oral cavity, oropharynx and swallowing Flashcards
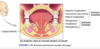
between the lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and gingiva internally.
What are the two regions of the oral cavity?
- oral cavity
- contents
-
oral vestibule
- between the lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and gingiva internally
- oral cavity proper
- internal to the teeth and gingivae
- regions
-
floor
- formed by the tongue and underlying U-shaped sublingual sulcus with muscular support provided by the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles
-
roof
- formed by the palate
-
palate
- separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity above it
-
floor
-
oral vestibule
- oral cavity opens posteriorly into the oropharynx
- is the path of a bolus of food or liquid during swallowing
- the boundary between the oral cavity and oropharynx is formed by the right and left palatoglossal arches (palatoglossal folds)
- folds of mucous membrane raised over the palatoglossus muscles
- contents
This is internal to the teeth of the gingivae.
answer the following about the regions: sttructure, supports/separates.
- oral cavity
- contents
- oral vestibule
- betwee nthe lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and gingiva internally
-
oral cavity proper
- internal to the teeth and gingivae
-
regions
-
floor
- formed by the tongue and underlying U-shaped sublingual sulcus with muscular support provided by the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles
-
roof
- formed by the palate
-
palate
- separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity above it
-
floor
- oral vestibule
- oral cavity opens posteriorly into the oropharynx
- is the path of a bolus of food or liquid during swallowing
- the boundary between the oral cavity and oropharynx is formed by the right and left palatoglossal arches (palatoglossal folds)
- folds of mucous membrane raised over the palatoglossus muscles
- contents
the oral pharynx opens posteriorly to into the ___. What is this the path for?
- oral cavity
- contents
- oral vestibule
- betwee nthe lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and gingiva internally
- oral cavity proper
- internal to the teeth and gingivae
- regions
- floor
- formed by the tongue and underlying U-shaped sublingual sulcus with muscular support provided by the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles
- roof
- formed by the palate
- palate
- separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity above it
- floor
- oral vestibule
-
oral cavity opens posteriorly into the oropharynx
- is the path of a bolus of food or liquid during swallowing
- the boundary between the oral cavity and oropharynx is formed by the right and left palatoglossal arches (palatoglossal folds)
- folds of mucous membrane raised over the palatoglossus muscles
- contents
whatt is formed by the palatoglossal arches(AKA ____)?
- oral cavity
- contents
- oral vestibule
- betwee nthe lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and gingiva internally
- oral cavity proper
- internal to the teeth and gingivae
- regions
- floor
- formed by the tongue and underlying U-shaped sublingual sulcus with muscular support provided by the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles
- roof
- formed by the palate
- palate
- separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity above it
- floor
- oral vestibule
- oral cavity opens posteriorly into the oropharynx
- is the path of a bolus of food or liquid during swallowing
-
the boundary between the oral cavity and oropharynx is formed by the right and left palatoglossal arches (palatoglossal folds)
- folds of mucous membrane raised over the palatoglossus muscles
- contents
the palatoglossal folds lay the boundary for?
what are they raised over?
- oral cavity
- contents
- oral vestibule
- betwee nthe lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and gingiva internally
- oral cavity proper
- internal to the teeth and gingivae
- regions
- floor
- formed by the tongue and underlying U-shaped sublingual sulcus with muscular support provided by the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles
- roof
- formed by the palate
- palate
- separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity above it
- floor
- oral vestibule
- oral cavity opens posteriorly into the oropharynx
- is the path of a bolus of food or liquid during swallowing
-
the boundary between the oral cavity and oropharynx is formed by the right and left palatoglossal arches (palatoglossal folds)
- folds of mucous membrane raised over the palatoglossus muscles, responsible for raising the back part of the tongue
- contents
describe the following
- V-shaped portion on the tongue
- small pit, at its angle. embryological origin of thy thyroid gland
- sulcus terminalis
- V-shaped portion on postterior portion of tongue with foramen cecum, small pit, at angle
- foramen cecum
- indicates the site of embryological orgin of the thyroid gland
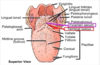
what is the foramen cecum important for?
- sulcus terminalis
- V-shaped portion on postterior portion of tongue with foramen cecum, small pit, at angle
-
foramen cecum
- indicates the site of embryological orgin of the thyroid gland

what portions of the tongue are extremely mobile?
Describe the structure connecting the inferior surface of the tongue to the floor of the oral cavity
tongue
-
anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
-
lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
- innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
- filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
- vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
- innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
- vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis

Describe the innervation of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
-
innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
- filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
- vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
- innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
- vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis

GSA from the lingual branch of the mandibular nerve and SVA from the chordatympani nerve VII innervate what structure of the face?
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
-
innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
- filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
- vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
- innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
- vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis

there are several taste buds on the dorsal body, describe them and give location if important.
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
- innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
-
fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
-
filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
-
vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
-
fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
- innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
- vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis

describe the lingual taste buds : fungiform, filiform, vallate
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
- innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
-
surface - dorsal body
-
lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
-
contain taste buds
-
fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
-
filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
-
vallate papillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
-
fungiform pappillae
-
contain taste buds
-
lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
- innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
- vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis

What is the posterior 1/3 of the tongue located in? describe th lingual papillae here.
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
- innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
- filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
- vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
-
posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
- innervation
- receives GVA and SVA (sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
- vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis

describ e the innervation to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
- innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
- filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
- vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
-
innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
-
vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis
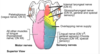
what portion of the face receive the following?
- GVA/SVA from the
- glossopharyngeal nerve IX
- Vagus neve X
tongue
- anterior2/3 - body and apex = extremely mobile
- body of the tongue
- anterior tip-apex
- lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the oral cavity by a midline fold of the mucous membrane
- innervation
- receives GSA from lingual branch of the mandibular nerve V3
- taste SVA from chorda tympani nerve VII
- surface - dorsal body
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- contain taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- appear grossly as scattered red spots among filiform papillae
- filiform papillae
- most numerous of the lingual papillae
- responsible for giving the tongue texture
- vallate ppapillae
- ro of 8-12 large cylindrival flattened structures anterior and parallell to the sulcus terminalis.
- carry taste buds
- fungiform pappillae
- contain taste buds
- lingual papillae -small projections of mucous membrane
- posterior 1/3
- root of the tongue
- located in the oropharynx
- has no lingual papillae, but has an irregular surface due to lymphod nodules of the ligual tonsils.
-
innervation
- receives GVA and SVA(sensattion) from the glossopharyngeal nerveIX
-
vagus nerve X conttributtes slightly to sensation
- SVA and GVA at the root of the tongue and epiglottis
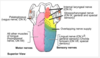
describe the structures with respect to the inferior surface of the tongue
- provide rapid drug absorption
- located on each side of the base of the lingual frenulum
- inferior surface of the tongue
- deep lingual veins
- provide rapid absorption of drugs
- nitroglycerin
- provide rapid absorption of drugs
- sublingual papillae (sublingual caruncle)
- located on each side of the base of the lingual frenulum
- contains the opening of the submandibular duct
- deep lingual veins

descirbe the structures with respect to the inferior surface of the tongue
- deep lingual veins
- sublingual papillae
- inferior surface of the tongue
- deep lingual veins
- provide rapid absorption of drugs
- nitroglycerin
- provide rapid absorption of drugs
- sublingual papillae (sublingual caruncle)
- located on each side of the base of the lingual frenulum
- contains the opening of the submandibular duct
- deep lingual veins

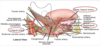
list the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
-
intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
-
muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
-
extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
-
muscles
-
hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
-
styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
-
genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
-
palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
-
hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

describe the disease/conditions to be considered for hypoglossal nerve and genioglossus muscle
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
- hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
- styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
- genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
- palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
- hyoglossus
-
disease
-
hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
-
supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
-
hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

describe the presentation of a patient with a hypoglossal nerve lession.
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
- hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
- styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
- genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
- palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
- hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

describe the concern with an unconsious person, with regard to the tongue muscles
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
- hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
- styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
- genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
- palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
- hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
-
supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation
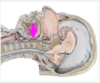
list the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
-
intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
-
muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
-
extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
-
muscles
-
hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
-
styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
-
genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
-
palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
-
hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation
describe the innervation of the tongue
- muscles of the tongue
-
innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
-
vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
- hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
- styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
- genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
- palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
- hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaxed genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
-
innervation

describe the function of the intrinic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
extrinsic: styologlossus, hyoglossus, genioslossus
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
-
function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
-
function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
-
hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
-
function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
-
styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
-
function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
-
genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
-
funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
-
palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
-
function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
-
hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

which muscle(s) are responsible for the following with respect to the tongue:
- change the tongues SHAPE
- changes the tongues POSITION
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
-
intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
-
function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
-
extrinsic
- have external attachments
-
function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
- hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
- styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
- genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
- palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
- hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

Which muscles are involved in the following actions with respect to the tongue muscles.
- depresses the tongue
- Elevates and Retracts the tongue
- protrudes the tongue
- known more for the interaction with the soft palate
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
-
hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
-
function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
-
styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
-
function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
- genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
-
funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
-
palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
-
hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

describe the muscles of the tongue based on following details
- interdigitate wit hthe styloglossus. Thin, quadrilateral. Ascending from the hyoid bone
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus. Descends anteriomedially into the tonguefrom the styloid process.
- Fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styoglossus. Originates from tthe superior mental spine.
- Innervated by the vagus. Passes from the soft palate into the tongue.
- muscles of the tongue
- innervation
- all by the GSE fibers of the hypoglossal nerve XII
- vagus nerve
- palatoglossus
- intrinsic
- contained entirely within the tongue
- function
- change the tongues shape
- muscles
- superior longitudinal
- transverse and vertical
- inferior longitudinal
- extrinsic
- have external attachments
- function
- change the tongues position
- help change its help
- muscles
-
hyoglossus
- interdigitate with the styloglossus
- thin, quadrilateral
- ascending from the hyoid bone
- function
- DEPRESSES THE TONGUE
-
styloglossus
- interdigitate with the hyoglossus
- descends anteriomedially into the tongue from the styloid process
- function
- ELEVATES and RETRACTS THE TONGUE
-
genioglossus
- fan shaped muscle located medial to the hypoglossus and styloglossus
- originates from the superior mental spine
- funtion
- PROTRUDES THE TONGUE
-
palatoglossus
- innervated by the vagus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- function
- helps to depress the soft palate
- better known for its contribution to the soft palate
-
hyoglossus
- disease
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- protruded tongue deviates TOWARD the side of the lesion
- supine unconsiuous person
- relaced genioglossus muscles allow the tongue to fall posteriorly. This obstructs the airway with danger of suffication.
- hypoglossal nerve lesion
- innervation

Describe the blood supply to the tongue
- artery?
- pathway?
-
blood supply to the tongue
-
lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
-
divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
-
anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
-
anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
-
lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins

the lingual artery courses ________ to the hypoglossal muscle
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins

describe the division of the lingual artery with ______ muscle.
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
-
divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
-
anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
-
anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins

why does the tongue bleed profusely when lacerated?
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- the tongue has a rich blood supply and may bleed profusely if lacerated
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins
describe the venous drainage of the oral cavity
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
-
venous drainage
-
veins
-
deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
-
sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
-
dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
-
deep lingual
-
veins

deep lingual vein passes where to join with the _____ vein?
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins

form a vein that accompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
-
sublingual
- form a vein that accompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins
run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
-
dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins

describe the pathway of the following vein:
deep lingual
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
-
deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
-
deep lingual
- veins

describe the pathway of the following vein:
sublingual
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
-
sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins
describe the pathway of the following vein:
dorsal lingual veins
- blood supply to the tongue
- lingual artery
- branches from the carotid artery
- courses MEDIAL (deep) to the hyoglossus muscle
- divides into three parts with respect to the hyoglossus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- deep lingual artery -> apex of the tongue
- sublingual artery->sublingual sulcus
- anterior aspect of the hyoglossus ( 3rd division) = terminal branches
- lingual artery
- venous drainage
- veins
- deep lingual
- passes posteriorly o nthe undersurface of the tongue joining the sublingual
- sublingual
- form a vein tha taccompanies the hypoglossal nerve LATERAL to the hyoglossus muscle
-
dorsal lingual
- run with the lingual artery MEDIAL to the hyoglossus muscle
- deep lingual
- veins

Describe the innervation of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
tongue parasympathetic innervation
- submandibular ganglion
- PSNS ganglion
- travels with the lingual nerve from the chorda tympani VII
- suspended from the lingual nerve of its side
- receives preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from chorda tympani VII
- nerve cell bodies in the ganlion send POSTGANGLIONIC PSNS fibers to
- submandibular sailavry glands
- sublingual salivary glands
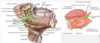
describe the pathway of the preganglionic PSNS fibers generating the submandibular ganglion
tongue parasympathetic innervation
- submandibular ganglion
- PSNS ganglion
- travels with the lingual nerve from the chorda tympani VII
- suspended from the lingual nerve of its side
- receives preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from chorda tympani VII
- nerve cell bodies in the ganlion send POSTGANGLIONIC PSNS fibers to
- submandibular sailavry glands
- sublingual salivary glands

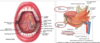
describe the contents and regions of the palate
- palate
-
consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
-
anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
-
posterior 1/3 soft palate
-
features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
-
uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
-
fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
-
muscles
-
levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
-
tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
-
palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
-
palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
-
musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
-
levator veli palitini
-
features
-
consists of the
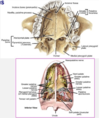
describe the following with respect to the hard palate
- what portion of the palate?
- palatine processes of the _____
- ______ _____ of the palatine bones
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
-
anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the
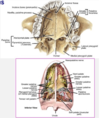
what meets at the transcverese palatine suture?
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatine foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

- what do thepalatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meet at?
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meet at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

describe the following with respect to the hard palate
- incisive fossa-3 parts
- what part is medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- what part is piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone?
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
-
incisive fossa
- anterior midline
-
greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
-
lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

answer the following with regard to the hard palate
- three regions make the ______ ______
- location of the greater palatine foramen
- location of the lesse palatine foramina
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
-
incisive fossa
- anterior midline
-
greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
-
lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

answer the following with respect to the muscles of the soft palate.
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
-
levator veli palitini
-
function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
-
function
-
tensor veli palatini
-
function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
-
function
-
palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
-
levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

answer the following with respect to the soft palate
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- associated with the uvula
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
-
palatopharyngeus
-
function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
-
function
-
musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- what are the features
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin?
- provide muscle attachments?
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
-
features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
-
uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
-
fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
- muscles
- levator veli palitini
- function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
- function
- tensor veli palatini
- function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
- function
- palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
- palatopharyngeus
- function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
- function
- musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
- levator veli palitini
-
features
- consists of the
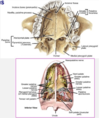
list the function of the following muscles
- levator veli palitini
- ttensor veli palatini
- palatoglossus
- palatopharyngeus
- musculus uvulae
- palate
- consists of the
- roof of the oral cavity + oropharynx
- anterior 2/3 = hard palate
- palatine processes of the maxillae
- horizontal plates of the palatine bones
- features
- palatine processes of the maxillae and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones meett at the transverse palatine suture
- incisive fossa
- anterior midline
- greater palatinve foramen
- medial to each maxillary 3rd molar
- lesser palatine foramina
- piercing the pyramidal process of the palatine bone
- posterior 1/3 soft palate
- features
- suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate
- uvula
- conical process hanging from the middle of its posterior free margin
- fibrous palatine aponeurosis
- strengthen and provide muscle attachments
- covering mucous membran has abundant mucous glands
-
muscles
-
levator veli palitini
-
function
- ELEVATES SOFT PALATE INTO CONTACT WITH THE POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
-
function
-
tensor veli palatini
-
function
- TENSES SOFT PALATE + OPENS AUDITORY TUBES
-
function
-
palatoglossus
- passes from the soft palate into the tongue
- helps DEPRESS THE SOFT PALATE
-
palatopharyngeus
-
function
- ELEVATES THE PHARYNX + PULLS THE WALL ANTERIOR +DEPRESS SOFT PALATE
-
function
-
musculus uvulae
- associated with the uvula
-
levator veli palitini
- features
- consists of the

describe the innervation of muscles of the soft palate.
- innervation
-
GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
-
vagus nerve X
- through the pharyngeal plexus except for the tensor veli palatini
-
veli palatini
- mandibular nerve V3
-
vagus nerve X
- sensory innervation
- from nasophalatine nerves + greater palatine nerves + lesser palatine nerves
- all originate from the maxillary nerveV2
-
GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- blood supply
- arteries
- greater palatine artery
- from the maxillary artery
- from the external carotid
- from the maxillary artery
- lesser palatine artery
- from the ascending palatine artery
- from the facial artery
- from the external carotid
- from the facial artery
- from the ascending palatine artery
- on the superior side, partly fro mthe ascending palatine branch of the facial artery and the palatine branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery
- greater palatine artery
- venous
- arteries

describe the sensory innervation involved with the soft palate
- innervation
- GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- vagus nerve X
- through the pharyngeal plexus except for the tensor veli palatini
- veli palatini
- mandibular nerve V3
- vagus nerve X
-
sensory innervation
- from nasophalatine nerves + greater palatine nerves + lesser palatine nerves
- all originate from the maxillary nerve V2
- GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- blood supply
- arteries
- greater palatine artery
- from the maxillary artery
- from the external carotid
- from the maxillary artery
- lesser palatine artery
- from the ascending palatine artery
- from the facial artery
- from the external carotid
- from the facial artery
- from the ascending palatine artery
- on the superior side, partly fro mthe ascending palatine branch of the facial artery and the palatine branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery
- greater palatine artery
- venous
- arteries

describe the two main arteries involved in the palatine artery.
- innervation
- GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- vagus nerve X
- through the pharyngeal plexus except for the tensor veli palatini
- veli palatini
- mandibular nerve V3
- vagus nerve X
- sensory innervation
- from nasophalatine nerves + greater palatine nerves + lesser palatine nerves
- all originate from the maxillary nerveV2
- GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- blood supply
-
arteries
-
greater palatine artery
-
from the maxillary artery
- from the external carotid
-
from the maxillary artery
-
lesser palatine artery
-
from the ascending palatine artery
-
from the facial artery
- from the external carotid
-
from the facial artery
-
from the ascending palatine artery
- on the superior side, partly fro mthe ascending palatine branch of the facial artery and the palatine branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery
-
greater palatine artery
- venous
-
arteries
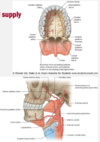
the muscle of the soft palate receive blood supply from what arteries?
They start with the external carotid?
- innervation
- GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- vagus nerve X
- through the pharyngeal plexus except for the tensor veli palatini
- veli palatini
- mandibular nerve V3
- vagus nerve X
- sensory innervation
- from nasophalatine nerves + greater palatine nerves + lesser palatine nerves
- all originate from the maxillary nerveV2
- GSE innervation to the muscles of the soft palate
- blood supply
-
arteries
-
greater palatine artery
-
from the maxillary artery
- from the external carotid
-
from the maxillary artery
-
lesser palatine artery
-
from the ascending palatine artery
-
from the facial artery
- from the external carotid
-
from the facial artery
-
from the ascending palatine artery
- on the superior side, partly fro mthe ascending palatine branch of the facial artery and the palatine branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery
-
greater palatine artery
- venous
-
arteries

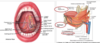
describe the pharynx.
-
pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
-
content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
- usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils
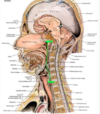
what are the subdivisions of the pharynx
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
-
subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
- usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils

lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue. describe the extension.
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
-
oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
- usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils

describe the contents of the oropharynx
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
-
oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
-
contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
- usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils
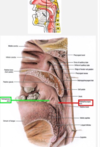
what are the tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
- usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils

in the lateral wall of the oropharynx.answer the following:
- between?
- what are the folds?
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
-
palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
-
in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
- usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
-
palatine tonsils

describe the palantine tonsils with age.
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
-
usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils

tonsilectomy can lead to injusry and heavy bleeding of what items?
- pharynx
- common chamber of the respiritory and digestive system
- content
- musculofibrous tube extending from the base of the skull to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
- subdivision
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- oropharynx
- lies behind the oral cavity and dorsum of the tongue
- extends from the soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
- contents
- palatoglossal
- palatopharyngeal arches in its lateral walls
- palatine tonsils between the folds
- lingual tonsils on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- tonsils
- palatine tonsils
- occupies the tonsillar fossa (tonsillar bed)
- in the lateral wall of the oropharynx between the palatoglossal fold anteriorly and palatopharyngeal fold posteriorly
- folds are the pillars of the fauces
-
usually atrophy with age but often are a site of infections in children
- during surgical removal (tonsilectomy), heavy bleeding from the tonsillar artery or paratonsillar vein or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX may occur
- palatine tonsils
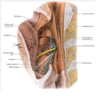
food or other foreign objects may become trapped in
food or other foreign objects may become trapped in depressions in valleculae, between the tongue and epiglottis on either side of the median glossoepiglottic fold.

describe the location valleculae
food or other foreign objects may becomettrapped in depressions in valleculae, between the tongue and epiglottis on either side of the median glossoepiglottic fold.
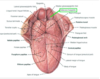
describe the layers of the pharynx.
wall of the pharynx
- contents
-
four layers-from internal to external
-
mucous membrane
- continuous with that lining the oral and nasal cavities, auditory tubes and larynx
- submucosa
- muscular layer
- buccophryngeal fascia
-
mucous membrane
-
four layers-from internal to external
- retropharyngeal space
- behind the pharynx
- disease
- site of abcess formation
- producing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- if the abscess ruptures the pharyngeal wall, it may enter the larynx and cause aspiration pneumonia
- is a pathway for the spread of infection into the thorax, producing life-threatening mediastinitis
- site of abcess formation
what is the space behind the pharynx? What important pathologies are possible here?
wall of the pharynx
- contents
- four layers-from internal to external
- mucous membrane
- continuous with that lining the oral and nasal cavities, auditory tubes and larynx
- submucosa
- muscular layer
- buccophryngeal fascia
- mucous membrane
- four layers-from internal to external
-
retropharyngeal space
- behind the pharynx
- disease
-
site of abcess formation
- producing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- if the abscess ruptures the pharyngeal wall, it may enter the larynx and cause aspiration pneumonia
- is a pathway for the spread of infection into the thorax, producing life-threatening mediastinitis
-
site of abcess formation

what is the mucous membrane continuous with?
wall of the pharynx
- contents
- four layers-from internal to external
-
mucous membrane
- continuous with that lining the oral and nasal cavities, auditory tubes and larynx
- submucosa
- muscular layer
- buccophryngeal fascia
-
mucous membrane
- four layers-from internal to external
- retropharyngeal space
- behind the pharynx
- disease
- site of abcess formation
- producing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- if the abscess ruptures the pharyngeal wall, it may enter the larynx and cause aspiration pneumonia
- is a pathway for the spread of infection into the thorax, producing life-threatening mediastinitis
- site of abcess formation

describe the complications invovled in a patient with abscess formation in the retropharyngeal space.
wall of the pharynx
- contents
- four layers-from internal to external
- mucous membrane
- continuous with that lining the oral and nasal cavities, auditory tubes and larynx
- submucosa
- muscular layer
- buccophryngeal fascia
- mucous membrane
- four layers-from internal to external
- retropharyngeal space
- behind the pharynx
- disease
-
site of abcess formation
- producing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- if the abscess ruptures the pharyngeal wall, it may enter the larynx and cause aspiration pneumonia
- is a pathway for the spread of infection into the thorax, producing life-threatening mediastinitis
-
site of abcess formation
retropharyngeal space can be a space for what to spread?
wall of the pharynx
- contents
- four layers-from internal to external
- mucous membrane
- continuous with that lining the oral and nasal cavities, auditory tubes and larynx
- submucosa
- muscular layer
- buccophryngeal fascia
- mucous membrane
- four layers-from internal to external
- retropharyngeal space
- behind the pharynx
- disease
- site of abcess formation
- producing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- if the abscess ruptures the pharyngeal wall, it may enter the larynx and cause aspiration pneumonia
- is a pathway for the spread of infection into the thorax, producing life-threatening mediastinitis
- site of abcess formation
list the the external circular layer of teh pharynx muscles
- muscles of the pahrynx
-
external circular layer
-
superior pharyngeal constrictor
- insert
- into the base of the skull + median fibrous raphe
- insert
-
middle pharyngeal constrictor
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
-
inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
- cricopharyngeus muscle
- lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- function
- acts as the upper esophageal sphincter
- relaxes for food to pass from the pharynx into the esophagus during swallowing
- normally prevents food that is regurgitated into the esophagus past an incompettent lower esophageal sphincter from entering the pharynx
-
superior pharyngeal constrictor
- internal longitudinal layer
- stylopharyngeus
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
- salpingopharyngeus
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
- palatopharyngeus
- origin
- in the soft palate
- insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
- origin
- stylopharyngeus
-
external circular layer
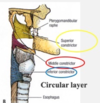
list the internal longitudinal layer of the pharynx
- muscles of the pahrynx
- external circular layer
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
- insert
- into the base of the skull + median fibrous raphe
- insert
- middle pharyngeal constrictor
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
- inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
- cricopharyngeus muscle
- lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- function
- acts as the upper esophageal sphincter
- relaxes for food to pass from the pharynx into the esophagus during swallowing
- normally prevents food that is regurgitated into the esophagus past an incompettent lower esophageal sphincter from entering the pharynx
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
-
internal longitudinal layer
-
stylopharyngeus
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
-
salpingopharyngeus
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
-
palatopharyngeus
- origin
- in the soft palate
- insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
- origin
-
stylopharyngeus
- external circular layer

list the muscles with the following description with respect to the pharynx
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
- lower portion of this muscle
- list the function of this muscle
- lower portion of this muscle
- muscles of the pahrynx
-
external circular layer
-
superior pharyngeal constrictor
-
insert
- into the base of the skull + median fibrous raphe
-
insert
-
middle pharyngeal constrictor
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
-
inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
-
cricopharyngeus muscle
- lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
-
function
- acts as the upper esophageal sphincter
- relaxes for food to pass from the pharynx into the esophagus during swallowing
- normally prevents food that is regurgitated into the esophagus past an incompettent lower esophageal sphincter from entering the pharynx
-
superior pharyngeal constrictor
- internal longitudinal layer
- stylopharyngeus
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
- salpingopharyngeus
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
- palatopharyngeus
- origin
- in the soft palate
- insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
- origin
- stylopharyngeus
-
external circular layer
list the important details of the following muscles in the external circular layer
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
- middle pharyngeal constrictor
- inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- cricopharyngeus
- muscles of the pahrynx
-
external circular layer
-
superior pharyngeal constrictor
-
insert
- into the base of the skull + median fibrous raphe
-
insert
-
middle pharyngeal constrictor
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
-
inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
-
cricopharyngeus muscle
- lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
-
function
- acts as the upper esophageal sphincter
- relaxes for food to pass from the pharynx into the esophagus during swallowing
- normally prevents food that is regurgitated into the esophagus past an incompettent lower esophageal sphincter from entering the pharynx
-
superior pharyngeal constrictor
- internal longitudinal layer
- stylopharyngeus
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
- salpingopharyngeus
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
- palatopharyngeus
- origin
- in the soft palate
- insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
- origin
- stylopharyngeus
-
external circular layer

list the muscles of the internal longitudinal layer given the following detail
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
- origin
- in the soft palate
- insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
- muscles of the pahrynx
- external circular layer
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
- insert
- into the base of the skull + median fibrous raphe
- insert
- middle pharyngeal constrictor
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
- inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
- cricopharyngeus muscle
- lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- function
- acts as the upper esophageal sphincter
- relaxes for food to pass from the pharynx into the esophagus during swallowing
- normally prevents food that is regurgitated into the esophagus past an incompettent lower esophageal sphincter from entering the pharynx
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
-
internal longitudinal layer
-
stylopharyngeus
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
-
salpingopharyngeus
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
-
palatopharyngeus
-
origin
- in the soft palate
-
insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
-
origin
-
stylopharyngeus
- external circular layer
list the important detail of the internal longitudinal layer of the pharynx muscles
- stylopharyngeus
- salpingopharyngeus
- palatopharyngeus
- muscles of the pahrynx
- external circular layer
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
- insert
- into the base of the skull + median fibrous raphe
- insert
- middle pharyngeal constrictor
- ovelap the superior constrictors above
- inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- overlap the middle constrictors above and are continuous inferiorly with muscle of the esophagus
- cricopharyngeus muscle
- lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- function
- acts as the upper esophageal sphincter
- relaxes for food to pass from the pharynx into the esophagus during swallowing
- normally prevents food that is regurgitated into the esophagus past an incompettent lower esophageal sphincter from entering the pharynx
- superior pharyngeal constrictor
-
internal longitudinal layer
-
stylopharyngeus
- passes between the superior and middle constrictors
-
salpingopharyngeus
- descends from the auditory tube cartilage
-
palatopharyngeus
-
origin
- in the soft palate
-
insert
- with the stylopharyngeus into the thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
-
origin
-
stylopharyngeus
- external circular layer

supply motor innervation to the stylopharyngeus muscles
pharynx innervation
-
glossopharyngeal nerves CN IX
- supply motor innervation to the stylopharyngeus muscles
- pharyngeal plexus
- nerves formed by branches of the
- sensory - green
- glossopharyngeal nerves
- motor - pink
- vagus CN X
- motor to all of the musclse except the stylopharyngeus
- vasomotor - blue
- superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
- sensory - green
- nerves formed by branches of the
describe the pharyngeal plexus contributions
pharynx innervation
- glossopharyngeal nerves CN IX
- supply motor innervation to the stylopharyngeus muscles
-
pharyngeal plexus
-
nerves formed by branches of the
-
sensory - green
- glossopharyngeal nerves
-
motor - pink
- vagus CN X
- motor to all of the musclse except the stylopharyngeus
-
vasomotor - blue
- superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
-
sensory - green
-
nerves formed by branches of the

describe the epiglottis movement.
epiglottic cartilage
- covered by mucous membrane to form the epiglottis
- pushed back and down over the laryngeal inlet and the vocal folds are adducted to prevent the entrance of food or drink into the larynx and trachea during swallowing

describe the three phases of deglitition.
deglutition (swallowing)
- process that transfers a food bolus from the mouth through pharynx and esophagus into the stomach. solid food is masticated (chewed) and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow.
-
3 stages
-
stage 1- voluntary
- bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate(ORAL PHASE)
-
stage 2-involuntary and rapid
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx (PHARYNGEAL PHASE)
-
Stage 3-involuntary
- sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach (ESOPHAGEAL PHASE)
-
stage 1- voluntary
- Disease
- Dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- usually caused by nerve or muscle problems
- may occur after
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
- Dysphagia

which phase of deglutition is described below?
bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate
deglutition (swallowing)
- process that transfers a food bolus from the mouth through pharynx and esophagus into the stomach. solid food is masticated (chewed) and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow.
- 3 stages
-
stage 1- voluntary
- bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate(ORAL PHASE)
- stage 2-involuntary and rapid
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx (PHARYNGEAL PHASE)
- Stage 3-involuntary
- sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach (ESOPHAGEAL PHASE)
-
stage 1- voluntary
- Disease
- Dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- usually caused by nerve or muscle problems
- may occur after
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
- Dysphagia
which phase of deglutition is described below?
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx
deglutition (swallowing)
- process that transfers a food bolus from the mouth through pharynx and esophagus into the stomach. solid food is masticated (chewed) and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow.
- 3 stages
- stage 1- voluntary
- bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate(ORAL PHASE)
-
stage 2-involuntary and rapid
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx (PHARYNGEAL PHASE)
- Stage 3-involuntary
- sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach (ESOPHAGEAL PHASE)
- stage 1- voluntary
- Disease
- Dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- usually caused by nerve or muscle problems
- may occur after
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
- Dysphagia

Which phase of deglutition is described below?
sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach
deglutition (swallowing)
- process that transfers a food bolus from the mouth through pharynx and esophagus into the stomach. solid food is masticated (chewed) and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow.
- 3 stages
- stage 1- voluntary
- bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate(ORAL PHASE)
- stage 2-involuntary and rapid
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx (PHARYNGEAL PHASE)
-
Stage 3-involuntary
- sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach (ESOPHAGEAL PHASE)
- stage 1- voluntary
- Disease
- Dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- usually caused by nerve or muscle problems
- may occur after
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
- Dysphagia
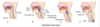
What is the an issue accompanied with the following implications
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
deglutition (swallowing)
- process that transfers a food bolus from the mouth through pharynx and esophagus into the stomach. solid food is masticated (chewed) and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow.
- 3 stages
- stage 1- voluntary
- bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate(ORAL PHASE)
- stage 2-involuntary and rapid
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx (PHARYNGEAL PHASE)
-
Stage 3-involuntary
- sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach (ESOPHAGEAL PHASE)
- stage 1- voluntary
- Disease
-
Dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- usually caused by nerve or muscle problems
-
may occur after
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
-
Dysphagia

discuss some issue that may lead to dysphagia
deglutition (swallowing)
- process that transfers a food bolus from the mouth through pharynx and esophagus into the stomach. solid food is masticated (chewed) and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow.
- 3 stages
- stage 1- voluntary
- bolus is compressed against the palate and pushed from the mouth in to the oropharynx, mainly by the coordinated movements of muscles of the tongue and soft palate(ORAL PHASE)
- stage 2-involuntary and rapid
- soft palate is elevated sealing off the nasopharynx from tthe ororpharynx and laryngopharynx.
- the pharynx widens and shortens to receive the bolus as the suprahyoid muscles and the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles contract, elevating larynx (PHARYNGEAL PHASE)
-
Stage 3-involuntary
- sequential contraction of all 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles forces the food bolus inferioly into the esophagus and propelled by persistalsis into the stomach (ESOPHAGEAL PHASE)
- stage 1- voluntary
-
Disease
-
Dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- usually caused by nerve or muscle problems
-
may occur after
- a stroke
- throat and mouth cancer
- GERD
- several different neurological disorders
-
Dysphagia



