Nose Flashcards
(54 cards)
list the following with respect to the external nose
- nasal bones
- frontal processes of the ______
- join the nasal septal cartilage in the midline
- cartilage
- name of the air space housed by the external nose
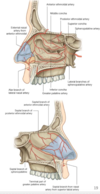
external nose
- 2 nasal nasal bones
- frontal processes of the maxillae
- 2 lateral nasal septal cartilages
- join the nasal septal cartilage in the midline
- 2 c-shapped major alar carttilages and 2-4 minor alar cartilages
air space housed by the external nose is known as the vestibule

muscles of the external nose are innervated
- muscles of the external nose are innervated by facial nerve
- skin of external nose is innervated by
- trigeminal nerve
- infratrochlearV1
- external nasal V1
- infraorbital V2
- trigeminal nerve
- external nose is supplied blood via
- facial - lateral nasal
- ophthalmis a - dorsal nasal and external nasal

skin of external nose is innervated by
- muscles of the external nose are innervated by facial nerve
-
skin of external nose is innervated by
-
trigeminal nerve
- infratrochlearV1
- external nasal V1
- infraorbital V2
-
trigeminal nerve
- external nose is supplied blood via
- facial - lateral nasal
- ophthalmis a - dorsal nasal and external nasal

external nose is supplied blood via
- muscles of the external nose are innervated by facial nerve
- skin of external nose is innervated by
- trigeminal nerve
- infratrochlearV1
- external nasal V1
- infraorbital V2
- trigeminal nerve
-
external nose is supplied blood via
- facial - lateral nasal
- ophthalmis a - dorsal nasal and external nasal

descfribe the bones involved in the formation of the nose and nasal cavity

describe the lateral skeleton of the nasal wall
- nasal skeleton
-
lateral nasal wall
- ethmoid
- inferior concha
- maxillary
- lacimal
- palatine
- sphenoid
- nasal
- frontal/alar
- lateral septal cartilages
- medial nasal wall
- ethmoid
- vomer
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- maxillary
- palatine
- septal cartilage
- floor
- macillary
- palatine
- roof
- ethmoid
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- comer/palatine
- septal and alar cartilages
-
lateral nasal wall

describethe medial nasal skeletal wall
- nasal skeleton
- lateral nasal wall
- ethmoid
- inferior concha
- maxillary
- lacimal
- palatine
- sphenoid
- nasal
- frontal/alar
- lateral septal cartilages
-
medial nasal wall
- ethmoid
- vomer
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- maxillary
- palatine
- septal cartilage
- floor
- macillary
- palatine
- roof
- ethmoid
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- comer/palatine
- septal and alar cartilages
- lateral nasal wall

describethe nasal fllor of the nasal skeleton
- nasal skeleton
- lateral nasal wall
- ethmoid
- inferior concha
- maxillary
- lacimal
- palatine
- sphenoid
- nasal
- frontal/alar
- lateral septal cartilages
- medial nasal wall
- ethmoid
- vomer
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- maxillary
- palatine
- septal cartilage
-
floor
- maxillary
- palatine
- roof
- ethmoid
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- comer/palatine
- septal and alar cartilages
- lateral nasal wall
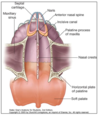
describe the roof of the nasal skeleton
- nasal skeleton
- lateral nasal wall
- ethmoid
- inferior concha
- maxillary
- lacimal
- palatine
- sphenoid
- nasal
- frontal/alar
- lateral septal cartilages
- medial nasal wall
- ethmoid
- vomer
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- maxillary
- palatine
- septal cartilage
- floor
- macillary
- palatine
-
roof
- ethmoid
- nasal
- frontal
- sphenoid
- comer/palatine
- septal and alar cartilages
- lateral nasal wall

describe the nasal passages and divisions
nasal septum divides the chamber of the nose into
- two nasal passages (or nasal cavities),
- each with anterior (nares) and
- posterior openings

opening to the nasal canities, on the cranium.
name and description
nasal aperture aka piriform aperture
- on the cranium
- opening to the nasal cavities
- the inferior margin of the nasal aperture has a bony prominence known as the anterior nasal spine (maxillae)
- posterior nasal apertures
- choanae -2x’s
- the posterior openings of the nasala passages
- together, the choanae form the posterior nasal apertures that open into the nasopharynx
- choanae -2x’s

what generates the posterior opening of the nasal passages?
nasal aperture aka piriform aperture
- on the cranium
- opening to the nasal cavities
- the inferior margin of the nasal aperture has a bony prominence known as the anterior nasal spine (maxillae)
-
posterior nasal apertures
-
choanae -2x’s
- the posterior openings of the nasala passages
- together, the choanae form the posterior nasal apertures that open into the nasopharynx
-
choanae -2x’s

Ethmoid bone forms the majority of the _____ and superior portion of the ____ _____ with respect to the nasal cavity
ethmoid bone
- details
- forms the majority of the ROOF of the nasal cavities and the superior portion of the LATERAL WALL
- perpendicular plate forms the suprior portions of the nasal septum
- cribriform pplatte forms the boundary with cranial cavity
- superior and middle nasal conchae and ethmoid air cells (sinuses) are partt of the ethmoid

what forms the superior portion of the nasal septum
ethmoid bone
- details
- forms the majority of the ROOF of the nasal cavities and the superior portion of the LATERAL WALL
- perpendicular plate forms the suprior portions of the nasal septum
- cribriform pplatte forms the boundary with cranial cavity
- superior and middle nasal conchae and ethmoid air cells (sinuses) are partt of the ethmoid

forms the boundary of the cranial cavity, witth respect to the nasal cavity.
ethmoid bone
- details
- forms the majority of the ROOF of the nasal cavities and the superior portion of the LATERAL WALL
- perpendicular plate forms the suprior portions of the nasal septum
- cribriform pplatte forms the boundary with cranial cavity
- superior and middle nasal conchae and ethmoid air cells (sinuses) are partt of the ethmoid

superior and middle nasal conchae and air cells (sinuses) are part of the _____
ethmoid bone
- details
- forms the majority of the ROOF of the nasal cavities and the superior portion of the LATERAL WALL
- perpendicular plate forms the suprior portions of the nasal septum
- cribriform pplatte forms the boundary with cranial cavity
- superior and middle nasal conchae and ethmoid air cells (sinuses) are partt of the ethmoid

what are the 3 scroll shaped structures that project into the nasal caviy?
conchae and meatus
-
each lateral wall has 3 scroll-shpaed structures that project into the nasal cavity - aka turbinattes
- inferior nasal conchae
- middle nasal conchae
- superior nasal conchae
- function
- primarily - incrase the surface area of the nasal mucosa
- meatus
- air space lateral and inferior to each concha
- house openings for communication channels with the paranasal sinuses and the orbit

what is the function of the turbinates?
conchae and meatus
- each lateral wall has 3 scroll-shpaed structures that project into the nasal cavity - aka tturbinattes
- inferior nasal conchae
- middle nasal conchae
- superior nasal conchae
- function
- primarily - incrase the surface area of the nasal mucosa
- meatus
- air space lateral and inferior to each concha
- house openings for communication channels with the paranasal sinuses and the orbit

air space lateral and inferior to each concha. function?
conchae and meatus
- each lateral wall has 3 scroll-shpaed structures that project into the nasal cavity - aka tturbinattes
- inferior nasal conchae
- middle nasal conchae
- superior nasal conchae
- function
- primarily - incrase the surface area of the nasal mucosa
-
meatus
- air space lateral and inferior to each concha
- house openings for communication channels with the paranasal sinuses and the orbit

list the three primary funcions of nasal airflow
nasal airflow
- function
- primary - modification of respired air
- particle filtration
- trap dust and pathogens
- modification of the temperature and moisture
- upon inspiration and expiration
- olfaction
- particle filtration
- primary - modification of respired air

olfaction and two other important functions characterize nasal airflow
nasal airflow
- function
- primary - modification of respired air
-
particle filtration
- trap dust and pathogens
-
modification of the temperature and moisture
- upon inspiration and expiration
- olfaction
-
particle filtration
- primary - modification of respired air

where is the olfatory mucosa limited to? what is it lined by?
mucosa
- nasal mucosa
- epithelium
-
nasal vestibule
- moderately keratinous and much like our external skin
-
nasal passages
- respiritory -see below
-
olfactory mucosa
- limited to the superior nasal concha and the adjacent portion of the septum.
-
lined by by olfactory epithelium
- olfactory receptor neurons CN1
- responsible for the detection of odor
-
nasal vestibule
- epithelium
- respiratory mucosa
- majority of the nasal passage
- thickest over the regions containing the vascular plexus, capable of rapid blood volume change
- the inferior and middle conchae, and the septum adjacent to the middle meatus
- this process is SNS fibers (GVE)
- origin from spinal cord level T1 ( preganglionicfiber), travel in sympathetic trunk ->synapse in the superior cervical ganglion
- postganglionic fibers join branches of the maxillary nerve (V2) via deep petrosal n. or follow blood vessels (plexus) to enter the nasal cavities
- contents
- pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- goblet cells
- seromucous glands
- innervated by PSNS GVE
- preganliongic fibers are carried in the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve that synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion
- later the nerve of the pterygoid canal )
- postganglionic fibers join branches of the macillary (tigeminal V2) nerve to enter the nasal cavity
- preganliongic fibers are carried in the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve that synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion
- innervated by PSNS GVE

describe the innervation of the respiritory mucosa with reference to PSNS and vsculature.
mucosa
- nasal mucosa
- epithelium
- nasal vestibule
- moderately keratinous and much like our external skin
- nasal passages
- respiritory -see below
- olfactory mucosa
- limited to the superior nasal concha and the adjacent portion of the septum.
- lined by by olfactory epithelium
- olfactory receptor neurons CN1
- responsible for the detection of odor
- nasal vestibule
- epithelium
- respiratory mucosa
- majority of the nasal passage
-
thickest over the regions containing the vascular plexus, capable of rapid blood volume change
- the inferior and middle conchdae, and the septum adjacent to the middle meatus
-
this process is SNS fibers (GVE)
- origin from spinal cord level T1 ( preganglionicfiber), travel in sympathetic trunk ->synapse in the superior cervical ganglion
- postganglionic fibers join branches of the maxillary nerve (V2) via deep petrosal n. or follow blood vessels (plexus) to enter the nasal cavities
- contents
- pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- goblet cells
-
seromucous glands
-
innervated by PSNS GVE
-
preganliongic fibers are carried in the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve that synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion
- later the nerve of the pterygoid canal )
- postganglionic fibers join branches of the macillary (tigeminal V2) nerve to enter the nasal cavity
-
preganliongic fibers are carried in the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve that synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion
-
innervated by PSNS GVE

Describe the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers involved with the PSNS of the nasal seromucosa.
mucosa
- nasal mucosa
- epithelium
- nasal vestibule
- moderately keratinous and much like our external skin
- nasal passages
- respiritory -see below
- olfactory mucosa
- limited to the superior nasal concha and the adjacent portion of the septum.
- lined by by olfactory epithelium
- olfactory receptor neurons CN1
- responsible for the detection of odor
- nasal vestibule
- epithelium
- respiratory mucosa
- majority of the nasal passage
- thickest over the regions containing the vascular plexus, capable of rapid blood volume change
- the inferior and middle conchae, and the septum adjacent to the middle meatus
- this process is SNS fibers (GVE)
- origin from spinal cord level T1 ( preganglionicfiber), travel in sympathetic trunk ->synapse in the superior cervical ganglion
- postganglionic fibers join branches of the maxillary nerve (V2) via deep petrosal n. or follow blood vessels (plexus) to enter the nasal cavities
- contents
- pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- goblet cells
- seromucous glands
-
innervated by PSNS GVE
-
preganliongic fibers are carried in the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve that synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion
- later the nerve of the pterygoid canal )
- postganglionic fibers join branches of the macillary (tigeminal V2) nerve to enter the nasal cavity
-
preganliongic fibers are carried in the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve that synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion
-
innervated by PSNS GVE