Pathology Flashcards
Elevated CRP levels indicates what?
What does CRP stand for?
Acute inflammation
C reactive protein
What does Increased eosinophils indicate?
allergy and parasitic infections
How is haematocrit calculated?
volume RBC/volume blood
What type of tissue is this?

Smooth muscle
What does haematoxylin bind to?
Acidic or anionic structures
What type of ttissue is this?

Skeletal muscle
What colour does eosin stain?
Pink/orange
What is type III collagen also known as?
Reticulin
What is the function of myoepithelial cells?
surround some exocrine glands to squeeze out contents
What type of tissue is this?

Cardiac muscle
What is the maximum resolving power of a light microscope and of an electron microscope?
- 2 um
- 2 nm
What are simple squamous epithelia specialised for?
Diffusion and protection from abrasion

A = Z disc
B = myosin = thick filament
C = actin = thin filament
D = Sarcomere
What type of tissue is this?

Cardiac muscle
In which 4 locations are simple squamous epithelia found?
Endothelium,
mesothelium,
alveoli,
glomerulus
What type of tissue is this?

Cardiac muscle
What type of tissue is this?

Cardiac muscle
What are simple columnar epithelia specialised for?
secretion and absorption
Pink on an H and E slide indicates what kind of compound?
Cationic and eosinophilic
Between which 2 layers is the basement membrane found?
Epithelium and underlying connective tissue
What type of tissue is this?

Skeletal muscle
What are the 3 types of fibre in connective tissue?
Collagen
Elastin
Reticulin
What is the function of myofibroblasts?
pull together damaged connective tissue to promote wound healing.
Blue on an H and E slide indicates what kind of compound?
Acidic or anionic
What is the function of reticulin?
It creates a supportive network for delicate organs such as the liver
What is the function of collagen type VII
Links basement membrane to underlying connective tissue
What type of collagen is basement membrane predominantly made of?
Type IV collagen
List 3 places where type 1 collagen is found
Bone, tendons and ligaments
What does eosin bind to?
Cationic tissue (ie positively charged)
A basophilic tissue will have an affinity for which dye?
Haematoxylin
What colour will a basophilic structure stain?
Blue
Where is type II collagen found?
cartilage
What is the function of desmosomes/adherens junctions between epithelial cells?
Strong mechanical attachments between cells, linking their cytoskeletons
What are stratified squamous epithelia specialised for?
protection from abrasion
What shape is the nucleus of a fibroblast?
Elongated
What is the function of tight/occluding junctions between epithelial cells?
To seal the intercellular space to prevent passage of substances between cells
What type of tissue is this?

Smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this?
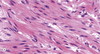
Smooth muscle
What is the ECM of connective tissue composed of?
Ground substance and fibres
What type of cell is this?
Describe 3 features that support your answer

Skeletal muscle
Striated
Multi nucleate
Peripheral nuclei
What are the 4 main functions of the basement membrane?
1) controls epithelial growth
2) selectively permeable barrier to nutrients
3) structural support
4) links epithelium to underlying tissue
What is the funciton of epithelial cilia?
Rhythmic beating for movement of eg mucus out of respiratory tract or ovum along fallopian tube
Which vitamin is required for collagen synthesis?
Vitamin C
What are stromal cells?
Supportive cells in an organ
What are the histological features of chronic ischaemia?
Fibrosis is seen microscopically only as patchy white areas
What are they typical microscopic features of a 1- to 2- day old pale infarct?
Acute inflammation
Which three substances mediate vasodilation in inflammation?
Histamine, NO, prostaglandin PGE2
What are the functions of histamine in inflammation?
1 Vasodilation
2 Endothelial contraction –> increased permeability of microcirculation
Describe the 4 steps in the mechanism of cell wall damage activating inflammation
1 Cell membrane damage activates phospholipase A2
2 Membrane lipids –> arachadonic acid
3 AA –> PG
4 PG –> leukotrienes
In inflammation, which 3 substances causes an increase in inter-endotheilal gaps?
Histamine, bradykinin and leukotrines
Where is histamine derived from?
Mast cells in pre-formed granules
Describe the arachidonic acid pathway and the action of steroids and NSAIDs
Cell membrane phospholipids -> arachidonic acid (enzyme: phosphilpase A2; activated by intracellular Ca2+; inhibited by steriods)
AA -> Prostaglandin E2 (enzymes: cyclooxygenase 1 and 2; inhibited by NSAIDs)
Define abscess
A localised collection of pus and necrotic tissue surrounded by inflamed tissues
Describe the mechanism of exudate formation
1 Vasodilation
2 Increased hydrostative pressure in capillary
3 Increased permeability of capillary wall due to contaction or retraction of endothelial cells
4 Escape of protein- and cell-rich fluid into interstitial comparment
5 Decrease in colloidal osmotic pressure
Define eedema.
Excessive fluid in interstitial compartment or body cavities
Define atrophy
A reduction in tissue or organ size due to decrease in cell size and number and thus decreased metabolic activity
A decrease in cell number due to reduced functional demand is termed what?
Involution
Define hyperplasia
Increase in cell number resulting in increased organ size/mass
List 5 ways in which necrosis and apoptosis differ
Necrosis Apoptosis
Reversibility Yes, if early No
Inflammation Yes Minimal
Area Large Small # cells
Cell swelling Yes No
Cell membrane Disrupted Intact
List the 5 commonest patterns of necrosis
Coagulative
Liquefecation
Casseous
Fat necrosis
Fibrinoid
Define hypertrophy
Increase in cell size, organ size and functional activity
Coagulative necrosis is typical of which damage to what type of organs?
Typical of infarction of solid organs (but not brain).
A red infarct typically arises from occlusion of what type of circulation?
Dual or collateral
In which organs is pale necrosis typically seen?
Seen in brain, heart, spleen and kidneys
In which organs is red infarct typically seen?
Lung, bowel and brain
Define infarction
area of necrosis caused by acute ischaemia
A pale infarct typically arises from occlusion of what type of arteries?
End arteries
What are the typical microscopic features of a 1- to 2- week old pale infarct?
Granulation tissue with macrophages, fibroblasts, lymphocytes
Define thrombus
Clotted mass of blood that forms within the cardiovascular system during life
What is involution?
A decrease in cell number due to reduced functional demand
Define dystrophic calcification and give an example
Abornal calcium depostits dye to damaged or necrotic tissue that has not been completely removed (eg atherosclerotic plaques)
What are the histological features of chronic ischaemia?
Fibrosis is seen microscopically only as patchy white areas
What are the macroscopic features of a , 1-2 old pale infarct?
Creamy yellow colour. Often in a wedge shape
What type of exudate is typically seen in the skin after a burn?
Serous exudate
When do neutrophils begin to appear in a tissue after an infarct?
About 12 hours
Which enzyme catalyses arachidonic acid –> 5-HPETE
5-lipoxygenase
Where is fibrinous exudate typically seen?
Typically seen with membrane-lined cavities such as pleura, pericardium and peritoneum
Define granuloma
A group of rounded (epithelioid) macrophages surrounding central caseous necrosis
What type of exudate is fypically seen with membrane-lined cavities such as pleura, pericardium and peritoneum?
Fibrinous exudate
How long after an infarct is scarring seen macroscopically?
6-8 weeks
What type of exudate is typically seen post a bacterial infection?
Suppurative
Fibrinous exudate is typically rich in what?
Plasma proteinssuch as fibrin
What are 4 preformed mediators in mast cells?
Histamine
Heparin
Tryptase
TNF-alpha
What effects does LTC4 cause?
Vasodilation,
diminshed cardiac output,
airway mucous,
airway oedema,
airway smooth muscle shortening
What is characterisitically present in suppurative exudate?
Neutrophils
The presence of granulation tissue suggests an infarct is how old?
Between 8-10 days and a couple of weeks
What histological feature may be a sign of atrophy or just normal wear and tear thus an old cell/tissue
Lipofuschin pigment
What type of exudate is most commonly seen in skin post burns
Serous exudate
When does atrophy of a tissue become irreversible?
When there is loss of cells and associated fibrosis
Marked infiltration with neutrophils suggests an infarcted tissue is how old?
2-3 days
What type of exudate is most commonly seen post bacterial infections?
Suppurative
What is an example of physiological metaplasia?
Cervical transformational zone during menstruation
How old is a bruise that is bluish-purple or blackish?
What chemicals give this colour?
1-2 days
deoxy and met-Hb
What are the cardinal features of inflammation?
Hot. Red. Swollen. Painful. Loss of funciton.
How old is a bruise that is greenish or yellowish?
What chemicals give this colour?
5-10 days
Biliverdin
How old is a bruise that is yellowish-brown or light brown?
What chemicals give this colour?
10-14 days
Bilirubin


