper’s fascia
- abundant in labia majora and mons pubis, non in scrotum
- colles’ fascia
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel
- not anal triangle
- continues to line scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia
- extends around penis (superficial penile fascia)
- continuous with Scarpas fascia of anterior abdominal wall
-
attaches to fascia lata of thighjust distal to inguinal ligament
- NO CONTINUATION WITH LOWER LIMB
- attaches to perineal membran and cover urogenital traingel

a patient has a catheter removed and during the procedure, the spongy urethra was damaged. What can potentially happen and where could it spread?
extravation of urine after rupture of spongy urethra due to injury of bulb of penis
- urine passes into the superficial perineal space
- under dartos fascia of scrotum
- around penis
- spreads upward into the anterior abdominal wall, under scarpas fascia
- DOES NOT go into the lower limb, blocked by deep fascia
infection or fluids can also move from superficial pouch to abdomen
deep fascia that sparates deep perineal pouch from superficial perineal pouch
perineal
- membrane
- deep fascia that aeparates deep perineal pouch from superficial perineal pouch
- site of attachment for external genitalia
- support of pelvic strctures
- body
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems
- perineal membran
- bulbospongiosus
- deep transverse muscle
- superficial transverse muscle
- exernal anal sphinter
- levator ani
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems

attachment for external genitalia
perineal
- membrane
- deep fascia that aeparates deep perineal pouch from superficial perineal pouch
- site of attachment for external genitalia
- support of pelvic strctures
- body
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems
- perineal membran
- bulbospongiosus
- deep transverse muscle
- superficial transverse muscle
- exernal anal sphinter
- levator ani
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems

supports pelvic structures superficial to the muscles in the pelvic outlet
perineal
- membrane
- deep fascia that aeparates deep perineal pouch from superficial perineal pouch
- site of attachment for external genitalia
- support of pelvic strctures
- body
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems
- perineal membran
- bulbospongiosus
- deep transverse muscle
- superficial transverse muscle
- exernal anal sphinter
- levator ani
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems
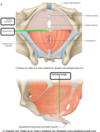
attachement point for many muscles and fascial structures
perineal
- membrane
- deep fascia that aeparates deep perineal pouch from superficial perineal pouch
- site of attachment for external genitalia
- support of pelvic strctures
- body
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems
- perineal membran
- bulbospongiosus
- deep transverse muscle
- superficial transverse muscle
- exernal anal sphinter
- levator ani
- attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perinems

helps to support pelvic viscera
perineal body is larger in females and helps to provide support for pelvic viscera
- if overstretched or torn during childbirth organ prolapse my occur
- the uerus, bladder or rectum may sag into the vagina
- response: episiotomy
- may be surgically incised during childbirth to prevent jagged tears and easier repair and healing

if damaged or overstretched during child birth what tcan happen?
perineal body is larger in females and helps to provide support for pelvic viscera
- if overstretched or torn during childbirth organ prolapse my occur
- the uerus, bladder or rectum may sag into the vagina
- response: episiotomy
- may be surgically incised during childbirth to prevent jagged tears and easier repair and healing

patient is struggling during child birth to pass the baby vaginally, what may be done to prevent loss of child and prevent organ prolapse in the future?
perineal body is larger in females and helps to provide support for pelvic viscera
- if overstretched or torn during childbirth organ prolapse my occur
- the uerus, bladder or rectum may sag into the vagina
- response: episiotomy
- may be surgically incised during childbirth to prevent jagged tears and easier repair and healing
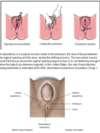
describe the contents of the supreficial perineal pouch that males and femals share
- male
- root of the penis (bulb and crura)
- probimal protino of spongy urethra
- bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus, superficial transverse perineal muscle
- deep perineal branches of internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve
- female
- crura of the clitoris and bulb of vestibule
- most distal part of the urethra and lower vagina
- bulbospongiosus, ischocavernosus, superfical transverse perineal muscle
- greater bestibular glands (barthoin’s glands and skenes glands
- deep perineal branches of inter pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve