Oral Cavity and Pharynx Picture Cards Flashcards
Name these structures, and also name what goes through #4 and #8.

- Medial and lateral pterygoid plates
- Horizontal plate of palatine bone
- Alveolar bone
- Incisive canal (connection to nasal cavity) - nasopalatine nerve (V2) comes through to supply sensation to the anterior hard palate
- Intermaxillary suture
- Palatine process (of maxilla)
- Interpalatine suture
- Greater and lesser palatine foramina - Greater and lesser palatine nerves (V2) come through along with piggybacking parasympathetic vidian nerve (from greater petrosal VII) to innervate the palatine glands
- Hamulus

What are these called and what attaches to them?

Genial spines. The Genioglossus muscle originates on the upper spine and the geniohyoid originates on the lower one.
What happened?

Mandibular tori - bone growth

- Soft palate
- Uvula
- Palatine tonsils
- Oropharynx
Name the arteries and what they arose from

- Tonsillar artery - from facial artery
- Dorsal lingual artery - from facial artery
- Descending palatine artery - from maxillary artery
- Ascending pharyngeal artery - from ECA
- Asecnding palatine artery - from facial artery

What did Dr. Marchant say is cool about #3?

- Incisive papilla
- Palatine raphe
- Transverse palatine folds - they are like fingerprints
Name the muscles and their innervation.

- Uvula - CN X
- Tensor veli palatini - V3
- Levator veli palatini - CN X
- Palatopharyngeus - CN X
- Palatoglossus - CN X

Also, what are the actions and innervations of 4 and 5?

- Pterygoid hamulus
- Scaphoid fossae
- Medial and lateral pterygoid plates
- Letator veli palatini - elevates palate CN X
- Tensor veli palatini - flattens palate CN V3

What nerves provide somatic sensory to these regions of the palate?

- Nasopalatine
- Greater palatine
- Lesser palatine
all are branches of V2
Name the nerves that supply sensation to these vestibular regions.

- V2 - posterior superior alveolar nerve
- V2 - middle superior alveolar nerve
- V2 - anterior superior alveolar nerve
- V3 - long buccal nerve
- V3 - mental nerve
Name the muscles, innervation, and action.

- Genial tubercles
CN XII:
- Styloglossus - retracts, cups the tongue
- Hyoglossus - depresses the tongue
- Genioglossus - protrudes tongue, depresses the central portion
C1 via hypoglossal:
- Geniohyoid - elevates hyoid bone


- Mylohyoid m.
- Hypoglossus m.
- Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- Occipital artery

- Foliate
- Fungiform
- Vallate
- Foramen cecum
- Terminal sulcus
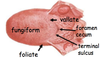
How can you clinically test for CN XII damage?
Have the patient stick their tongue out. This involves contraction of the genioglossus muscle. Damage to CN XII unilaterally will result in deviation to the side that is damaged. That side of the tongue will be atrophied also.

Does the glossopharyngeal supply taste sensation over a slightly larger area than it does somatic sensory? Explain.
Yeah, its somatic sensation ends at the sulcus terminalis, but the taste innervation extends anteriorly to the anterior line of the vallate. Check it…

1 is a muscle

- Hyoglossus muscle
- Sublingual artery and vein
- Deep lingual artery and vein
- Lingual artery (deep to hypoglossus)
- Dorsal lingual artery and vein

Name these minor glands.

- Labial
- Palatine
- Pharyngeal

What is the submandibular gland duct’s relation to the lingual nerve?
The duct passes over the lingual nerve.

Also, which two muscles originate at #1?

- Pterygomandibular raphe - buccinator and superior constrictor orignate here
- Hyoid bone
- Oblique line
- Pharyngeal raphe
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- Middle pharyngeal constrictor
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor
- Hyoglossus

Name the three muscles and their innervation.

- Salpingopharyngeus - CN X
- Palatopharyngeus - CN X
- Stylopharyngeus - CN IX
Stylopharyngeus is the only pharyngeal muscle not innervated by CN X.

These are gaps in…? What goes through these?

Gaps between/above pharyngeal constrictors.
The eustachian tube and levator veli palatini go through #1.
The stylohyoid ligament, stylopharyngeus muscle, and CN IX (not shown) go through #2.
Dr. Marchant said “don’t worry about it:” internal laryngeal nerve and superior laryngeal artery go through a gap b/t hyoid bone and inferior constrictor
Recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior laryngeal artery go beneath the inferior constrictor.
For the muscles, state their action and innervation.

- Tensor veli palatini: flattens the palate, V3
- Pterygoid hamulus
- Stylohyoid ligament
- Stylohyoid muscle - draws the hyoid bone backwards, facial nerve CN VII
- Stylopharyngeus muscle - shortens pharynx for swallowing, CN IX
- Genioglossus - protrudes tongue, CN XII hypoglossal
- Geniohyoid - elevates hyoid bone, C1 via hypoglossal
- Thyrohyoid - brings hyoid and thyroid cartilage together, C1 via hypoglossal
Also state their action and innervation.

- Salpingopharyngeus - aids in shortening the pharynx while swallowing, CN X
- Muscular uvula - separates the oropharynx from the nasopharynx, CN X
- Palatopharyngeus - shortens pharynx while swallowing, CN X
- Hyoglossus - depresses the tongue, CN XII hypoglossal
Also state the actions and innervations.

- Styloglossus - retracts and cups the tongue, Hypoglossal n (CN XII)
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor - CN X
- Middle pharyngeal constrictor - CN X
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor - CN X
- Mylohyoid - elevates the floor of the mouth, nerve to mylohyoid (branch of inferior alveolar V3)












