Neuroanatomy Flashcards
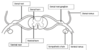
Label the cross section of the spinal cord.

What is found in a dorsal root ganglion?
Contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons that bring information from the periphery to the spinal cord.
What are the posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) rami?
The dorsal and ventral rami contain nerves that provide visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information.
Dorsal ramus feeding the dorsal trunk (skin and muscles of the back).
Ventral ramus feeding the ventral trunk and limbs through the ventrolateral surface.
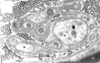
The image shows a transverse section of the cervical spinal cord. The area arrowed at (a) and (b) has been stained to show the grey matter, which resembles a butterfly in shape. What are structures a and b known as ?

a-Dorsal horn
b-Ventral horn
What kinds of nerve fibre will enter the spinal cord at (a)?

Nerve fibres from the Peripheral Nervous System(PNS).
The cell bodies of which type of neurone will be found in (b)?

The ventral horns contains the cell bodies of motor neurons that send axons via the ventral roots of the spinal nerves to terminate on striated muscles.
What are the large, dark blue-staining projections (c) on either side of this section of the spinal cord?
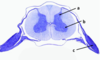
Dorsal root ganglion-Whihc contain cell bodies of sensory neurons which relay information form the periphery to the spinal cord through the dorsal horns.
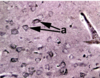
Identify the type of neurone arrowed at (a) and describe the appearance of its nucleus. What does this tell you about this cell’s activity?
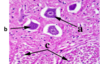
Motor neuron cell body.The nucleus is large(white ring within the cell body). High quantity of rNA for high rate of protein synthesis.
The cell arrowed at b lacks a visible nucleus – what would this be called and why is a nucleus not present?

Motor neuron cell body sectioned in a plane away from its nucleus.
Imagine slicing through a boiled egg away from the yoke(nucleus).
What are the structures labelled c?
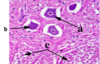
Neurological cells-cells that provide support and nutrition, regulate the internal environment of the brain
What are Nissl bodies and where would you find them?

Nissl bodies are the blue staining patches in the cytoplasm of the cell.These are aggregations of rough endoplasmic reticulum for high rate of protein synthesis.
Is the cerebral cortex grey matter or white matter? Identify the structures arrowed at (a) and (b).
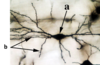
The cerebral cortex is gray matter.As it is the outer surface of the brain.
A-Cell body
B-Dendrites
What is the structure arrowed at (a)?

the ring of myelin
Identify the tissue arrowed at (b). State the function of tissue B.

It is the perineurium- creates an internal versus an external environment for the neurons.it is basically the sheath of connective tissue surrounding a bundle (fascicle) of nerve fibres within a nerve.
What are the structures arrowed at (a) and (b)?

A-Motor neuron
B-Neuromuscular junction (motor end plate)