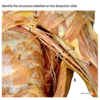
MSK 2 - Upper Limbs Flashcards
a

Lesser tubercle
b

Coronoid fossa
c

Trochlea
d

Greater tubercle
e

Intertubercular groove
f

Deltoid tuberosity
g

Radial fossa
h

Capitulum
i

Surgical neck
j

Radial groove
k

Head
l

Anatomical neck
m

Shaft/diaphysis
n

Olecranon fossa
o

Medial epicondyle
what are muscle compartments?
An important concept when studying anatomy of the extremities is the arrangement of muscle groups within fascial compartments.
Fascial compartments contain groups of muscles and neurovascular structures enveloped by a layer of connective (fibrous) tissue.
Muscles in each compartment often (but not always) act similarly on a joint, sharing a common nerve and blood supply
what is in the Anterior Compartment of the Arm?
The anterior compartment contains 3 important muscles and their accompanying neurovascular supply. The muscles act on the elbow joint and superior radio-ulnar joint
1

Biceps brachii
2

Brachialis
3

Musculocutaneous nerve
4

Coracobrachialis
where is the biceps brachii located?
The biceps brachii is the most superficial muscle of the anterior compartment.
It arises from the scapula via. two heads. Both heads unite at the distal third of the upper arm forming a short tendon which inserts onto the radial tuberosity.
It also attaches through the bicipital aponeurosis to the deep fascia of the forearm
The muscle has a powerful action on the shoulder, elbow and radio-ulnar joints
The short head of the biceps muscle originates from the ________ process of the scapula
coracoid
The long head of the biceps muscle originates from the __________ tubercle of the scapula
Its tendon passes through the shoulder joint and runs down the _______ groove of the humerus
supraglenoid
bicipital