Non-Melanocytic Tumours Flashcards
what is Benign seborrheic keratosis
a benign warty spot that appears during adult life as a common sign of skin ageing
(basal cell papilloma)

Benign seborrheic keratosis appearance
stuck on and greasy hyperkeratotic surface (basal cell papilloma)
Benign seborrheic keratosis histology
- benign proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes
- keratin filled HORN CYSTS and ACANTHOSIS

what can the sudden emergence of lots of Benign seborrheic keratosis lesions indicate
- The sudden emergency of many lesions may indicate internal malignancy – Leser-Trélat sign
- Often occurs with malignant acanthosis nigricans when there is underlying adenocarcinoma of the stomach

BCC clinical presentation
- Slow growing lump which may go on to form a non-healing ulcer (centrally – rodent ulcer).
- Pearly/translucent edge with visible dilated blood vessels.
- painless and often ignored
*

BCC describe central ulceration
rodent ulcer

superficial variant of BCC
- Most common type in younger adults
- More common on upper arms and shoulders

morphoeic variant of BCC
- A flat, diffuse superficial form exists as an ill-defined morphoeic variant – infiltrative (greater degree of morbidity)
- These are often found on mid facial sites
- Waxy scar-like plaque with indistinct borders

BCC where/who
sun exposed skin of middle aged and elderly white people
rarely found on ear
BCC histology
basal cells sprout from epidermis, groups of cells invade the dermis
desmoplastic stroma
there is characteristic PALISADING

BCC treatment
normally cured by total excision
BCC effect of delay in treatment
less important as invade locally but do not spread widely - metastases are rare
BCC what mutation is associated
PTCH1 - component of the hedgehog signalling pathway
what does the hedgehog signalling pathway do
activate transcription factors leading to induction of cell proliferation genes and angiogenesis activators
what blocks hedgehog signalling
vismodegib
what is naevoid BCC also known as
gorlins syndrome
gorlins syndrome inheritance
Au D
gorlins syndrome features
multiple early onset basal cell skin cancers and other cancers
palmar pits, jaw cysts and ectopic
what is butterfly disease caused by
genetic defects in the genes that encode for type VII collagen

another name for butterfly disease
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
name two precursors to SCC
acitinic keratosis and bowen disease
acitinic keratosis
Frequently develop later in life in white-skinned people who have had significant sun exposure.
They appear on the skin as erythematous silver-scaly plaques or patches with a conical surface and a red base.
The background skin is often inelastic, wrinkled and may show flat brown macules (solar lentigos) reflecting diffuse solar damage.
a small proportion may transform into SCC, but only after many years

bowen disease
intra-epidermal carcinoma in situ (no dermal invasion), which can rarely become invasive
thought to be due to long term sun exposure, presents on exposed skin (most commonly womens legs)
epidermal neoplastic lesions that cannot yet invade the underlying tissues

bowens disease features
erythematous scaly patches/plaques with an irregular border
can mimic inflammatory conditions
lesions do not clear but slowly increase in size with time

where is bowens disease most commonly found
legs
what is a viral lesion that is a pre cancerous disease of the penis
erythroplasia of Queryat-penile
what is erythroplasia of Queryat-penile associated with
HPV
SCC features
hyperkeratotic (crusted) nodule or area of induration. can advance to ulceration and destruction of underlying tissues may be painful or bleed

fast!!
do SCC grow fast or slow
fast - more aggressive than BCC
do SCC metastase
5% risk - incurable to regional lymph nodes and bone
where can SCC occasionally arise
on chronic leg ulcers eg stasis ulcers
sites of burns, sinuses eg chronic osteomyelitis
chronic lupus vulgaris
chronic lupus vulgaris
chronic inflammation, invasion of the skin by M. Tuberculosis
can rarely be complicated by SCC

what is SCC rarely associated with
xeroderma pigmentosum (cant repair skin damage from UV light so obv get cancer) and dystrophic variant epidermolysis bullosa (butterfly disease)
what are some adverse prognosis features of SCC
thickness >4mm and poor differentiation
lymphatic/vascular space invasion
perineural spread
specific sites - ear, nose, scalp
ulceration
keratocanthoma
Keratocanthoma is a skin cancer tumour that is benign.
- It originates in the pilosebaceous glands.
- Clinically and pathologically resembles SCC and rarely progresses into an invasive SCC
- Typically grow rapidly (faster than a SCC would)
- Tend to develop on sun-exposed skin
- Nodular with a central crater containing a keratin plug
- As it cannot reliably be clinically distinguished from SCC, is usually surgically removed. If left untreated, most resolve in 4-6 months but leave residual scarring.

merkel cell carcinoma
highly aggressive, readily metastases
Present as a red/blue nodule
Merkel cells exist in the basal layer between keratinocytes and nerve fibres – act as mechanoreceptors. Carcinomas are referred to as neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin.
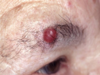
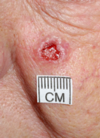
rodent ulcer - BCC

nodular BCC

superifical BCC
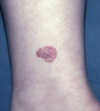
bowens disease
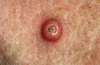
keratocanthoma (subtype of SCC)
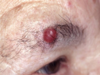
merkel cell carcinoma
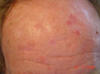
acitinic keratosis
BCC or SCC

BCC
BCC or SCC
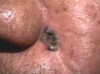
BCC
BCC or SCC
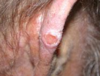
SCC
BCC or SCC
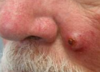
SCC

keratocanthoma
thought it was an SCC? clinically hard to distinguish, this is why they are removed

cutaeneous horn - subtype of SCC
also associated with viral warts (HPV)
what disease is this a feature of
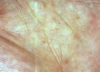
palmar pits - Gorlins syndrome
kaposi’s sarcoma
This is a tumour of vascular and lymphatic endothelium that presents as purplish nodules and plaques. There are 3 types:
- Classic/sporadic
- Endemic
- Immunosuppression related form - more severe and common in HIV positive men who have sex with men
Can cause chronic adrenal insufficiency



