Muscle Tissue Flashcards
What does muscle tissue allow? How?
Through muscle contraction, muscle tissue allows:
- Movement of material through the body
- Movement of parts of the body
- The generation of heat
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle
Define: Skeletal muscle

Define: Cardiac muscle

Define: Smooth muscle

What are the four properties of muscle tissue?
- Excitability
- Contractility
- Extensibility
- Elasticity
Define: Excitability

Define: Contractility

Define: Extinsibility

Define: Elasticity

What is the difference between relaxed and contracted sarcomere?



What are the roles of arteries, veins, and nerves?

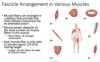
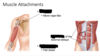
What is the anatomy of a muscle?

What are the connective tissues associated with muscle?

What is the structure of muscles?

Individual muscle fibers are made of cylindrical organelles called ______
Myofibrils

Myofibrils are made up of repeating units called ______
Sarcomeres



______ are made of two types of myofilaments: ______ and ______. Also made of _____ filament.

The ___ filament is made up of three proteins:
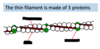



How do tropomyosin and troponin interact with each other?

____ shortening leads to muscle shortening