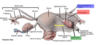
pelvis viscera 2 of 2 Flashcards
specify the location of the following
- bulbourethral glands
- seminal vesicles
- testes
- urethra
- prostatic
- membranous
- spongy (penile)
- prostate
- ductus (vas) deferens
- epididymis
- ejaculatory ducts
- perineum
- testes
- epididymus
- urethra
- membranous
- spongy (penile)
- bulbourethral glands
- pelvis
- seminal vesicles
- ejeactularoy ducts
- prostate
- urethra
- prostatic
- perinemu and pelvis
- ductus (vas) deferens

describe the contents of the testes
- location
- function
- structure
- location
- scrotum- perineum
- function
- sperm production
- produced in the seminiferous tubules
- stored
- in the body of the epididymis
- transported by the vas deferens
- a continuation of tail of theepididymic
- sperm production
- structures
- tunica albuginea
- tough outer surface of testes
- tunica vaginalis
- peritoneal sac
- visceral layer covering testes epididymis
- parietal layer adjacent to internal spermatic fascia
- cavity with small amount of liquid between parietal and visceral layers
- peritoneal sac
- tunica albuginea

tough outer surface of testes
tunica albuginea
where sperm are produced, stored, transported
- sperm
- made in the seminiferous tubules
- stored in the body of the epididymis
- transported by the vas deferens- conitnuation of epididymis
describe the embryonic descent of testes
- origination, what is carried
- testes descend from the posterior abdominal wall** through the **inguinal canal into the scrotum
- carry with them vessels, nerves, vas deferens found in the spermatic cord
- testes and spermatic cord acquire coverins from inguinal canal
- Processes vaginalis (peritoneum) close off to become the tunica vaginalis

how does the tunica vaginalis form?
processes vaginalis (peritoneum) closes off to become the tunica vaginalis

list the contents of the spermatic cord-9 total
- ductus deferens
- artery to ductus deferens
- testicular artery
- pampiniform plexus -> testicular vein
- lymphatic vessels
- autonomic nerves
- remnants of processus vaginalis
- cremasteric artery
- genital branch of genitofemoral nere
- motor component of cremaster reflex
motor component of cremaster reflex
genitofemoral nerve
list the three coverings of the spermatic cord, respectivly, and the origin of said layer
- internal spermatic fascia
- transversalis fascia
- cremaster muscles and fascia
- interal obliqu
- external spermatic fascia
- external oblique aponeurosis

describe the cremasteric reflex
stimulation to the GSA fibers of the femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve and ilioinguinal nerve, stimulates the activation of GSE fibers of genital branch of genitofemoral nerve->contraction of cremaster muscle that pulls up the ipsilateral testes
- GSA fibers of femoral branch of gentiofemoral nerve and iliolinguinal nerve
- GSE fibers of genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
- response is contraction of cremaster muscle
describe the following of the spermatic cord
- vessels
- lymphatic
- nerve
- vessels
- arterial
- testicular artery
- ductus deferens artery
- venous drainage
-
testicular vein
- receives the blood from the pampiniform plexus of veins
-
testicular vein
- arterial
- lymphatics
-
lateral aortic nodes
- in abdominal cavity
- route for testicular cancer to spread to the abdomen
-
lateral aortic nodes
- nerve
- sympathetic
- GVE
- for sperm transport and vasoconstriction
- GVA
- afferent sensory fibers
- GSE
- genitofemoral nerve to cremaster muscles of cord
- GVE
- sympathetic
accumulation of serous fluid or blood with in the cavity of the tunica vaginalis
Hydrocele and hematocele of testis
What layer acculumates fluids in the following cases of hydrocele and hematocele
hydrocele and hematocele of testis
- accumulation of serous fluid or blood within cavity of tunica vaginalis
spermatoceoele
sperm-filled cyst near the head of the epididymis; is usually asymptomatc
sperm filled cyst near the head of the epididymis
spermatocelel- ususally asymptomatic
varicocoele-of the spermatic cord
elongation and dilation of the pampiniform plexus of veins (bag of worms)
elongation and dilation of the pampiniform plexus of veins. appears as bag of worms
varicocoele- of the spermatic cord
passes through the inguinal canal, enters the abdominal cavity and courses posterior to the urinary bladder.
forms a specific ampulla at the distal end
Vas Deferens
- passes through the inguinal canal, enters the abdominal cavity and courses posterior to the urinary bladder
- at distal end form the AMPULLA OF THE DUCTUS DEFERENS
- Transmits sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
describe the following for the Vas Deferens
- function
- location (route)
vas deferens
- function
- transmits sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
- route
- epididymis
- through inguinal canal
- enters abdominal cavity
- passes posterior to the urinary bladder
- form ampulla of the ductus deferens, towards the prostate
- deferent duct (ductus deferens) merges with the seminal vesicle to generate the ejaculaory duct as it connects to the urethra
describe th following for seminal vesicles
- function
- structure
seminal vesicles
- function
- secrete seminal fluid
- contributes a thick, alkaline fluid containing fructose
- frustose is essential to spermatozoa
- contributes a thick, alkaline fluid containing fructose
- DOES NOT STORE SPERM
- secrete seminal fluid
- structure
- 2 tortuous coiled tubes that merge with the ampulla of the Vas Deferens
contributes thick, alkaline fluid contining fructose
seminal vesicles

formed by the union of the seminal veicles and the ducuts deferens
describe the route and what it bifurcates.
ejaculatory ducts
- route
- transverses the posterior part of the prostate
-
separating the prostate lobes
- MIDDLE LOBE(CENTRAL ZONE) and the POSTERIOR LOBE (PERIPHERAL ZONE)
-
separating the prostate lobes
- opens into the prostatic urethra
- transverses the posterior part of the prostate

compare the two close but different funcitons
- generates alkaline fluid to neutralize the vagina acidity
- contributes a thick, alkaline fluid containing fructose
- prostate
- produces an alkaline fluid that is added to seminal fluid to neutralize vaginal acidity
- prostatic fluids empty into the prostatic urethra throug hindividual duct openings
- seminal vesicles
- tortuous, coild tube that contributes a thick, alkaline fluid containing fructose to the seminal fluid
- does not store sperm
what structure contributes to fluids DIRECTLY into the prostatic urethra?
prostate- via the individual duct openings