Nitrogen Metabolism I and II Flashcards
(60 cards)
nitrogen balance
in a normal human adult N(in) = N(out)
in a growing child, adolescent, pregnancy N(in) > N(out)
eating too little protein or lacking essential amino acids N(in) < N(out)
three sources for the amino acid pool
degradation of body proteins
dietary proteins
synthesis of non-essential amino acids
three fates of amino acids in the amino acid pool
synthesis of body proteins
precursors for essential nitrogen-containing small molecules
conversion to clucose, glycogen, fatty acids, or CO2
two main routes for amin removal
alanine aminotransferase transfers amino group from alanine to a-KG to make glutamate
aspartate aminotransferase transfers amino groups from glutamate to oxaloacetate to form aspartate

What coenzyme is required for aminotransferase reactions?
pyridoxal phosphate, a derivative of vitamin B6
What are the main sources for the nitrogen cycle?
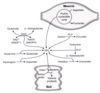
What amino acid undergoes rapid oxidative deamination, and what is the enzyme that catalyzes this?
glutamate, glutamate dehydrogenase
uses NAD+ or NADP+ as the coenzyme
GTP is an allosteric inhibitor and ADP is an allosteric activator
What happens to D-amino acids from plants?
metabolized by D-amino acid oxidase in a FAD-dependent reaction in peroxisomes
Which amino acids do not undergo transamination reactions?
lysine, threonine, proline, and HO-proline
alanine aminotransferase reaction

aspartate aminotransferase reaction

glutamate dehydrogenase reaction

Describe the glucose/alanine cycle.
transfers nitrogen to the liver, ammonia in the blood is toxic so adds it onto alanine for transport
done primarily in muscle tissue

Describe the process of transporting nitrogen through blood as glutamine.
primarily used by peripheral tissues, but if there is a lot of tissue breakdown, muscle will use this process as well

Describe the oxidative deamination process by amino acid oxidases in peroxisomes.
Flavoprotein and FAD are the same

Describe the urea cycle.
Ornithine is an amino acid not used in proteins and is recycled
fumarate is a byproduct, connecting this with the TCA cycle
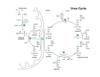
three mechanisms that regulate the urea cycle
substrate availability in a feed-forward mechanism
allosteric activation of carbamoyl phosphate synthease I (CPSI) by N-acetylglutamate (NAG)
induction/repression of urea cycle enzyme synthesis during high protein diet or during starvation
regulation of CPSI
main method of regulation, senses how much amine is coming in

How are the urea and TCA cycles linked?

Name and describe how the glucogenic amino aicds contribute to the TCA cycle.
carbons of these amino acids can be used in gluconeogenesis:
Thr, Gly, Trp, Ala, Ser, Cys, Asp, Asn, Tyr, Phe, Val, Ile, Met, Arg, His, Gln, Pro

Identify and describe how the ketogenic amino acids feed into the TCA.
ketogenic amino acids made acetyl CoA or acetoacetate:
Trp, Thr, Lys, Ile, Leu, Tyr, Phe
asparagine to oxaloacetate

a-KG from glutamine

a-KG from proline
type I hyperprolinemia - defect in proline dehydrogenase
typw II hyperprolinemia - defect in glutamate semialdehyde dehydrogenase