Perineum 1 of 2 Flashcards
the region of the trunk below the pelvic diaphragm bounded by _____ _____
- perineum
- below the pelvic diaphragm
- bound by the pelvic outlet
what divides the 2 triangles?
ischial tuberosities divide the 2 triangles :
- urogenital triangle
- horizonatal
- posterior anal triangle
- almost verticle
describe the innervation, vasculature and lymphatics of the perineum
- perineum
- nerves
- pudendal nerve
- vasculature
- internal pudendal artery
- internal pudendal vein
- lymphatics
- superficial and deep inguinal nodes
- nerves
describe the two triangles and contents
- urogenital triangle
- transversed by the urethra and vagina(female)
- divided into 2 compartments by the perineal membrane
-
superficial perineal pouch
- anchors external genitalia
-
deep perineal
- includes the external urethral sphincter
-
superficial perineal pouch
- anal triangle
- tranversed by the anal canal surrounded by external anal sphincters and borderd by 2 ishianal fossae(filled with fat)
what are the main nerve and vessels to the perineum?
Pudendal nerve and internal pudendal vessels are the main nerve band blood supply of the perineum
What is the route of the pudendal nerve?
pudendal nerve
- route
- contributions from S2-S4-> pundendal nerve
- leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen
- enters the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen
- inferior to ischial spine, it enters pudendal canal
- pudendal canal is formed by the obturator internus fascia ( below pelvic diaphragm)
- accompanied by the internal pudendal artery and vein

why is the pudendal nerve called a mixed somatic nerve?
the pudendal nerve contains
- GSA and GSE
- nerves branched into
- inferior rectal nerve-GSE/GSA
- perineal nerve
- cutaneous posterior scrotal or labial branches-GSA
- deep perineal nerve-GSE/GSA(skin)
- Dorsal nerve of the penis or clitoris-GSA

Describe the branches of the pudendal nerve
- inferior rectal nerve
- go to
- external anal sphincter- (GSE)
- levator ani(GSE)
- perianal skin (GSA)
- go to
- perineal nerve
- curaneous posterior scrotal/labial branches
- go to
- posterior scrotum/labia-GSA
- go to
- Deep perineal nerve
- go to
- superficial perineal pouch-GSE
- deep perineal pouch-GSE
- external urethral sphincter-GSE
- skin of vestibule/lower vagina-GSA
- go to
- curaneous posterior scrotal/labial branches
- dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris
- GSA-sensory

DESCRIBE the sympathetic contribution to the pudendal nerve
branches of pudendal nerve- NO PSNS
- sympathetic -L1-L2)
- skin of perineum
- vessels of skeletal muscles of perineum and mucosa of lower anal canal
- erectile tissues of penis and clitoris
what is the innervation contribution of the inferior hypogastric plexus
inferior hypogastric plexus
- sympathetic(L1-L2)
-
- parasympathetis (S2-S4)
- GVA travel with PSNS (S2-S4)
- upper anal canal
- internal anal sphincter
- membranous urethra
- glands
- erectile tissues of penis and clitoris
Desrice the route, branches and location of the internal pudendal
- internal iliac ->internal pudendal , travels with the pudendal nerve
- enters pelvis through the greater sciatic, then enters the perineum through the lesser sciatic
- branches
- inferior rectal artery-> anal canal and sphincter
- perineal artery->
- posterior scrotal/labial
- perineal muscles
- terminal
- artery to the bulb of the penis or vestibule
- bulbar erectile tissues, bulbar urethra and glands in superficial pouch
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- each entering a crus (corpora cavernosa)
- essential for male erection
- dorsal artery of the penis /clitoris
- coprus spongiosum
- glans ang spongy urethra
- skin/fascia
- artery to the bulb of the penis or vestibule

describe the areas of the perineum and the venous drainage tributaries.
- deep dorsal vein
- male
- prostatic plexus and penis
- female
- vesical plexus and clitoris
- male
- superficial dorsal vein of the penis or clitoris
- penis and clitoris -> external pudendal vein (femoral vein)
- rectum->inferior rectal vein->internal pudendal
- testes/labia->posterior scrotal/labial vein->internal pudendal
- vein to bulb ofthe penis/vestibule->internal pudendal
describe the lymph flow of the perineum with exception for the testes
- superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes
- main
- testes -> lateral aortic nodes
filled with fat and loose connective tissue
- borders
- nerve and vessel content
ishioanal fossa
- filled with fat and loose connective tissue
- bordered by
- skin
- gluteus maximus
- obturator internus and fascia
- levator ani and fascia
- external anal sphincter
- lateral wall
- pudendal canal
- contains= pudendal nerve and vessel
- pudendal canal
- nerve
- crossing are inferior rectal nerves** and **vessels
- pudendal
- crossing are inferior rectal nerves** and **vessels

common site fo abscess formation
ishioanal fossae
- infection in one ishioanal fossa may spread behind the anal canal into the other ishioanal fossa

the continuation of the rectum. surrounded by(3)
anal canal
- continuation of rectuum
- surrounded by
- internal anal sphincter
- smooth muscle
- external anal sphincter
- skeletal muscle
- fat of the ishioanal fossa
- internal anal sphincter
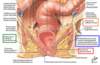
what divideds the anal canal? describe the contents
pectinate line divides the anal canal into superior and inferior
- superior
- anal column joined by anal valves
- terminal rectal vessels
- Anal sinuses
- exude mucus during defecation
- anal column joined by anal valves
- inferior
- anal pecten (transition mucosa->skin) ending at anocutaneous (white line)

mucosa above pectinate line derviced from?
- innervated
- vasculature
mucosa derived from endoderm
- nerves
- innervated by GVA fibers (S2-S4) from inferior hypogastric plexus (PAINLESS)
- vasculature
- artery
- superior reactal artery
- vein
- internal rectal venous plexus throug hthe superior rectal vein to the portal venous system
- artery
- lymphatics
- internal iliac lymph nodes

structure formed by terminal branches of superior rectal vessels
anal columns
exude mucus during defecation
anal sinuses
internal sphincter
- muscle
- nerves
internal sphincter
- smooth muscle continuous with musculature of rectum
- sympathetic and parasympathetic
- GVE from inferior hypogastric

external shpincter
- muscle
- nerves
external sphincter
- skeletal muscle
- fuses with puborectalis
- nerves
- inferior rectal nerves
- GSE
- inferior rectal nerves

below the pectinate line mucosa?
- innervation
- vasculature
below the pectinate line
- derived from the ectoderm
- innervated
- GSA fibers (S2-S4) from inferior rectal nerves (PAINFUL)
- inferior rectal nerves
- vasculature
- inferior rectal artery
- vein
- external rectal venous plexus->inferior rectal vein->caval venous system
- lymph
- drains into the superficial inguinal lymph node
portal hypertension straining or compression can lead to? compare the two types and vasculature involved
hemorrhoids
- enlarged submucosal rectal veins that are partocaval anastamoses between
- superior
- middle
- inferior rectal veins
- due to portal hypertension, straining or compression of abdominal veins during pregnancy
- type
- internal hemorrhoids-ABOVE PECTINATE LINE
- dilated superior rectal veins
- bleeds are painless
- external hemorrhoids-BELOW THE PECTINATE LINE
- dilated tributaries of inferior rectal veins
- presence of GSA=painful bleeds
- internal hemorrhoids-ABOVE PECTINATE LINE





