Approach to Lymphadenopathy Flashcards
the lymph node at the the left super calvicular area is aka
the virchows node
in terms of node consistency:
normal is _____; hard may be ___, rubbery may be ___, fluctuant may be ___
normal is soft; hard may be carcinoma, rubbery may be lymphoma, fluctuant may be infectious
if a node is tender, you must consider:
the first thing to think about is infection or inflammation. usually malignant ones are painless but not all the time
outline the scheme for the classification and differential diagnosis of localized lymphadenopathy
reactive vs neoplastic

outline the scheme for the classification and differential diagnosis for DIFFUSE lymphadenopathy

outline the scheme for hematological malignancies
“Lymphoma” is the malignant neoplasm of lymphoid tissue or “monoclonal proliferation of cells of Immune system

lymphoma can be ____ or ___ lymphoma
non-hodgkin or hodgkin lymphoma

if you do flow cytometry and it revelas that the excess proteins are polyclonal, it indicates ____. If monoclonal, it indicates ____
polyclonal ; indicates reactive
monoclonal; indicates malignant

compare and contrast lymphoma and leukemia

compare and contrast the incidience of non-hodkin and hodgkin lymphoma
non: more prevalent in older people
hodgkin: common in young people and then old people, with less liklihood aat middle age.

what’re the types of non-hodgkin lymphomas?
- B cell lymphoma (85%)
- T cell lymphoma (13%)
- NK cell lymphoma
how does B cell lymphoma (non-hodgkin) occur?
lymphoma occurs when enough genetic insults freeze the cells during differentiation.
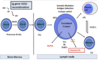
methods of getting a definite diagnosis of lymphoma
- fine need aspiration
- needle core biopsy
- surgical biopsy (best preference)
essential information required to start treatment

classical hodgkin lymphoma has a ____ age distribution and mostly presents as ___ lymphadenopathy. The lymph nodes tend to be ___ ____ and ___, and spreads in an orderly fashion (nodal). Is it curable?
it is curable. it’s one of the few curable cancers.
classical hodgkin lymphoma has a BIMODAL age distribution and mostly presents as CERVICAL lymphadenopathy. The lymph nodes tend to be NONTENDER, SOFT and MOBILE, and spreads in an orderly fashion (nodal).
this is a slide of a lymph node biopsy. what type of lymphoma might this person have?

hodgkins lymphoma. faint hypotrophic lymph nodes indicate a fibrosis.

which cells are characteristically seen in a classical hodgkin lymphoma PBS?
reed-sternberd cells that are surrounded by reactive cells like eosinophils, neutrophils, lypmohcytes and plasma cells.

what is the circled cells and what disease might this person have

reed-sternberg cells. characteristic of hodgkin lymphoma
most common subtypes of non-hodgkin lympoma
- diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- follicular lymphoma
- CLL/SLL
- T cell and NK cell lymphoma aren’t that common.
Follicular lymphoma is a common ____-cell lymphoma in adults. It’s associated with the ___ translocation and has an ____ clincal course except in high grade cases.
Relapse and progression to aggressive disease is common.
common B cell lymphoma.
14;18 translocation
INDOLENT
compare and contrast these two lymph node slides

left: follicular lymphoma
right: normal
hodgkin lymphoma is associated with the ___ and ___ variant antigens
cd15 and cd30

which antigens are follicular lymphomas associated with
cd3 (t)
cd20 (b)
Bcl-2

diffuse large B-cell lymphnoma is a common B-cell lymphoma that can present at ____ age. it has an ____ clinical course and usually presents as advance stage. A high percentage of patients can be cured
present at any age. it has an AGGRESSIVE clinical course.










