Nuclei/Tract Cross-Sections: Images from Semmelweis Flashcards
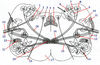
Midbrain
1
What type of nucleus is this?

- Edinger-Westphal Nucleus - Accessory Oculomotor
General Visceromotor (parasympathetic, performs pupil constriction)

Midbrain
2
What neurotransmitter is produced here?

- Substantia Nigra

Dopamine
Midbrain
3
Which funiculus of the spinal cord contains this pathway?

- Rubrospinal Tract - see it coming from Red Nucleus and crossing
Runs through Lateral Funiculus (with the lateral corticospinal tract)

Midbrain
4
What sensation is it involved in?
What type of nucleus?
What is the morphology of this neuron (multipolar, unipolar etc?)

- Mesencephalic Trigeminal Nucleus
Proprioception of Head/Face
General Somatosensory
Pseudounipolar morphology

Midbrain
5
Where do the central branches go?
What is unique about this tract?

- Mesencephalic Trigeminal Tract
Central branches descend into pons, and the fibers synapse with the trigeminal motoneurons innervating the masticatory muscles
Forms the only monosynaptic reflex arc in the brainstem, creating the jaw jerk reflex when the jaw is extended

Midbrain
6
What cranial nerves are involved in this pathway?
Between what places does it travel?

- Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF)
Primarily involved in the directing eye movement via cranial nerves III, IV, VI, connecting them with the vestibular nucleus, also involving CN VIII for head movement information
Travels from the Interstitial Nucleus of Cajal to the cervical spinal cord

Midbrain
7
What type of information does it carry, and to where?

- Brachium of Inferior Collicle
Carries auditory information to the Medial Geniculate Body (MGB) of the thalamus

8
What type of information does it receive?

- Medial Geniculate Body (MGB) of (meta)thalamus

Not part of midbrain, but must have been drawn this way to show a connection between midbrain and thalamus
An intermediate connection in the auditory pathway, between inferior collicle and auditory cortex
Midbrain
9
What tract(s) originate here?
What tract(s) terminate here?

- Red Nucleus
Rubrospinal Tract (#3) originates from here and crosses in midbrain, then goes to affect lower motor neurons. Has limited function in humans, most of voluntary control is from corticospinal tract
Some branches called the rubro-olivary tract also go to the inferior olive (uncrossed pathway)
Dentatorubro tract terminates here; it comes from dentate nucleus of cerebellum

Midbrain
10
What type of information do these fibers carry?
Where do these fibers originate from?
Where do these fibers decussate?
Where do these fibers go?

- Medial Lemniscus
Carries epicritic information from the body
Contains the afferent fibers coming from gracile and cuneate nuclei (Dorsal Column)
Decussate in the medulla
Goes to Thalamus VPL, then to sensory cortex

Midbrain
11
Which part of the internal capsule does this pass through?

- Türck Tract (temporo-parieto-occipito-pontine)
Passes through posterior limb of internal capsule

Midbrain
12
Which part of the internal capsule does this travel through?

- Corticospinal Tract
Posterior Limb of internal capsule

Midbrain
13
Which limb of the internal capsule does this pass through?

- Arnold Tract (fronto-pontine)
Anterior limb of internal capsule

Midbrain
14

- Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)

Midbrain
15

- Tectospinal Tract (see the tract originating from tectum)

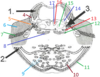
upper medula
1
what type of nucleus?
What nerve(s) have fibers with this nucleus in this section?

Solitary nucleus and Solitary tract
Special Viscerosensory Nucleus (taste)
Nerves IX and X have afferent fibers to the solitary nucleus here in the medulla
Nerve VII has a connection more superiorly!

upper medulla
2
what type of nucleus is it?
which cranial nerve(s) have fibers here?

2 dorsal vagal nucleus
aka medial ala cinera nucleus
General Visceromotor (parasympathetic)
Only Vagus

upper medulla
3
What type of nucleus is it?

- Hypoglossal nucleus
Somatomotor nucleus

upper medulla
4

4 medial longitudinal fasciculus

upper medulla
5

5 tectospinal tract

upper medulla
unlabelled black line between 5 and 6
What cranial nerve(s) have fibers here?
What type of nucleus?

unlabelled line btwn 5 and 6
lateral ala cinerea nucleus
Glossopharyngeus and Vagus have sensory fibers that go here
General Viscerosensory (GVS) - the only nucleus like this!

upper medulla
6

6 area postrema

upper medulla
7
which order neuron is this?

7 nucleus gracilis
second order neuron

upper medulla
8

8 nucleus cuneate