MSK 2 - Lower Limbs Flashcards
what is the pelvic girdle and what makes it up?
The pelvic girdle is a bony ring consisting of the sacrum and right and left hip bones, joined anteriorly at the pubic symphysis and posteriorly by the sacroiliac joints.
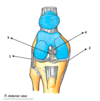
a

Greater sciatic foramen
b

Sacrotuberous ligament
c

Sacrospinous ligament
d

Lesser sciatic foramen
Which sciatic foramen is the route for structures entering or leaving the pelvis?
Greater sciatic foramen
Which sciatic foramen is a route for structures entering or leaving the perineum?
Lesser sciatic foramen
Gluteal region - this posterior muscle group is organised into a _________ and ____ layer
superficial
deep
what is muscle 1 and its innervation?

Gluteus maximus
inferior glutel nerve (L5, S1 and S2)
what is muscle 2 and its innervation?

Gluteus medius
superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5 and S1)
what is muscle 3 and its innervation?

Gluteus minimus
superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5 and S1)
what is muscle 4 and its innervation?

Tensor Fascia Lata
superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5)
The deep muscles of the hip ________ rotate and _______ the hip, and are covered in Lesson 1.
These are all supplied by branches of the ______ plexus
externally
stabilise
sacral
What are the actions of gluteus maximus muscle?
Hip extensor and external rotator
What is the action of gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae?
They are hip abductors and internal rotators of hip joint
The deep fascia of the thigh is called what?
the fascia lata
Fascia lata - It extends posteriorly from the front of the thigh and is thickened laterally to form the iliotibial tract.
2 muscles attach to the iliotibial tract – these are what?
tensor fascia lata and gluteus maximus
why is the iliotibial tract important?
The iliotibial tract is important, as it provides stabilisation to the lateral aspect of the knee joint
The sacral plexus lies on which muscle?
Piriformis muscle
The sacral plexus is formed by the union of the ventral rami of what spinal nerves?
L4, L5 and S 1 to S 4
The supply from the lumbar ventral rami comes from the ________ trunk
lumbosacral
The sarcal plexus supplies what?
the posterior aspect of the lower limb plus the perineum
What are the two main branches of the sacral plexus?
Main branch to lower limb - Sciatic nerve
Main branch to perineum - Pedundal nerve
The superior and the inferior gluteal nerves are smaller motor branches of what?
sacral plexus