Nervous 1 Flashcards
Which cranial fossa does the brainstem lie in?
Foramen magnum
What cavity of the ventricular system that lie within the brainstem?
Ventricle IV
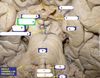
What is A?

Pons
What is B?

Pontomedullary junction
What is C?
Medulla
What cranial nerves can you see emerging from the pontomedullar junction?
CV VI
CN VII
CN VIII
What cranial nerve emerges from the pontomedullary junction and has the longest course?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
What is D?

CN VI
What is E?

VII/VIII
The long course course of CN VII makes it vulnerable to what?
Injury by increased cranial pressure or other mechnical factors
Consequences of this nerve being damaged is Bell’s palsy
What is A?

Pyramid
What is B?

Anterior fissure
What is C?

Ventero-lateral sulcus
What is D?

Postero-lateral sulcus
What is E?

Decussation of pyramids
What is F?

Olive
What is G?

Pons
What produces the pyramids?
Corticospinal tract
Corticobulbar tract
Where does the corticospinal tract run between?
From cerebral cortex to spinal cord
Where does the corticobulbar tract run between?
From motor cortex in front lobe to CN in brainstem
What produces the decissation of the pyramids?
Corticospinal tracts crossing
What forms the olives?
Inferior olivary nucleus
Posteriorly on the medulla, some parts can be identified as “open” and some as “closed”, which is more superior?
Open is superior
Closed in inferior

What structure does the “open” part of the medulla open into?
Ventricle IV