Integumentary System Flashcards
(55 cards)
What percentage of human body weight does the integumentary system compose?
~ 7% of total body weight
The superficial epidermis overlies the _______
the dermis
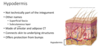
The _____ is technically not part of the integument
the hypodermis
Why is skin considered an organ?
Because it is made up of different tissue types with a common function
What are the layers of the integument?



What are the functions of the integument? (5 of them)
- Protection
- Body temperature regulation
- Excretion of wastes through sweat
- Vitamin D synthesis
- Sensory Reception

What are the four types of epidermal cells?
- Keratinocytes
- Melanocytes
- Tactile epithelial cells (Merkel cells)
- Dendritic cells
What are the characteristics of: Keratinocytes?

What are the characteristics of: Melanocytes?

What are the characteristics of: Tactile epithelial cells (Merkel cells)?

What are the characteristics of: Dendritic cells?

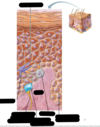



What are the four main epidermal layers from most superficial (nearest to outside of body) to least superficial (inside body)?
(Most Superficial)
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
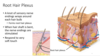
Stratum Basale
(Least Superficial)



What is the stratum lucidum? Where is it found?





What is the difference between thick skin and thin skin?



What are the characteristics and differences between callus, corn, and blister?

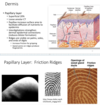
What are the layers of the dermis?
Papillary
Reticular
What are the characteristics of the papillary layer of the dermis?