NMR Flashcards
(11 cards)
1H NMR features
- one peak for each set of equivalent H atoms
- equivalent H atoms are bonded to the same groups/atoms
- the intensity of the peak is proportional to the number of equivalent H atoms within the set
- area of peak is proportional to the number of H atoms it represents - given as a number usually a decimal
- the simplest whole number ratio of the relative areas tells you how many equivalent H atoms for each peak
- chemical shift tells you how far along the x-axis the peak will be found
- protons in the same environment are shifted by the same amount
- the size of chemical shift depends on the atoms/groups bonded to the H
- the more electronegative the group , the greater the shift
*

samples are dissolved in solvent free of 1H atoms, explain why and give examples of alternative solvents
to prevent signals in spectrum due to H atoms in solvent
CCl4 and CDCl3
what is the standard used for NMR why is it used?
TMS (tetramethylsilane)
low electronegativity of Si means the signal produced is far away to the right from other organic molecules (chemical shift of 0ppm)
only produces one signal as all H and C atoms in the same environment
non-toxic
inert
volatile due to low BP so easily removed from sample

how many signals would be produced for ethylpropanoate and what is the ratio of each signal

what does splitting mean?
the number of smaller peaks a signal is split into gives us information about the H atoms on adjacent C atoms
n+1 rule = number of Hs on adjacent Carbon + 1

here is the spectrum for a compound with molecular formula C4H8O2 , deduce its structure
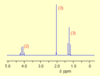
when you see a quartet and a triplet this usually indicates a ethyl group is present

when does splitting not occur?
equivalent H atoms on the next atoms and OH groups do not cause splitting (so produce a singlet)

deduce the structure of this compound
its molecular formula is C6H14O

the IR spectrum tell us the O is part of an OH group
integration ratio is 4:1:3:6
4 peaks so there are 4 different H environments
singlet with integration 1 must be due to H in OH alcohol group
singlet with integration 3 due to CH3 with no adjacent H (attached to 3 R groups)
quartet + triplet indicates CH3CH2 group
integration 4 and 6 indicates there are 2 CH3CH2 groups

deduce the structure of this compound


13C NMR
no link between area under peak and number of equivalent C atoms
no splitting
spectrum contains a number of single peak that correspond to the number of sets of equivalent C atoms, the chemical shift determines how far along the x-axis the peak is
determine the number of peak in the 13C spectrum for each compound and give the IUPAC name




