Oral and Esophageal Pathology Pictures Flashcards

apthous ulcer or canker sore

Irritation fibroma

pyogenic granuloma

geographic tongue

Fordyce’s granules: heterotopic collections of sebaceous glands in the oral cavity.

hairy leukoplakia
EBV in immunocompomise

squamous papilloma of tonsil

squamous papilloma

leukoplakia

erythroplakia

actinic cheilitis

actinic cheilitis

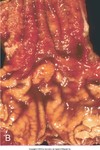
squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue

Sinonasal polyps. Above, low-power magnification showing edematous polypoid masses lined by epithelium. Right, high-power view showing edema and eosinophil-rich inflammatory infiltrate.

Schneiderian papilloma, exophytic (septal) type. Above, the tumor has a papillary growth protruding from the surface respiratory epithelium composed of a thickened non-keratinized squamous (epidermoid) epithelium

Schneiderian papilloma, inverted type. Endophytic or ‘inverted’ growth pattern consisting of thickened epithelial nests arising from the surface and growing down into the stroma; the surface epithelium has undergone squamous metaplasia and the stroma is composed of a myxomatous to fibrous tissue with admixed chronic inflammatory cells.

, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, undifferentiated type. The syncytium-like nests of epithelium (arrow) are surrounded by lymphocytes. Right, in-situ hybridization for EBV (EBER) is positive in the neoplastic cells.

Above right, oral cavity showing a white stone situated within the orifice of the parotid (Stensen’s) duct causing an obstructive sialadenitis (arrow).

sialidenitis
salivary gland parenchymal changes include marked inflammation and acinar atrophy; ducts are dilated and filled with mucopurulent material (arrow).
If this was taken from the parotid…

LESA
, the parotid gland parenchyma is replaced by a mature lymphocytic infiltrate in association with multiple germinal centers (arrows), as well as acinar atrophy and formation of lymphoepithelial lesions; this process is well demarcated from the adjacent salivary gland parenchyma, seen along the left side of this illustration.

mucocele


Pleomorphic adenomas may occur in major as well as minor salivary glands; above left, presentation as a firm, freely movable, painless parotid gland mass (arrow); above right, submucosal painless palatal swelling (arrow); MRI of parotid pleomorphic adenoma (lower right, arrow).

pleomorphic adenoma
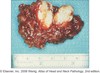

warthin tumor