Oogenesis and Follicular Development Flashcards
(18 cards)
Label each part of the female reproductive system.


What are the components of the fundamental reproductive unit of the female?
A single ovarian follicle, composed of one germ cell (oocyte), surrounded by endocrine cells.
What are the functions of the ovary?
- Oogenesis (the production of gametes)
- Maturation of oocyte
- Expulsion of the mature oocyte (ovulation)
- Secretion of female sex steroid hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) and peptide hormone inhibin
Describe the first phase of oogenesis.
- Occurs during fetal life
- Oogonia develop in the embryonic yolk sac 3 weeks post conception
- Migrate to ovary
- Colonise the cortex
- Undergo mitosis
- At 8-10 weeks meiosis begins
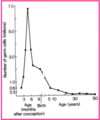
- Millions of oocytes degenerate before birth.
- 1-2 million at birth
- 400,000 around puberty
- Remaining oocytes are arrested in meiotic prophase until last oocytes are ovulated (~50 years).
Describe the second phase of oogenesis.
- Second phase occurs at ovulation.
- Meiosis resumes, stimulated by LH.
- The first division of meiosis is completed and the haploid nuclei separate to form 2 cells.
- The cytoplasm is unequally shared, forming:
- a large secondary oocyte
- a polar body (PB has no further role)
- Meiosis arrests again at metaphase II and the secondary oocyte is ovulated.
- 2nd division of meiosis is only completed in those oocytes that are fertilised.
- Completion of meiosis occurs at the time of fertilisation.

How is the primary oocyte formed?
- Oogonia are produced by mitotic division (maximum ~7 million).
- Then, at 8-10 weeks gestation, prophase of 1st meiosis begins - becomes primary oocyte.
- Surrounded by pre-granulosa cells
- Called the primordial follicle
Where do eggs reside in the female reproductive system?
- Eggs exist in ovaries in structues known as follicles.

Describe the evolution of a follicle.
- Primordial follicle = single layer of granulosa cells around oocyte.
- Oocyte size increases; multiple layers of granulosa cells.
- separation of oocyte from granulosa cells by thick
layer of material (zona pellucida).
- BUT, cytoplamic processes cross the zona pellucida and form gap junctions with oocyte, and nutrients and chemical messengers are passed to oocyte.
- Follicle grows by mitosis of granulosa cells and some differentiate to become theca.
- Antrum begins to form amongst granulosa cells from fluid they secrete.
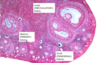
Describe the structure of a primordial follicle.
Identify the structures on the slide.

- Most numerous follicles at any time
- Non-growing (stock pile)
- Oogonium nucleus
- Single layer of follicular cells (granulosa cells)
- Secrete Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
- levels reflect the ovarian follicular reserve and therefore can be measured to assess ovarian ageing

Describe the structure of a primary follicle.
- At puberty ≈ 300,000 oocytes
- May experience 450 cycles
- Loses approx. 650 per cycle
- Throughout life, cohorts of small follicles recruited to begin a period of slow growth.
- Follicular (granulosa) cells divide, forming 3 layers around the oocyte.
- Growth is independent of hormones.
- Takes 85 days (3 cycles) to reach three layers of follicular cells.

Describe the structure of a secondary follicle.
- Also known as antral follicle, Graafian follicle or preovulatory follicle.
- FSH stimulates rapid development of medium follicles over 14 days; leads either to ovulation or to atresia.
- Zona pellucida develops, enclosing the oocyte and masking its antigens.
- Rapid mitotic division in follicular cells forms many layers.
- Antrum develops and fills with fluid.
- LH activates the theca interna to synthesise androstenedione, the precursor for estradiol 17β synthesis by granulosa cells.

Describe the menstrual cycle.

Describe the relationship between ovarian and uterine changes during the menstrual cycle.

Describe how LH and FSH fluctuate in comparison to how oestrogen and progesterone fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle.

What drives the hormonal cycle?
- Anterior pituitary gonadotrophins
- LH
- FSH
- Gonadal sex hormones
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
Describe the chemical mechanisms of ovulation.
-
LH surge
- Induces prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase in granulosa cells (sets up pseudoinflammatory response).
-
FSH (some LH)
- Stimulates release of plasminogen activator from granulosa cells (converts plasminogen to plasmin).
-
Prostaglandins E and F
- release lysosomal enzymes that digest follicular wall - not completely understood.
- “Stigma”
- Forms on surface of follicle, balloons out, forms vesicle and ruptures - oocyte expelled.
- Process facilitated by intrafollicular pressure and contraction of smooth muscle in theca.
Describe the formation of the corpus luteum.
- Mature follicle discharges its antral fluid and egg.
- Collapses around the antrum and undergoes rapid transformation.
- Granulosa cells enlarge, and form gland-like structure (corpus luteum).
- Corpus luteum secretes:
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
- Inhibin
- If there is no egg fertilisation, CL development reaches maximum within approximately 10 days.
- Rapidly degenerates by apoptosis.
Compare and contrast spermatogenesis vs. oogenesis.
- In females, mitotic proliferation of oogonia occurs prior to birth.
- In males, spermatogonia proliferate only after puberty.
- In females, meiotic divisions of oocyte produces only one mature ovum.
- In males, meiotic divisions of primary spermaatocyte produces 4 mature spermatozoa.
- In females, second meiotic division is completes only upon fertilisation.
- In males, the products of meiosis (spermatids) undergo substantial differentiation in the maturing process.



