Muscle Activation during Gait Flashcards
what produces an external torque during gait?
GRF
will cause movement at each joint of the LE
what produces an internal torque during gait?
primarily muscle activation
it is produced to match/overcome the external torque
when and why do concentric muscle contractions occur during gait?
they occur when the internal torque is moving the joint in the direction of the muscle’s activity
these provide stability and produce movement of a segment
when and why do eccentric muscle contractions occur during gait?
they occur when an internal torque is moving the joint in the direction opposite of the muscle’s action
these help with shock absorption and deceleration of a limb segment
what can cause muscular dysfunction and how will it impact gait?
Causes:
- weakness
- loss of power
- decreased endurance
- spasticity
- contracture
leads to altered gait patterns and compensations as the torque GRFV doesn’t change but the individual’s ability to counter it does
what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during IC?
ALL hip extensors contract concentrically to prepare for LR
what muscles are activated at the knee in the sagittal plane during IC?
eccentric hamstring contraction to counteract extension torque
knee extensions transition from concentric to eccentric contraction in preparation for LR
what muscles are activated at the ankle in the sagittal plane during IC?
pretibials (tibialis anterior, big toe extensors) contract concentrically
what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during LR?
concentric contraction of hip extensors
(Glute max, adductor magnus, TFL, Glute med peak)

what muscles are activated at the knee in the sagittal plane during LR?
eccentric contraction of knee extensors
(quad activity peaks)

what muscles are activated at the ankle in the sagittal plane during LR?
eccentric contraction of ankle DF (tibialis anterior peaks)
Transition to eccentric contraction of ankle PF in late LR

what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during MSt?
no hip muscular activity requried in the sagittal plane

what muscles are activated at the knee in the sagittal plane during MSt?
quads eccentric to no activity

what muscles are activated at the ankle in the sagittal plane during MSt?
eccentric contraction of the gastroc/soleus

what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during TSt?
minimal activity in the sagittal plane

what muscles are activated at the knee in the sagittal plane during TSt?
no quad or HS activity
tibial position maintained by gastroc

what muscles are activated at the ankle in the sagittal plane during TSt?
concentric contraction of ankle PF to prevent tibial collapse with heel rise
Gastroc/Soleus activity peaks
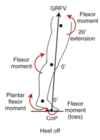
what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during PSw?
concentric contraction of hip flexors
adductor longus peaks

what muscles are activated at the knee in the sagittal plane during PSw?
knee flexion is mainly passive
slight concentric contraction of knee flexors and eccentric rectus

what muscles are activated at the ankle in the sagittal plane during PSw?
ankle PF activity ceases in early PSw and passive tension contributes to ankle moving in PF
ankle DF concentric initiated at the end of PSw

what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during ISw?
continued concentric contraction of hip flexors
Iliacus peaks
what muscles are activated at the knee in the sagittal plane during ISw?
concentric contraction of knee flexors
(biceps femoris SH, sartorius, gracilis peak)
flexion continues to be aided by flexion at the hip
what muscles are activated at the ankle in the sagittal plane during ISw?
concentric contraction of tibialis anterior
toe extensor activity peaks
what muscles are activated at the hip in the sagittal plane during MSw?
continued concentric contraction of hip flexors
initation of eccentric hip extensors (HS) to control hip flexors








