Pancreas II: Cystic Fibrosis, Cystic Disorders, Pancreatic CA Flashcards
What changes do you expect to see in the pancreas of someone with early cystic fibrosis?
Early:
• Severly Distented and inspissated (thick, dry, hard) DARK PINK SECRETIONS (this is just tenacious mucus)

What changes are seen in this late state biopsy of a CF pancreas?

Ducts that are PURPLE (b/c they are full on inspissated secretions)
• ATROPHIC ACINI - white arrows
• DYING ISLETS - black arrows
This is a late stage CF pancreas with FIbroadipose replacement of exocrine portion of the gland.

What is this?
• what would you expect to see on histology?
• What condition is this associated with?
Pancreatic pseudocysts are associated with acute pancreatitis
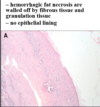
Describe the key features of the pancreatic tissue shown here.

This is pancreatic adenocarcinoma - but hard to tell from fibrosis without zooming in and seeing cellular atypia
Key features:
• Desmoplastic Response (fibrosis surrouding cancerous glands)

What is shown in this biopsy from the pancreas?
• what features would you expect to see if you zoomed out?

This is pancreatic adenocarcinoma displaying anaplastic cells with poorly formed glands
Zoomed out:
• you would see back to back glands

What pancreatic abnormalities are seen here?

Radiolucent area in the pancreas is likely cancer
What kinds of pancreatic cyst is this tissue most representative of?
• Key features?

lined by glycogen-rich cuboidal cells, and
contain clear, thin, straw-colored fluid

Shown here is a Mucinous Cyst from the pancreas.
• what key histological features would you look for?

columnar mucin-producing epithelium associated with a dense stroma similar to ovarian stroma
Thick tenacious mucin

What genes are often mutated in Mucinous Cysts?
• what mutations does this have in common with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms?
Mucinous Cysts often have mutations in KRAS and p53
IPMNs have KRAS, p53 mutations as well as GNAS mutations occasionally
What Key features are seen in this tissue?
• what is it?

Still has a somewhat mucinous epithelial lining as a Mucin Cyst but there are 2 key differences:
- No ovarian stroma behind epithelial lining
- Often involves the pancreatic duct

This tissue was taken from the pancreas, what is it?
• key features?

This is a Solid Papillary Neoplasm
• Solid and Cystic components filled with hemorrhagic debris
• Solid sheets become dishesive



