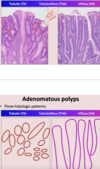
Normal Histology "Pathology" of GI Flashcards
how to tell it’s esophageal tissue
stratified squamous epithelium


stomach

small intestine

large intestine, has smaller villi
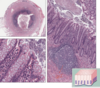
Appendix

surface mucous cells of the stomach
in barretts esophagus, ___ ___ epithelium (normal) becomes:
The process of cell change from flat, layered squamous to tall columnar epithelium is an example of metaplasia.
which the normal squamous cells lining the distal esophagus are replaced by intestinal-type columnar cells7. Barrett’s esophagus develops through the process of metaplasia, the replacement of one adult cell type by another.
causes of this

this is esophagitis.
causded by
- GERD (can progress to barretts and then carcinoma)
- pills/medications wihtout sufficient fluids/food
- irradiation
- caustic/corrosive
- infectious (fungal or herpes)
- Graft vs Host
- Immunoallergic (esosinophilic esophagitis)



CMV esophagitis

mechanism for GERD aka Reflux esophagitis

name these states


endoscopal findings of eosinophilic esophagitis
Endoscopically characterized by esophageal rings and furrows
Common presentation of symptoms that include food impaction
and dysphagia in adults, feeding intolerance and GERD-like
symptoms in children • Many have atopy, including eczema, allergic rhinitis, asthma and
modest peripheral eosinophilia
(trachealization)


eosinophilic esophagitis
metaplasia
reversible change in which one differentiated cell type is replaced by another celltype. often an adaptive mechanism substition of cells tha are sensitive to stress.
The influences that predispose to metaplasia, if persistent, may initiate malignant
transformation in metaplastic epithelium

Barrett Esophagus

• Increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma
– Barrett Esophagus can develop dysplasia, considered premalignant
(0.2-2.0%/year)
• Risk of cancer progression: low grade (0.7%) or high grade (6%) depending on
how close to cancer it looks like (more later on dysplasia) • Endoscopic surveillance is required
– Vast majority of esophageal adenocarcinoma are associated with
Barrett Esophagus



benign or malignant?

benign peptic ulcer. often flat erosion through mucosa to deeper layer

duodenal ulcer
ulcers erode through the ___ and into the ____
erodes through the mucosa, goes through submucosa

this ulcer bed is in a state of____ how?
inflammation. you can see neutrophils and fibrin

features of benign vs peptic ulcers