Cells and Tissue Types Flashcards
(28 cards)
What are the six levels of organization in anatomy?
- Chemical
- Cellular
- Tissue
- Organ
- Organ system
6, Organism
What are the subcategories of the chemical level of anatomy?
Atoms
Molecules
Macromolecules
What are the subcategories of the cellular level of anatomy?
Macromolecules
Organelles
Define Tissue:
Group of cells that work together for a common function
Define Organ
A discrete structure made of more than one tissue functioning together
Define Organ System:
Group of organs functioning together
Define: Glycocalyx
What is it?
How does its structure relate to its function?
Where is it found?

What are the functions of the plasma membrane? (four of them)
- Separates intracellular components from extracellular ones
- Regulates what can enter or exit the cell
- Protection
- Intracellular communication
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?

What structural components make up the cytoplasm?
Microtubules
Intermediate filaments
Microfilaments

From largest to smallest diameter, what are the sizes of the cytoplasmic structural elements?
(largest) Microtubules > Intermediate filaments > Microfilaments (smallest)
What is the structure and function of a microtubule?
Hollow tube of tubulin proteins
Supports and gives shape to cell
Organelle attachment
Involved in intracellular and cellular movement
Form centrioles (mitosis)
What is the structure and function of intermediate filaments
- Insoluble protein fibers wound like a rope
- Most stable and permanent
- Resist pulling forces
- Less dynamic than microtubules and microfilaments
- Link adjacent cells together by attaching to specific cell junctions called desmosomes

What is the structure and function of microfilaments
Made of actin
involved in cell movement (i.e. muscle contraction and movement)
Structure and function of myofibrils
Thin: actin
Thick: myosin
Parallel columns
Muscle contraction caused by interactions betwenn actin and myosin
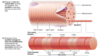
What is a smooth muscle cell composed of?
Intermediate filaments attached to dense bodies
Actin
Myosin
Define: cytoplasmic inclusions
Temporary structures in the cytoplasm
Content depends on cell function
Can be food stores (lipid droplets, glycosomes), protein crystals, or pigments
The lipid droplets have the same appearance as lysosomes but can be distinguished because they lack a membrane
Glycosomes (sugar-containing bodies) store glycogen

Where is the nucleolus?
What is its structure and function?
In the nucleus (can be one or several)
rRNA production
site of ribosome assembly unit
Subunits leave nucleus through nuclear pores
How do cells connect to one another?
Cell junctions

Where would be a good place to find tight junctions? Why?
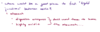
Define: Tight Junction
Belt-like junction on apical surface of cell
Main function is to prevent substances from moving between adjacent cells
Form a “seal”
An adhesive belt junction reinforces the tight junction

What are three types of cell junctions:
- Tight Junctions
- Desmosomes
- Gap Junctions
Define: Desmosomes
Structure and Function?
- Bind adjacent cells together through “disk-like plaques” connected across intercellular space
- Linker proteins “zip” together
- Intermediate filaments extend through cytoplasm, distributing force from cell to cell (tissue acts as one sheet)
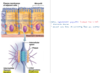
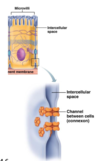
Define: gap junction
Structure and function?
Allows ions and small molecules to move from cell to cell through small channels
Involved in intercellular communication