Neuro - Special Senses Vision & Hearing Flashcards
What are the 2 photoreceptors of the eyeball?
- Cones
- Rods
Where are the photoreceptors of the eye located?
Retina
What vision are the cones responsible for?
Vision in the dalylight
What vision are rods responsible for?
Dim light
What is the term for the part of the retina on the nasal side (medial)?
Nasal hemiretina

The nasal hemiretina receives stimulie from what visual field?
From the temporal visual field

What is the term for the part of the retina on the temporal side?
Temporal hemiretina

The temporal hemiretina receives stimuli from which visual field?
The nasal visual field

If you damage your right temporal retina what could you not see?
Objects to the left of your right eye (obj. in the nasal visual field of the right eye)

If you damage your left temporal retina what could you not see?
Obj. in the right side of your left eye (obj. in the nasal visual field of your left eye)
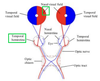
Does the nasal retina cross the optic chiasm to the opposite side?
YES

Does the temporal retinal cross the optic chiasm to the opposite side?
NO

What forms the optic nerve?
axons of ganglion cells of the retina
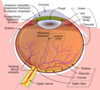
Where does the optic nerve exit the orbit?
Optical canal

Is the optic nerve considered a peripheral nerve or a tract?
Tract - b/c it’s surronded by cranial meninges and subarachnoid space
Are the fibers of the optic n. myelinated or unmylinated?
Myelinated by oligodendrocytes (like CNS tracts)
What is the optic disc?
- Blind spot
- point of exit of the optic n. from the eyeball

Does the optic disc have photoreceptors?
NO - it’s a blind spot
What part of the eye has the greatest acuity (sharpness)
Fovea Cetralis

Does the fovea contain cones and rods?
ONLY cones
Is the fovea lateral or medial to the optic n.?
Lateral

Where is the fovea located?
In the Macula Lutea

What is the visual pathway?
Visual Pathway
Light –> Rods & cones –> Bipolar cells –> Ganglion cells –> Optic Nerve –> Optic Chiasm –> Optic Tract –> LGB –> Optic Radiations –> Primary Visual Cortex
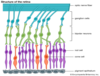
Another pic of the visual pathway showing the end of it
Visual Pathway
Light –> Rods & cones –> Bipolar cells –> Ganglion cells –> Optic Nerve –> Optic Chiasm –> Optic Tract –> LGB –> Optic Radiations –> Primary Visual Cortex

What is a visual field?
All of what you see
How many visual fields are there for both eyes?
ONE visual field for both eyes
How many quadrants is the visual field divided in to? And what are they?
4 quadrants:
- Upper Left
- Lower Left
- Upper Right
- Lower Right

What is the function of the optic chiasm?
Allows images from one side of the visual field to go to the contralateral visual cortex

Do both nasal retina fibers and temporal retina fibers cross the optic chiasm?
NO - only nasal retina fibers

Is the internal carotid a. located lateral or medial to the optic chiasm?
Lateral

If there is an aneurysm in the ICA what will it do to the optic chiasm?
It can press on the lateral side of the optic chiasm - which would affect the temporal retina fibers
If the ICA presses on the lateral side of the optic chiasm and the temporal retina fibers are affected, what can you not see?
You can’t see out of your nasal visual fields

Bilateral atherosclerosis and calcification of the ICA affects BOTH temporal retina fibers, what would not be able to see?
You would not be able to see out of your left and right nasal visual fields
so you’d only be able to see peripherally

Where is the pituitary gland located in regards to the optic chiasm?
Deep underneather the optic chiasm

If there is a pituitary tumor present how will it affect the optic chiasm?
It will press on the middle of it

If a pituitary tumor is pressing on the middle of the optic chiasm, which retinal fibers are affected?
Nasal retinal fibers
If the nasal retina fibers of BOTH EYES are affected, what will you not be able to see?
You will not be able to see the temporal visual field of either eye
So you lose peripheal vision and can only see centrally

Where do the optic tracs travel to?
- From the optic chiasm
- To the pretectal area
- To the LBG of the thalamus

If 90% of retinal afferent fibers go to the LGB of the thalamus, where do the remiander go?
Pretectal area - for the pupillary light reflex

Where do the optic radiation run?
From the LGB to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe

Why are optic radiation called “radiations”?
The fibers spead out through 3 lobes of the barin before reaching the visual cortex
What 3 lobes of the brain can you find the optic radiations?
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
What is the part of the temporal lobe that has optic radiations called?
Meyer’s loop - it relays in the lingual guyrus of the visual cortex

What is the orientation of Myer’s loop
- In the anterior temporal lobe
- Adjacent to the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
- Dips forward, down then back

Where is Broadmann are 17 (primary visual cortex) located?
Adjacent to the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe

The INFERIOR retina fibers are stimulated by things seen in which visual field? And will end up in what part of the primary visual cortex?
Simulated by things seen in the SUPERIOR visual field and will end up on the contralateral lingual guyrus (below the calcarine fissure/lower part of the primary visual cortex)

The SUPERIOR retina fibers are stimulated by things seen in which visual field? And will end up in what part of the primary visual cortex?
Simulated by things seen in the INFERIOR visual field and will end up on the contralateral cuneus (above the calcarine fissure/upper part of the primary visual cortex)

Lower retina visual fields
L. upper visual field —> inferior retina fibers —> R. lingual gyrus
R. upper visual field —> inferior retina fibers —> L. lingual gyrus
Upper retina visual field
L. lower visual field —> upper retina fibers —> R. cuneus gyrus
R. lower visual field —> upper retina fibers —> L. cuneus gyrus
*** NO Meyer’s loop in upper retina visual field
Images from the fovea are represented where?
Larger area on the lateral aspects of the each primary cortex


