Infections in Children (Fever) Flashcards
What is the difference between normal temperature and fever in babies?
- Normal temperature in babies and children is ~36.4°, but this can vary slightly from child to child.
- Fever is a high temperature of 38° or more.
What questions should you ask in the hx of a child with a fever?
- Presenting symptoms and hx of presenting complaint.
- Specific symptoms.
- Illness of other family members?
- Specific illness prevalent in the community?
- Lack of immunisations?
- Recent travel abroad (consider malaria, typhoid and viral hepatitis)?
- Increased susceptibility from immunodeficiency?
- This is usually secondary (e.g. post-autosplenectomy in sickle cell disease or nephrotic syndrome, resulting in increased susceptibility to encapsulated organisms such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae and salmonella species).
- Primary immunodeficiency?
- Contact with animals? (Consider brucellosis and Q fever).
- In patients from countries with a high prevalence of HIV, undiagnosed HIV infection in the child must be considered.
What is the importance of considering the age of the child when thinking of differentials for a fever?
- Febrile infants <3 months old present with non-specific clinical features, often have a bacterial infection, which cannot be identified reliably on clinical examination alone.
- It is uncommon for them to have the common viral infections of older infants and children because of passive immunity from their mothers.

What are the clinical features of neonatal sepsis?
- Fever or temperature instability or hypothermia
- Poor feeding
- Vomiting
- Apnoea and bradycardia
- Respiratory distress
- Abdominal distension
- Jaundice
- Neutropaenia
- Hypoglycaemia / hyperglycaemia
- Shick
- Irritability
- Seizures
- Lethargy, drowsiness
-
In meningitis:
- Tense or bluging fontanelle
- Head retraction (opisthotonos)
What are the differentials for a child with a fever and a maculopapular rash?
-
Viral
- HHV6 or 7 (Roseola infantum) - <2 years old.
- Enteroviral rash.
- Parvovirus (‘slapped cheek’) - usually school age.
- Measles - uncommon if immunised.
- Rubella - uncommon if immunised.
-
Bacterial
- Scarlet fever (group A strep).
- Erythema marginatum - rheumatic fever.
- Salmonells typhi (typhoid fever) - classically rose spots.
- Lyme disease - erythema migrans.
-
Other
- Kawasaki disease.
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
What are the differentials for a child with a fever and a vesicular, bullous or pustular rash?
-
Viral
- Varicella zoster virus - chickenpox, shingles.
- Herpes simplex virus.
- Coxsackie - hand, foot and mouth.
-
Bacterial
- Impetigo - characteristic crusting.
- Boils - infection or hair follicles / sweat glands.
- Staphylococcal bullous impetigo.
- Staphylococcal scalded skin.
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis.
-
Other
- Erythema multiforme; Stevens-Johnson syndrome
What are the differentials for a child with a fever and a petechial or purpuric rash?
-
Viral
- Enterovirus and other viral infections
-
Bacterial
- Meningococcal
- Other bacterial sepsis
-
Other
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP)
- Thrombocytopaenia
- Vasculitis
- Malaria
What are the clinical features and complications of chickenpox?

What are the clincal features and complications of measles?
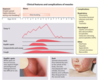
What are the clinical features of streptococcus pyogenes (GABHS)?

Describe the Jones criteria for diagnosis of rheumatic fever.
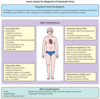
How do you manage a fever with a focus vs. a fever without a focus?
- Examination may identify a focus of infection.
- If identified, investigations and management will be directed towards its treatment.
- However, if no focus is identified, this is often because it is the prodromal phase of a viral illness, but may indicate a potentially serious bacterial infection, especially urinary tract infection or septicaemia.
- If no clear cause for the fever is identified, they require urgent investigation with a septic screen and intravenous antibiotic therapy given immediately to avoid the illness becoming more severe and to prevent rapid spread to other sites of the body.
Give a systematic overview of the differentials for a febrile child.

What are the infectious presentations in the respiratory tract?

Describe the traffic light system for identifying risk of serious illness in a child.

How do you manage a child with a fever without a focus?
- Children who are significantly unwell, particularly if there is no focus of infection, will require investigations and observation or treatment in a paediatric assessment unit, accident and emergency department, or children’s ward.
- A septic screen will be required.

How do you manage a febrile infant <3 months old?
- Unless a clear cause for the fever is identified, they require urgent investigation with a septic screen and broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotic therapy given immediately to avoid the illness becoming more severe and to prevent spreading of the infection to other sites of the body.

What are the most common organisms responsible for intrapartum infections in neonates?
- Group B strep
- E. coli
- Listeria monocytogenes
What is sepsis?
- Bacteria causes a focal infection or proliferates in the bloodstream where there is a host response which includes inflammatory cytokines.
Describe the history and findings on examination of child with sepsis.

Describe the management of a child with septic shock.

What are the clinical signs of shock (early and late)?

Describe toxic shock syndrome.
What are the signs and symptoms?
- Toxin-producing S. aureus and Group A Streptococci can cause this rare syndrome, which is characterised by:
- Fever >39°
- Hypotension
- Diffuse erythematous, macular rash
- The toxin can be released from infection at any site, including small abrasions or burns, which may look minor.
- The toxin acts as a superantigen and causes organ dysfunction.
-
Signs and symptoms:
- GI dysfunction - vomiting and diarrhoea
- Renal impairment
- Liver impairment
- Clotting abnormalities and thrombocytopaenia
- CNS - altered consciousness.
- Intensive care support is required to manage the shock.
Describe the management of TSS.
- Areas of infection should be surgically débrided.
- Antibiotics often include a third-generation cephalosporin (such as ceftriaxone) together with clindamycin, which acts on the bacterial ribosome to switch off toxin production.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin may be given to neutralise the circulating toxin.
- About 1 week to 2 weeks after the onset of the illness, there is desquamation of the palms, soles, fingers, and toes.


