neck 1/2 Flashcards
list the regions of vulnerability for the neck
- transitional area between the base of the cranium and the clavicles
- joins the head with the trunk and upper limbs
- region of vulnerability
-
carotid arteries and jugular veins
- main blood vessels of head and neck
- cervical spinal cord
- brachial plexuses of nerve (roots, trunks, divisions) origin in neck and supply upper limbs
- larynx and trachea
- esophagus
- thyroid and parathyroid glands: submandibular glands
-
carotid arteries and jugular veins

regions of vulnerability, what is missing?
- carotid arteries and jugular veins
- main blood vessels of head and neck
- cervical spinal cord
- brachial plexuses of nerve (roots, trunks, divisions) origin in neck and supply upper limbs
- transitional area between the base of the cranium and the clavicles
- joins the head with the trunk and upper limbs
- region of vulnerability
- carotid arteries and jugular veins
- main blood vessels of head and neck
- cervical spinal cord
- brachial plexuses of nerve (roots, trunks, divisions) origin in neck and supply upper limbs
- larynx and trachea
- esophagus
- thyroid and parathyroid glands: submandibular glands
- carotid arteries and jugular veins

regions of vulnerability for the neck, what is missing?
- larynx and trachea
- esophagus
- thyroid and parathyroid glands: submandibular glands
- transitional area between the base of the cranium and the clavicles
- joins the head with the trunk and upper limbs
- region of vulnerability
-
carotid arteries and jugular veins
- main blood vessels of head and neck
- cervical spinal cord
- brachial plexuses of nerve (roots, trunks, divisions) origin in neck and supply upper limbs
- larynx and trachea
- esophagus
- thyroid and parathyroid glands: submandibular glands
-
carotid arteries and jugular veins
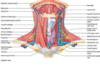
what are the palpable bones of the neck?
bones and cartilages ofthe neck
- deeper structures of the neck may be located in reference to palpable bones and cartilages
- bones include the 7 cervical vertebrae, hyoid bone, manubrium of sternum and clavicles
- cartilages includes the thyroid, cricoid and tracheal cartilages and other non palpable cartlages

what are the palpable cartilages of the neck?
bones and cartilages ofthe neck
- deeper structures of the neck may be located in reference to palpable bones and cartilages
- bones include the 7 cervical vertebrae, hyoid bone, manubrium of sternum and clavicles
- cartilages includes the thyroid, cricoid and tracheal cartilages and other non palpable cartlages
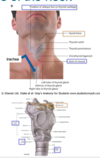
near C3 with the angle of the neck. what makes up the structure of this item?
hyoid bone
-
location
- angle of the neck
- near C3
-
contents
-
comprises of
- body
- greate horn
- lesser horn
-
comprises of
- fnotes
- fractured if manually strangled by compression of throat
- bound to thyroid cartilage by a THYROHYOIDmembran
- suspended by extrinsic muscle of the larynx
- some mucles of the tongue an pharynx

what is the hyoid bone bound by and suspended by?
hyoid bone
- location
- angle of the neck
- near C3
- contents
- comprises of
- body
- greate horn
- lesser horn
- comprises of
- fnotes
- fractured if manually strangled by compression of throat
- bound to thyroid cartilage by a THYROHYOIDmembran
- suspended by extrinsic muscle of the larynx
- some mucles of the tongue an pharynx
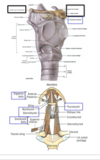
strangulation of the throat is identified by?
hyoid bone
- location
- angle of the neck
- near C3
- contents
- comprises of
- body
- greate horn
- lesser horn
- comprises of
- fnotes
- fractured if manually strangled by compression of throat
- bound to thyroid cartilage by a THYROHYOIDmembran
- suspended by extrinsic muscle of the larynx
- some mucles of the tongue an pharynx
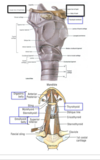
what does the superficial fascia of the neck contain?
-
superficial fascia
- subcutaneous connective tissue that contains the platysma
- deepfascia
- forms a series of cylindrical comparment
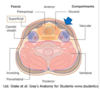
forms a series of cylindrical compartment around the neck
- superficial fascia
- subcutaneous connective tissue that contains the platysma
-
deepfascia
- forms a series of cylindrical comparment

muscle of facial expression. innervation?
platysma
- muscle of facial expression
-
innervated
- facial nerve CN7
- crosses the anterior and lateral regions of the neck
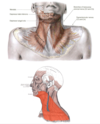
facial nerve goes to which muscle in the neck? What does it cross?
platysma
- muscle of facial expression
- innervated
- facial nerve CN7
- crosses the anterior and lateral regions of the neck

investing layer of deep fascia contains what items?
deep fascia
-
investing layer
- surrounds the neck
-
encloses the following muscles
- sternocleidomastoid
- trapezius
- strap muscles (infrhyoid)
- prevertebral fascia
- encloses
- vertebral column
- spinal cord
- roots of brachial plexus
- associted muscles of vertebral compartment
- encloses
- pretracheal fascia
- enclose the following of the visceral compartment
- thyroid gland
- esophagus
- larynx
- trachea of visceral compartment
- enclose the following of the visceral compartment
- bilateral carotid sheaths
- enclose the following ofthe vascular compartment
- carotid arteries
- jugular veins
- enclose the following ofthe vascular compartment

prevertebral fascia of the the deep fascia contain what items?
deep fascia
- investinglayer
- surrounds hte neck
- encloses the following muscles
- sternocleidomastoid
- trapezius
- strap muscles (infrhyoid)
-
prevertebral fascia
-
encloses
- vertebral column
- spinal cord
- roots of brachial plexus
- associted muscles of vertebral compartment
-
encloses
- pretracheal fascia
- enclose the following of the visceral compartment
- thyroid gland
- esophagus
- larynx
- trachea of visceral compartment
- enclose the following of the visceral compartment
- bilateral carotid sheaths
- enclose the following ofthe vascular compartment
- carotid arteries
- jugular veins
- enclose the following ofthe vascular compartment

the bilateral carotid sheath contain what items?
deep fascia
- investinglayer
- surrounds hte neck
- encloses the following muscles
- sternocleidomastoid
- trapezius
- strap muscles (infrhyoid)
- prevertebral fascia
- encloses
- vertebral column
- spinal cord
- roots of brachial plexus
- associted muscles of vertebral compartment
- encloses
- pretracheal fascia
- enclose the following of the visceral compartment
- thyroid gland
- esophagus
- larynx
- trachea of visceral compartment
- enclose the following of the visceral compartment
-
bilateral carotid sheaths
-
enclose the following ofthe vascular compartment
- carotid arteries
- jugular veins
-
enclose the following ofthe vascular compartment

infection can spread inferiorly into thoracic cavity anterior to pericardium
fascial compartments
- fascial (potential) spaces
- important to provide a conduit for the spread of infecttion, fluid, gas and tumors. Two spaces
-
pretracheal space
- infection can spread inferiorly into thoracic cavity anterior to pericardium
- retropharyngeal space
- infection can form a bulge in pharynx affecting swalloing and speaking
- can spread infeiorly to posterior mediastinum
-
pretracheal space
- important to provide a conduit for the spread of infecttion, fluid, gas and tumors. Two spaces
infection in this space can form a bulge in pharynx affecting swallowing and speaking
fascial compartments
- fascial (potential) spaces
- important to provide a conduit for the spread of infecttion, fluid, gas and tumors. Two spaces
- pretracheal space
- infection can spread inferiorly into thoracic cavity anterior to pericardium
-
retropharyngeal space
- infection can form a bulge in pharynx affecting swalloing and speaking
- can spread infeiorly to posterior mediastinum
- pretracheal space
- important to provide a conduit for the spread of infecttion, fluid, gas and tumors. Two spaces
what aret he potential spacies in the neck and why are they clinically relevant?
fascial compartments
- fascial (potential) spaces
- important to provide a conduit for the spread of infecttion, fluid, gas and tumors. Two spaces
- pretracheal space
- infection can spread inferiorly into thoracic cavity anterior to pericardium
- retropharyngeal space
- infection can form a bulge in pharynx affecting swalloing and speaking
- can spread infeiorly to posterior mediastinum
- pretracheal space
- important to provide a conduit for the spread of infecttion, fluid, gas and tumors. Two spaces
list the extrinsic back muslces of the vertebral compartment
muscles of the vertebral compartment
-
extrinsic back muscles
- levator scapulae
- rhomboid minor
- intrinsic back muscles
- splenius
- ererctor spinae
- semispinalis
- muscles of suboccipital triangle
- prevertebral muscles
- longus colli
- longus capitis
- rectus capitis anterior
- rectus capits lateralis
- middle scalene
- posterior scalene

list the intrinsic back muscles of the vertebral compartment
muscles of the vertebral compartment
- extrinsic back muscles
- levator scapulae
- rhomboid minor
-
intrinsic back muscles
- splenius
- ererctor spinae
- semispinalis
- muscles of suboccipital triangle
- prevertebral muscles
- longus colli
- longus capitis
- rectus capitis anterior
- rectus capits lateralis
- middle scalene
- posterior scalene
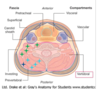
list the prevertebral muscle of the vertebral column
muscles of the vertebral compartment
- extrinsic back muscles
- levator scapulae
- rhomboid minor
- intrinsic back muscles
- splenius
- ererctor spinae
- semispinalis
- muscles of suboccipital triangle
-
prevertebral muscles
- longus colli
- longus capitis
- rectus capitis anterior
- rectus capits lateralis
- middle scalene
- posterior scalene

of the prevertebral muscle which assist with flexing the head?
prevertebvral muslces
-
flex head
- rectus capitis anterior
- rectus capitis lateralis
- longus capitis
- anterior scalene
- flex neck with rotation on opposite side if aciting unilaterally
- longus colli
- flex neck and elevate first or second rib during forced inspiration
- middle scalene
- posterior scalene
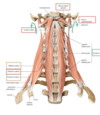
of the prevertebral muscles which felx the neck with rotation on opposite side if acting unilaterally?
prevertebvral muslces
- flex head
- rectus capitis anterior
- rectus capitis lateralis
- longus capitis
- anterior scalene
-
flex neck with rotation on opposite side if aciting unilaterally
- longus colli
- flex neck and elevate first or second rib during forced inspiration
- middle scalene
- posterior scalene
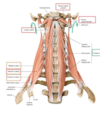
of the prevertebra lmuslces, whic flex neck and elevate first or second rub during forced inspiration?
prevertebvral muslces
- flex head
- rectus capitis anterior
- rectus capitis lateralis
- longus capitis
- anterior scalene
- flex neck with rotation on opposite side if aciting unilaterally
- longus colli
-
flex neck and elevate first or second rib during forced inspiration
- middle scalene
- posterior scalene
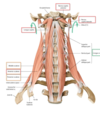
describe theneck division in the cervical regions
the neck is divided in cervical regions
-
posterior cervical region-B
- covered by
- trapezius
- superficial to suboccipital region
- covered by
-
latteral cervical region-C
- posterior triangle
-
anterior cervical region-D
- anterior triangle
-
sternocleidomastoid region-A
- dividing line between anterior triangle and posterior tirangle of the neck

This cervical region is covered by trapezius superficial to________region
the neck is divided in cervical regions
-
posterior cervical region-B
-
covered by
- trapezius
- superficial to suboccipital region
-
covered by
- latteral cervical region-C
- posterior triangle
- anterior cervical region-D
- anterior triangle
- sternocleidomastoid region-A
- dividing line between anterior triangle and posterior tirangle of the neck

list the posterior and tanterior trangles of the cervical regions
the neck is divided in cervical regions
- posterior cervical region-B
- covered by
- trapezius
- superficial to suboccipital region
- covered by
-
latteral cervical region-C
- posterior triangle
-
anterior cervical region-D
- anterior triangle
- sternocleidomastoid region-A
- dividing line between anterior triangle and posterior tirangle of the neck

this muscle acts as the dividing line between the anterior triangle and posterior triangle of the neck
the neck is divided in cervical regions
- posterior cervical region-B
- covered by
- trapezius
- superficial to suboccipital region
- covered by
- latteral cervical region-C
- posterior triangle
- anterior cervical region-D
- anterior triangle
-
sternocleidomastoid region-A
- dividing line between anterior triangle and posterior tirangle of the neck

principal muscular landmark in the superficial neck. What is it innervation?
sternocleidomasteoid
-
landmark
- the principal muscular landmark in thte superficial neck
-
innervation
- spinal accessory nerve CN9
- contains proprioceptive fibers from the anterior ramus of C2
- movements
- unilaterally-laterally
- Flex the neck ipsilaterally, while rotating tthe face towards the contalateral side
- bilaterally - two movements, other muscles are not included
- neck extension- draw the head forward and chin upward
- flexes cervical vertebrae
- unilaterally-laterally
- disease
- toticolli
- due to either a congenital shortening or spasmodic contraction of the SCM.
- pretty much the muscle is shorter on one side compared to the other side
- toticolli
contain proprioceptive fibers fro mthe anterior ramus of C2. describe the unilaterall flexion of this muscle
sternocleidomasteoid
- landmark
- the principal muscular landmark in thte superficial neck
- innervation
- spinal accessory nerve CN9
- contains proprioceptive fibers from the anterior ramus of C2
-
movements
-
unilaterally-laterally
- Flex the neck ipsilaterally, while rotating tthe face towards the contalateral side
- bilaterally - two movements, other muscles are not included
- neck extension- draw the head forward and chin upward
- flexes cervical vertebrae
-
unilaterally-laterally
- disease
- toticolli
- due to either a congenital shortening or spasmodic contraction of the SCM.
- pretty much the muscle is shorter on one side compared to the other side
- toticolli
unilareral flexion of this muscle -> rotataing the face toward the contralateral side. What does bilateral contraction lead to?
sternocleidomasteoid
- landmark
- the principal muscular landmark in thte superficial neck
- innervation
- spinal accessory nerve CN9
- contains proprioceptive fibers from the anterior ramus of C2
-
movements
-
unilaterally-laterally
- Flex the neck ipsilaterally, while rotating tthe face towards the contalateral side
-
bilaterally - two movements, other muscles are not included
- neck extension- draw the head forward and chin upward
- flexes cervical vertebrae
-
unilaterally-laterally
- disease
- toticolli
- due to either a congenital shortening or spasmodic contraction of the SCM.
- pretty much the muscle is shorter on one side compared to the other side
- toticolli
Describe the involved componenents of the a child born with its head pulled in one direction due to a muscle in the neck
sternocleidomasteoid
- landmark
- the principal muscular landmark in thte superficial neck
- innervation
- spinal accessory nerve CN9
- contains proprioceptive fibers from the anterior ramus of C2
- movements
- unilaterally-laterally
- Flex the neck ipsilaterally, while rotating tthe face towards the contalateral side
- bilaterally - two movements, other muscles are not included
- neck extension- draw the head forward and chin upward
- flexes cervical vertebrae
- unilaterally-laterally
-
disease
-
toticolli
- due to either a congenital shortening or spasmodic contraction of the SCM.
- pretty much the muscle is shorter on one side compared to the other side
-
toticolli
what forms theexternal jugular vein?
external jugular vein
-
formed by the union of
- posterior branch of retromandibular vein
- posterior auricualr vein
- descends across the SCM and pierces the investing layer of deep cervical fascia (rrof of posterior triangle ) to enter the subclavian vein
- associated with superficial cervical nodes
- if the external jugular vein is cut wher it pierces the investin layer of fascia, a venous air embolism may obstruct blood flow through the heart
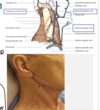
descends across the SCM and pierces the investing layer of deep cervial fascia. What is this and what does it enter?
external jugular vein
- formed by the union of
- posterior branch of retromandibular vein
- posterior auricualr vein
- descends across the SCM and pierces the investing layer of deep cervical fascia (rrof of posterior triangle ) to enter the subclavian vein
- associated with superficial cervical nodes
- if the external jugular vein is cut wher it pierces the investin layer of fascia, a venous air embolism may obstruct blood flow through the heart

the descends across the SCM, pierces the roof of the posterior triangle entering the subclavian vein. But, what is it associated with ?
external jugular vein
- formed by the union of
- posterior branch of retromandibular vein
- posterior auricualr vein
- descends across the SCM and pierces the investing layer of deep cervical fascia (rrof of posterior triangle ) to enter the subclavian vein
- associated with superficial cervical nodes
- if the external jugular vein is cut wher it pierces the investin layer of fascia, a venous air embolism may obstruct blood flow through the heart

what occurs if the external jugular vein is traumatized where it pierces the investing fascia?
external jugular vein
- formed by the union of
- posterior branch of retromandibular vein
- posterior auricualr vein
- descends across the SCM and pierces the investing layer of deep cervical fascia (rrof of posterior triangle ) to enter the subclavian vein
- associated with superficial cervical nodes
- if the external jugular vein is cut wher it pierces the investin layer of fascia, a venous air embolism may obstruct blood flow through the heart
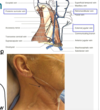
list the boundaries of the posterior cervical triangle
posterior cervical triangle
-
boundaries
- the posterior border of SCM
- anterior border of Trapezius
- middle 1/3 of the clavicle
- investing layer of deep cervical fascia (roof)
- prevertebral fascia and subjacent muscles (floor) in vertebral compartment
- con be further divided by the inferior belly of the omohyoid into
- occipital trianble
- supraclavicular (subclavian) triangle

What can the posterior cervical triangle be further divided into, past the boundaries?
posterior cervical triangle
- boundaries
- the posterior border of SCM
- anterior border of Trapezius
- middle 1/3 of the clavicle
- investing layer of deep cervical fascia (roof)
- prevertebral fascia and subjacent muscles (floor) in vertebral compartment
-
can be further divided by the inferior belly of the omohyoid into
- occipital trianble
- supraclavicular (subclavian) triangle

describe the branches of the cervical plexus in with respect to the cervical triangle
-
posterior cervical triangle
- can be thought of as the part of the neck most associated with the upper limb
-
content
-
branches of the cervical plexus
- cervical plexus and major somatic nerve plexus are formed from the ANTRIOR RAMI OF SPINAL NERVES C1-C4
-
cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipital(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transvers cervical(C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- spinal accessory nerve
- descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles
- may be injured in the posterior triangle by a tumor, stab wound, or during surgery
- subclavian vein
- passes anterior to the anterior scalene muscle and joins the internal jugular vein ( VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalc vein
- receives the external jugular vein as a tributary
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- arteries
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- medial to the sclaneus anterior and superior to the subclavius and subclavian vein
- transverse cervical artery
- cervicodorsal trunk
- divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and thomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- root, trunks and branches of the brachial plexus
- 5roots emerge with the sublavian artery into the interscalene triangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunks that descen inferolaterally toward the axilla
-
branches of the cervical plexus
- the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior triangle
- splenius capitis
- levator scapulae
- posterior scalene
- middle scalene
- anterior scalene
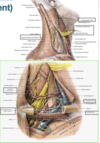
descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles.
What is this nerve susceptible to?
- posterior cervical triangle
- can be thoug hof as the part of the neck most associated with the upper limb
- content
- branches of the cervical plexus
- cervical plexus and major somatic nerve plexus are formed from the ANTRIOR RAMI OF SPINAL NERVES C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipital(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transvers cervical(C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
-
spinal accessory nerve
- descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles
- may be injured in the posterior triangle by a tumor, stab wound, or during surgery
- subclavian vein
- passes anterior to the anterior scalene muscle and joins the internal jugular vein ( VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalc vein
- receives the external jugular vein as a tributary
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- arteries
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- medial to the sclaneus anterior and superior to the subclavius and subclavian vein
- transverse cervical artery
- cervicodorsal trunk
- divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and thomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- root, trunks and branches of the brachial plexus
- 5roots emerge with the sublavian artery into the interscalene triangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunks that descen inferolaterally toward the axilla
- branches of the cervical plexus
- the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior triangle
- splenius capitis
- levator scapulae
- posterior scalene
- middle scalene
- anterior scalene

describe the passage of the subclavian vein. tributaries. What is it the continuation of?
- posterior cervical triangle
- can be thoug hof as the part of the neck most associated with the upper limb
- content
- branches of the cervical plexus
- cervical plexus and major somatic nerve plexus are formed from the ANTRIOR RAMI OF SPINAL NERVES C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipital(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transvers cervical(C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- spinal accessory nerve
- descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles
- may be injured in the posterior triangle by a tumor, stab wound, or during surgery
-
subclavian vein
- passes anterior to the anterior scalene muscle and joins the internal jugular vein ( VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalc vein
- receives the external jugular vein as a tributary
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- arteries
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- medial to the sclaneus anterior and superior to the subclavius and subclavian vein
- transverse cervical artery
- cervicodorsal trunk
- divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and thomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- root, trunks and branches of the brachial plexus
- 5roots emerge with the sublavian artery into the interscalene triangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunks that descen inferolaterally toward the axilla
- branches of the cervical plexus
- the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior triangle
- splenius capitis
- levator scapulae
- posterior scalene
- middle scalene
- anterior scalene

describe the arteries with respect to the posterior cervical triangle. Include direction.
- posterior cervical triangle
- can be thoug hof as the part of the neck most associated with the upper limb
- content
- branches of the cervical plexus
- cervical plexus and major somatic nerve plexus are formed from the ANTRIOR RAMI OF SPINAL NERVES C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipital(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transvers cervical(C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- spinal accessory nerve
- descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles
- may be injured in the posterior triangle by a tumor, stab wound, or during surgery
- subclavian vein
- passes anterior to the anterior scalene muscle and joins the internal jugular vein ( VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalc vein
- receives the external jugular vein as a tributary
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
-
arteries
-
subclavian artery (3rd part)
- medial to the sclaneus anterior and superior to the subclavius and subclavian vein
-
transverse cervical artery
- cervicodorsal trunk
- divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and thomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
-
suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
-
subclavian artery (3rd part)
- root, trunks and branches of the brachial plexus
- 5roots emerge with the sublavian artery into the interscalene triangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunks that descen inferolaterally toward the axilla
- branches of the cervical plexus
- the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior triangle
- splenius capitis
- levator scapulae
- posterior scalene
- middle scalene
- anterior scalene

describe the brachial plexus with respect to the posterior cervical triangle
- posterior cervical triangle
- can be thoug hof as the part of the neck most associated with the upper limb
- content
- branches of the cervical plexus
- cervical plexus and major somatic nerve plexus are formed from the ANTRIOR RAMI OF SPINAL NERVES C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipital(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transvers cervical(C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- spinal accessory nerve
- descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles
- may be injured in the posterior triangle by a tumor, stab wound, or during surgery
- subclavian vein
- passes anterior to the anterior scalene muscle and joins the internal jugular vein ( VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalc vein
- receives the external jugular vein as a tributary
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- arteries
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- medial to the sclaneus anterior and superior to the subclavius and subclavian vein
- transverse cervical artery
- cervicodorsal trunk
- divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and thomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
-
root, trunks and branches of the brachial plexus
- 5roots emerge with the sublavian artery into the interscalene triangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunks that descen inferolaterally toward the axilla
- branches of the cervical plexus
- the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior triangle
- splenius capitis
- levator scapulae
- posterior scalene
- middle scalene
- anterior scalene

describe the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior cervical triangle
- posterior cervical triangle
- can be thoug hof as the part of the neck most associated with the upper limb
- content
- branches of the cervical plexus
- cervical plexus and major somatic nerve plexus are formed from the ANTRIOR RAMI OF SPINAL NERVES C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipital(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transvers cervical(C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- spinal accessory nerve
- descends through the posterior triangle between the posterior border of the SCM and the anterior border of trapezius and supplies both muscles
- may be injured in the posterior triangle by a tumor, stab wound, or during surgery
- subclavian vein
- passes anterior to the anterior scalene muscle and joins the internal jugular vein ( VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalc vein
- receives the external jugular vein as a tributary
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- arteries
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- medial to the sclaneus anterior and superior to the subclavius and subclavian vein
- transverse cervical artery
- cervicodorsal trunk
- divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and thomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- subclavian artery (3rd part)
- root, trunks and branches of the brachial plexus
- 5roots emerge with the sublavian artery into the interscalene triangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunks that descen inferolaterally toward the axilla
- branches of the cervical plexus
-
the muscles that make up the FLOOR of the posterior triangle
- splenius capitis
- levator scapulae
- posterior scalene
- middle scalene
- anterior scalene

the cervical plexus is a major ____ ____ plexus. what does this mean?
what forms the cervical plexus?
Cutaneous nerves of the cervical plexus
- the cervical plexus, a major somatic nerve plexus, is formed from the ANTERIOR RAMI of the spinal nerves C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipitalv(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transverse cervical (C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- note the relation with SCM

describe the curaneous branches of the cervical plexus and their origination
Cutaneous nerves of the cervical plexus
- the cervical plexus, a major somatic nerve plexus, is formed from the ANTERIOR RAMI of the spinal nerves C1-C4
-
cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipitalv(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transverse cervical (C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- note the relation with SCM
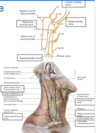
note the relationship of the cervical plexus, the path of the nerves and how it involves the SCM.
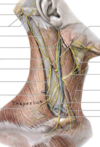
Cutaneous nerves of the cervical plexus
- the cervical plexus, a major somatic nerve plexus, is formed from the ANTERIOR RAMI of the spinal nerves C1-C4
- cutaneous branches include
- lesser occipitalv(C2)
- greater auricular(C2-C3)
- transverse cervical (C2-C3)
- supraclavicular (C3-C4)
- note the relation with SCM

is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
subclavian vein
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- passessANTERIOR TO THE ANTERIOR SCALENE muscle and joins the internal jubular vein (VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalic vein
- receives the external jubular vein as tributary
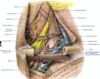
The subclavian vein passes what direction, with respect to the muscles around? What structure manifests when it joins the internal jugular?
subclavian vein
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- passessANTERIOR TO THE ANTERIOR SCALENE muscle and joins the internal jubular vein (VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalic vein
- receives the external jubular vein as tributary
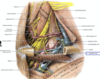
what contributes to the subclavian vein as tributaries?
subclavian vein
- is the continuation of the axillary vein at the lateral border of the first rib
- passessANTERIOR TO THE ANTERIOR SCALENE muscle and joins the internal jubular vein (VENOUS ANGLE) to form the brachiocephalic vein
- receives the external jubular vein as tributary

describe the arteris crossing the posterior cervical triangle
arteries crossing posterior triangle
- third part of subclavian artery
-
occipital artey
- br of external carotid, not shown
-
branches of the thyrocervical trunk
- from the 1st part of the subclavian artery in anterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- transverse cervical artery (cervicodorsal trunk)
- may divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and rhomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- from the 1st part of the subclavian artery in anterior triangle

what portion of the subclavian artery crosses the posterior trangle?
arteries crossing posterior triangle
- third part of subclavian artery
- occipital artey
- br of external carotid, not shown
- branchses of the thyrocervical trunk
- from the 1st part of the subclavian artery in anterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- transverse cervical artery (cervicodorsal trunk)
- may divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and rhomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
- suprascapular artery
- from the 1st part of the subclavian artery in anterior triangle

describe the branches from the 1st part of the subclavian artery with respect to the posterior triangle. note image in answer
arteries crossing posterior triangle
- third part of subclavian artery
- occipital artey
- br of external carotid, not shown
-
branchses of the thyrocervical trunk
-
from the 1st part of the subclavian artery in anterior triangle
-
suprascapular artery
- supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
-
transverse cervical artery (cervicodorsal trunk)
- may divide into superficial branch to trapezius and deep branch to levator scapulae and rhomboid
- if only the superficial branch exists, the deep branch is replaced by a dorsal scapular artery from 3rd part of subclavian artery in posterior triangle
-
suprascapular artery
-
from the 1st part of the subclavian artery in anterior triangle
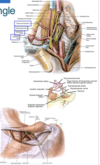
Describe the tunks form from the brachial plexus and the route
the brachial plexus
- 5 roots (anterior rami) emerge with the subclavian artery into the interscalene trangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunk that descend inferiolaterally toward the axilla.

describe the route for the brachial plexus with respect to the subclavian artery
the brachial plexus
- 5 roots (anterior rami) emerge with the subclavian artery into the interscalene trangle formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib
- they unite to form 3 trunk that descend inferiolaterally toward the axilla.
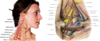
This nerve provides motor innervation to the diaphragm. Describe its origination and the path of its descent.
important nerves with respect to the posterior cervical triangle
-
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
- motor innervation to the diaphragm
- descends along the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle
- suprascapular nerve (C5-C6)
- accompanying the suprascapular artery and vein behind the clavivle en route to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- nerve to the subclavius muscle (C5)
- may have an accessory phrenic nerve branch
- long thoracic nerve (C5-C7)
- to the serratus anterior
- Dorsal scapluar nerve (C5)
- the rhomboids and levator scapulae
- it pierces the middle scalene muscle

describe the following nerves with respect to the posterior triangle
- suprascapular
- subclavius
- long thoracic
- dorsal scapular
important nerves with respect to the posterior cervical triangle
- phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
- motor innervation to the diaphragm
- descends along the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle
-
suprascapular nerve (C5-C6)
- accompanying the suprascapular artery and vein behind the clavivle en route to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
-
nerve to the subclavius muscle (C5)
- may have an accessory phrenic nerve branch
-
long thoracic nerve (C5-C7)
- to the serratus anterior
-
Dorsal scapluar nerve (C5)
- the rhomboids and levator scapulae
- it pierces the middle scalene muscle

answer the following with respect to the phrenic nerve
- innervation
- route of descent
important nerves with respect to the posterior cervical triangle
-
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
- motor innervation to the diaphragm
- descends along the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle
- suprascapular nerve (C5-C6)
- accompanying the suprascapular artery and vein behind the clavivle en route to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus
- nerve to the subclavius muscle (C5)
- may have an accessory phrenic nerve branch
- long thoracic nerve (C5-C7)
- to the serratus anterior
- Dorsal scapluar nerve (C5)
- the rhomboids and levator scapulae
- it pierces the middle scalene muscle

what are the boundaries of the anterior cervical triangle?
Anterior cervical triangle
- boundaries
- anteriorborder of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
- midline of the neck (right and left)
- inferior border of the mandible
- manubrium of the sternum

fill in the following for the anterior cervical triangle
- anteior border of what muscle?
- midline of the ____?
- inferior border of the mandible(given)
- what portion of the sternum
Anterior cervical triangle
- boundaries
- anterior border of teh sternocleidomastoid muscle
- midline of the neck (right and left)
- inferior border of the mandible
- manubrium of the sternum

list the anterior cervical triangle subdivisions
anterior cervical triangle - subdivisions
-
submandibular/digastric triangle
- bounded by the digastric muscle and the mandible
-
submental triangle
- above the hyoid bone between the anterior belly of the digastric muscle and the midline of the neck
-
carotid triangle
- bounded by the posterior digastric, superior belly of the omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
-
muscular triangle
- defined by the midline of the neck, superior belly of the, omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
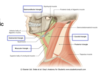
describe the following subdivision of the neck
- submandibular/digastric triangle
- submental triangle
- carotid triangle
- muscular triangle
anterior cervical triangle - subdivisions
- submandibular/digastric triangle
- bounded by the digastric muscle and the mandible
- submental triangle
- above the hyoid bone between the anterior belly of the digastric muscle and the midline of the neck
- carotid triangle
- bounded by the posterior digastric, superior belly of the omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
- muscular triangle
- defined by the midline of the neck, superior belly of the, omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid

list the following anterior triangle subdivisions of the neck.
- bounded by the digastric muscle and the mandible
- above the hyoid bone between the anterior belly of the digastric muscle and the midline of the neck
- bounded by the posterior digastric, superior belly of the omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
- defined by the midline of the neck, superior belly of the, omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
anterior cervical triangle - subdivisions
- submandibular/digastric triangle
- bounded by the digastric muscle and the mandible
- submental triangle
- above the hyoid bone between the anterior belly of the digastric muscle and the midline of the neck
- carotid triangle
- bounded by the posterior digastric, superior belly of the omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
- muscular triangle
- defined by the midline of the neck, superior belly of the, omohyoid, and the sternocleidomastoid
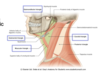
what are the three superficial structures of the neck?
anterior triangle of the neck - superficial structures
- platysma muscles
- anterior jugular veins
- descending near the midline; the paired veins anastomes through a fascial suprasternal space via a jugular venous arch
- each anterior jugular drains into an external jugular vein
- may receive a large communicating (connecting) vein from the facial vein
- can cause bleeding following a neck injury or during atracheostomy
- transverse cervical nerves

describe the venous structures associated with the anterior triangle
anterior triangle of the neck - superficial structures
- platysma muscles
-
anterior jugular veins
- descending near the midline; the paired veins anastomes through a fascial suprasternal space via a jugular venous arch
- each anterior jugular drains into an external jugular vein
-
may receive a large communicating (connecting) vein from the facial vein
- can cause bleeding following a neck injury or during atracheostomy
- transverse cervical nerves

descrie the suprahyoid region border and contents
the suprahyoid region
- is located between the hyoid bone and the inferior border of the mandible
- contents
- submandibular triangle
- submandibular gland
- lymph nodes
- submental triangle
- submental lymph nodes
- submandibular triangle
what contains the submandibular triangle and sumbental triangle?
List the contents of the the above mentioned triangles.
the suprahyoid region
- is located between the hyoid bone and the inferior border of the mandible
- contents
- submandibular triangle
- submandibular gland
- lymph nodes
- submental triangle
- submental lymph nodes
- submandibular triangle
define the borders of the submandibular triangle
submandibular triangle
- border
- inferior border of the mandible
- anterior (CNV) and posterior (CNVII) bellies of the digastric muscle
- can elevate the hyoid bone or depress the mandible (open the jaws)
-
floor
- formed by the two mylohyoid muscles (CNV), which fuse in a midline fibrous raphe to form the floor of the oral cavity
- mylohyoid muscles can help elevate the hyoid bone and tongue or depress the mandible
- has the stylohyoid muscle running parallel to the posterior belly of the digastric ( attaches to styloid process)
- innervated by CN VII
- draws the hyoid bone upward and backward
- named submandibular triangle due to containing the moser of the submandibular salivary glands

draws the hyoid bone upward and backward. What is it innervated by?
submandibular triangle
- border
- inferior border of the mandible
- anterior (CNV) and posterior (CNVII) bellies of the digastric muscle
- can elevate the hyoid bone or depress the mandible (open the jaws)
- floor
- formed by the two mylohyoid muscles (CNV), which fuse in a midline fibrous raphe to form the floor of the oral cavity
- mylohyoid muscles can help elevate the hyoid bone and tongue or depress the mandible
-
has the stylohyoid muscle running parallel to the posterior belly of the digastric ( attaches to styloid process)
- innervated by CN VII
- draws the hyoid bone upward and backward
- named submandibular triangle due to containing the moser of the submandibular salivary glands

elevate the hyoid bone and tongue or depress the mandible. What is the structure and what is it innervated by?
submandibular triangle
- border
- inferior border of the mandible
- anterior (CNV) and posterior (CNVII) bellies of the digastric muscle
- can elevate the hyoid bone or depress the mandible (open the jaws)
- floor
- formed by the two mylohyoid muscles (CNV), which fuse in a midline fibrous raphe to form the floor of the oral cavity
- mylohyoid muscles can help elevate the hyoid bone and tongue or depress the mandible
- has the stylohyoid muscle running parallel to the posterior belly of the digastric ( attaches to styloid process)
- innervated by CN VII
- draws the hyoid bone upward and backward
- named submandibular triangle due to containing the moser of the submandibular salivary glands
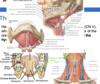
can elevate the hyoid bone or depress the mandible(open the jaws)
submandibular triangle
- border
- inferior border of the mandible
-
anterior (CNV) and posterior (CNVII) bellies of the digastric muscle
- can elevate the hyoid bone or depress the mandible (open the jaws)
- floor
- formed by the two mylohyoid muscles (CNV), which fuse in a midline fibrous raphe to form the floor of the oral cavity
- mylohyoid muscles can help elevate the hyoid bone and tongue or depress the mandible
- has the stylohyoid muscle running parallel to the posterior belly of the digastric ( attaches to styloid process)
- innervated by CN VII
- draws the hyoid bone upward and backward
- named submandibular triangle due to containing the moser of the submandibular salivary glands
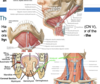
describe the innervation to the submandibular glands
submandibular triangle
- name is due to the submandibular glands housed inside
- gland innervated
- postganglionic PSNS fibers from cell bodies in the submandibular ganglion
- gland innervated

submandibular gland is innervated by ____ fibers from cell bodies in the ______ ______
submandibular triangle
- name is due to the submandibular glands housed inside
- gland innervated
- postganglionic PSNS fibers from cell bodies in the submandibular ganglion
- gland innervated



