Neoplasia 3 Flashcards
Carcinogenesis=
causes of cancer
name some intrinsic factors of neplasia
Hereditary
- Autosomal dominant genes most likely to cause tumour in the young
- Will develop neoplasia
- E.g. breast cancer
- Less frequent genes- neoplastic phenotype
- Multiple abnormalities which lead to an increased risk
Age
- The older you are the longer you’ve had to develop
Sex (particularly hormone)
- E.g. breast cancer predominately a female cancer due to oestrogen exposure
Extrinsic factors
Environment
- Chemical
- Radiation
- X-ray
Infection
- HPV
Behaviour (30%)
- Tobacco smoke
- Obesity
- Sun exposure (UV damage)
- Alcohol
- Lack of exercise (independent to BMI)
Being overweight and obese is the 2nd biggest cause of cancer
Keeping a healthy weight reduces the risk of 13 different types of cancer
smoking is the biggest
preventable cause of cancer (25%)
which cancers is smoking a risk factor for?
- Lung cancer 7/10- most common cause of cancer death
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Nose
- And sinuses
- Larynx
- Oesophagus
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Stomach
- Kidney
- Bowel
- Ovary
- Bladder
- Cervix
- Some type of leukaemia
if you drink and smoke it increases your risk of which cancers
upper airwars and digestive tract cancer
evidence of cancer
- Animal studies
- Epidemiological studies
- Studies of migrating population
- Look at baseline risk in original country
- Then look at the rate of cancer once they have migrated
- E,g, Japanese migrants to USA
approx how much of cancer risk is due to environment/ extrinsic factors
85%

example of a chemical that is a carcinogen
2-napthylamine (also present in smoke) is an industrial carcinogen used in the dye manufacturing industry
2-napthylamine
This dye causes cancer
Malignant neoplasms caused by 2-napthylamine showed that:
- There is a long delay between carcinogen exposure and malignant neoplasm onset
- The risk of cancer depends on total carcinogen dosage
- There is sometimes organ specificity for particular carcinogens e.g. bladder cancer

chemical carcinogenesis involves
initiation and promotion
initiation and promotion
- Sequence in which carcinogens are administered is critical
- Initiators must be given first
- Followed by a second class carcinogen called promoters

Test used to tell if chemical is a carcinogen
AIMS test
AIMs test
positive result- carcinogen capable of causing mutation

why is rat liver used in AIMs test?
most chemicals are pro-carcinogens until they are been activated in the liver (by cytochrome P450)
people with germline mutations get
cancer earlier
- neoplastic cells get a head start

an initiator=
anything that causes mutation e.g. radiation
promoters
anything that causes expansion of that population
examples of chemicals
- polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- aromatic amines
- N-nitroso compounds
- alkylating agents
- natural products
example of aklylating agent
Vinyl chloride
- mainly found in factories
natural products
aflatoxin B1
- found in virus- liver cancer
asbestos
natural products
- okay if left as it is
- as soon as disrupted will be inhalte and irritate alveoli
- both initiator and promotor
type of radiation that are mutagenic
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
X ray
Uv ray
how can radiation cause cancer
- damage DNA directly
- or indirectly generating free radicals
how does radiation create free radicals
by crashing into water
25% of all malignant neoplasms are
skin neoplasms- UV
sources of ionising radiation
- radon gas
- medical tests
infections and cancer
- Some infections directly affect genes that control cell growth
- Others do so indirectly by causing chronic tissue injury and the resulting regeneration acts either as a promoter for pre-existing mutations or causes new mutations from DNA replication errors
example of infection with direct effect
HPV
Indirect effect
HEP B virus
- chronic inflammation= promotor
Human papilloma virus (HPV)
- Makes 2 proteins E6 and E7
- Virus infects cell
- ensures it doesn’t die and then hijacks its DNA replication machinery to make more virus particles
- E6 inhibits P53 which prevents cells from undergoing apoptosis
- Hijacks cell cycle by interfering with Rb protein which is an important cell cycle checkpoint
example of an inherited cancer
retinoblastoma - rare tumour of the eye
how many Rb cases are familial or sporadic
40% familial
60% sporadically
familial Rb
- Autosomal dominant means more likely to get it young
- Occurs early
- Can affect both eyes
Sporadic Rb
- In one eye
- Generally, aren’t at increased risk of other cancer
- Need 2 sporadic hits (mutations)
- Occurs later

Tumour suppressors
- Normal function to stop proliferation
- Loss of function
- Most instances both alleles must be damaged for transformation to occur
- Abnormalities in these genes leads to failure of growth inhibition
example of tumour suppressor gene
Retinoblastoma gene
- Key gene regulation of G1/s cell cycle checkpoint
- Also controls cellular differentiation
Proto-oncogenes
- Drive proliferation
- Gain of function mutation
example of protooncogene
- Most common type of abnormalities involving proto-oncogenes in human tumours
- They are mutated in approx. 15-20% of all malignant neoplasm
- Some types of cancers the frequency of RAS mutation is much higher e.g. 90% of pancreatic adenocarcinomas
- They were discovered initially in transforming retroviruses (HIV)
protoncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
play opposing roles in the cell signalling pathways
accumulation of mutations leads to
malignant cancers
proto-oncogenes can encode
- growth factors (e.g. PGDF),
- growth factor receptors ( e.g. HER2),
- plasma membrane signal transducers (e.g. RAS),
- intracellular kinases (e.g. BRAF),
- transcription factors (e.g. MYC),
- cell cycle regulators (e.g. Cyclin D1) apoptosis regulators (e.g. BCL2)
DNA repair genes
- caretakers genes prevent accumulation of DNA damage
- familial cancer syndromes help our understaning
- some inherited cancer syndromes have germline mutations that indirectly affect DNA repair
familial breast cancer
- BRAC1/ BRAC2 genes
- Involved in repairing double strand DNA breaks
- Can also be found in sporadic malignant neoplasms
Chromosome aggregation during mitosis can also be abnormal in malignant cells
- Alterations account for accelerated mutations found in malignant neoplasms known as genetic instability
- Genes that maintain stability belong to a class of tumour suppressor genes called caretaker genes
malignant neoplasm = ………………. mutations
10 or less
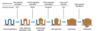
hallmarks of cancer (6)
- Self sufficiency in growth signals
- Resistance to growth stop signals – TSG’s (tumour suppressor genes)
- Cell immortalisation (no limitation on the number of times a cell can divide)
- Sustained ability to induce new blood vessels (angiogenesis)
- Resistance to apoptosis
- Ability to invade and produce metastases
example of self0sufficient growth signal
HER2 gene amplification (breast cancer)
example of resistance to anti-growth signals
CDKN2A gene deltion
(CDK inhibitor)
Melanoma
example of grow indefinitley
telomorase gene activation
- most cancers
example of induce new blood vessels
activation of VEGF expression
- many cancers
example of resistance to apoptosis
BCL2 gene translocation (lymphoma)
example of inavade and produce metastases
E-cadherin mutation
- gastric cancer


