Atherosclerosis Flashcards
(52 cards)
define atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of intracellular and extracellular lipid in the intima and media of large and medium sized arteries
Common sites
- Aorta- especially abdominal (AAA- Abdominal aortic aneursym)
- Coronary arteries
- Carotid arteries
- Cerebral arteries
- Leg arteries
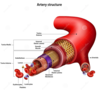
normal arterial structure
- Endothelium
- Subendothelial connective tissue
- Internal elastic lamina
- Muscular media
- External elastic lamina
- Adventitia
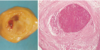
macroscopic features of atherosclerosis
- Fatty streak
- Simple plaque
- Complicated plaque
fatty streak
early age of atheroma
- Lipid deposits in intima
- Yellow
- Relationship to atherosclerosis somewhat debatable

Simple plaque
- Raised yellow/white
- Irregular outline
- Widely distributed

Complicated plaque
- Thrombosis
- Haemorrhage into plaque
- Calcification- degenerate lipid material
- Aneurysm formation

microscopic features: early changes
1) Proliferation of smooth muscle cells
2) Accumulation of foam cells
3) Extracellular lipid

microscopic features: later changes
4) Fibrosis
5) Necrosis
6) Cholesterol cleft- where cholesterol used to be
7) +/- inflammatory cells
8) Disruption of internal elastic lamina
9) Damage extends into media
10) Ingrowth of blood vessels
11) Plaque fissuring
clinical effects of atherosclerosis
ischaemic heart disease
cerebral ischameia
mesenteric ischaemia
abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
peripheral vascular disease
ischaemic heart disease
- Sudden death
- MI
- Angina pectoris
- Arrhythmias- irregular heart beats
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Cardiac failures
Cerebral ischaemia
- Transient ischaemic attack
- Cerebral infarction (stroke)
- Multi-infarct dementia

Mesenteric ischaemia
in which injury to the small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply
- Ischaemic colitis
- Malabsorption
- Intestinal infarction

Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
is a localized enlargement of the abdominal aorta such that the diameter is greater than 3 cm or more than 50% larger than normal. They usually cause no symptoms, except during rupture.

peripheral vascular disease
- Intermittent claudication
- Leriche syndrome
- Ischaemic rest pain
- Gangrene

intermittent claudication
painful to walk
- pain onset for a given distance gets shorter overtime
Leriche syndrome
- pain the buttock on exercise (erectile dysfunction)
Ischaemic rest pain
risk factors of atherosclerosis pathogenesis
age
gender
hyperlipidaemia
cigarette smoking
hypertension
DM
alcohol consumption
infection
Age
- Slowly progressive throughout adult life
- Risk factors operate over years
Gender
- Women protected relatively before menopause
- Presumed hormonal basis
Hyperlipidaemia
- High plasma cholesterol associated with atherosclerosis
- LDL most significant
- HDL protective
lipid in the blood is carried on
lipoproteins
lipoproteins carry
cholesterol and TAG