Cholestatic Diseases, Autoimmune Cholangiopathies, Structural Anomalies of the Biliary Tree Flashcards
(25 cards)
What disease of the liver is seen here?
• what would you expect to see microscopically?

Dubin Johnson (defective MRP2 to get bile to canaliculis)
Histo:
• Darkly Pigmented Cytoplasmic Granules
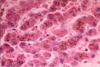
What features do you expect to see histologically in someone who is suffering from cholestatic disease?
Green granules and plugs

What are the key features of this tissue that was biopsied from the liver following a bile duct obstruction?

What has likely happened secondary to a bile duct obstruction in this patient?
• what would you expect to see histologically?

Ascending Cholangitis has been superimposed on a bile duct obstruction as a result of bacterial infiltration
**Key Histological features below:
• Neutrophils in the bile duct lining and also in the lumen

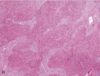
How do the histological patterns of biliary cirrhosis differ from that of other types of cirrhosis?
Biliary Cirrhosis:
• Typically has a Jigsaw-like pattern (most cirrosis is rounded)
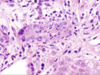
What is the appearance of the macrophages in this histology of someone suffering from chronic biliary obstruction?
• What gives them this appearance?

Macrophages = Foamy from Retained Bile Salts
What is seen at the top of this picture?
• likely cause?

Bile Infarct due to bile duct obstruction
**Remember that Mallory-Denk bodies will also likely be present in patients that have NASH and

Cholestasis of Sepsis
What are the key gross features shown here?
• what are they at risk for?

These people are at risk of Biliary Neoplasia

A neonate presents with high conjugated bilirubin and jaundice. Ultrasound rules out Biliary Atresia. What is the next most likely cause?
• Histological Appearance?
Next Most Likey = Neonatal Hepatitis
Histo:
• Multinucleated giant cells
• Lobular Dissarry, apoptosis, and necrosis
***See below
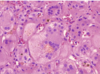
Compare the pathology on the left to the histology on the right.
• what disease process has likely occured in this neonate?

Inflammatin and Fibrosing Stricture is indicative of Biliary Atresia
What is seen here?
• Key features?

Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
• Destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts (small and medium)
• Notice lymphocytic infiltration near the biliary tract
What feature is seen in this picture of Primary Bilary Cirrhosis?
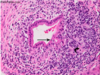
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
• Lymphocytic infiltration around the bile duct + Poorly Formed Granuloma (see curved arrow)
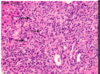
What disease is shown by this trichrome stain?
• key features?

Fibrosis can be seen in this slide of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
**Note that compensatory bile duct proliferation is also a feature of this disease***
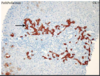
What stain can be used to see proliferating bile ducts in primary biliary cirrhosis?
• where in the portal region would you expect the staining to be strongest?
CK7 can be used to see proliferating bile ducts - proliferation will be seen in the periphery of the portal region
What feature of PBC is seen here?
Frank Cirrhosis

How would you identigy Primary Sclerosing Choleangitis on Radiograph with contrast dye in the biliary tree?
a Beads on a String appearance woul be seen

What disease is shown?
• Key features?
• Where along the biiary tree is this most likely located?
Disease:
• Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
• Onion Skinning appearance
Disease?

Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Que es?

Choledochal Cysts
• usually females under 10 with jaundice and biliary colic
• Increased risk of cancer from cholangiocarcinoma
What Is shown here?
• key features?

Von Meyenburg complex = Bile duct hamartoma
• Irregularly shaped bile ducts in the absence of inflammation
Liver Disease?

Caroli Syndrome - cysts + fibrosis
Disease(s)?
• Key features?

This is Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis - mimicks Von Meyenburg Complex
Key:
• Irregular Ducts embedded in fibrous tissue
• low power jigsaw pattern similar to secondary obstructive biliary cirrhosis - but THIS IS NOT TRUE CIRRHOSIS





