Pelvic Organ prolapse Flashcards
What is the defintion of prolapse?
Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal anatomical confines
What is the defintion of female pelvic organ prolapse?
Refers to the descent of the pelvic organs towards or through the vagina
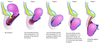
What is a urethrocele?
Prolapse of the lower anterior vaginal wall involving the urethra only

What is a cystocele?
Prolapse of the upper anterior vaginal wall involving the bladder

What is a rectocele?
Prolapse of the lower posterior wall of the vagina involving the rectum bulging forwards into the vagina

What is an enterocele?
Prolapse of the upper posterior wall of the vagina usually containing loops of small bowel
What is a uterovaginal prolapse?
This term is used to describe prolapse of the uterus, cervix and upper vagina

What are risk factors for the development of pelvic organ prolapse?
- Pregnancy and labour related issues - Large baby (>4500 gms), Prolonged Second stage, Forceps delivery, Parity
- Advanced Age
- Obesity
- Previous Pelvic Procedures
- Continence procedures - Burch culposuspension, Hysterectomy
- Hormonal Factors
- Quality of Connective Tissue
- Increased IAP - Constipation, chronic coughing
- Occupation with Heavy Lifting
- Exercise - Weight Lifting, High Impact
What are general symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse?
- Dragging sensation/Something coming down
-
Depending on site of prolapse
- Cystitis
- Frequency
- Stress incontinence
- Difficulty defecating
What are symptoms of vaginal prolapse?
- Sensation of a bulge or protrusion
- Seeing or feeling a bulge or protrusion
- Pressure
- Heaviness
- Difficulty in inserting tampons
- Dysparuenia
What are symptoms of a rectocele/Enterocele?
- Incontinence of flatus, or liquid or solid stool
- Feeling of incomplete emptying/ Straining
- Urgency
- Digital evacuation to complete defecation
- Splinting, or pushing on or around the vagina or perineum, to start or complete defecation
How would you examine someone with symptoms of a prolapse?
Left lateral side with Sim’s speculum - ask the patient to bear down

What investigations would you consider doing in a woman with pelvic organ prolapse?
- Bedside - Dipstick
- Bloods - none
- Imaging - Bladder scan, IVU/renal USS
- Other - urodynamics
What is the POPQ scoring system?
Pelvic organs prolapse quantification (POP-Q) is a standardised tool for documenting the examination findings
What is stage 0 POPQ prolapse?
No prolapse