Motor Proteins (associated with actin filaments) Flashcards
makes muscles contract
myosin II
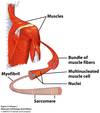
structure in skeletal muscle made of multiculeated cells
fibers
each cell from fibers contain a bundle of:
myofibrils

each myofibril contains thousands of contractile units called:
sarcomeres
links ECM to cytoskeleton in muscle cells
dystrophin glycoprotein complex
signaling molecule in skeletal muscle
NOS
muscle contraction increases levels of:
Ca2+
Ca2+ increase during muscle contraction activates:
NOS
activation of NOS in skeletal muscle produces:
NO
caused by NO diffusion to blood vessels
smooth muscle relaxation
relaxing smooth muscle causes increased:
blood flow to muscle tissue
label the parts of a sarcomere


thin actin filament charge type embedded in Z-disk
positive charge
consists of thin filaments
I-band
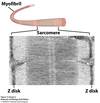
consists of bipolar myosin thick filaments
A-band
first molecular motor identified from skeletal muscle
Myosin II
this part located at myosin N-terminus
globular heads
myosin globular heads at N-terminus contain:
force generating machinery
myosin globular heads, light chains, and hinge region connected to:
coiled-coil of two alpha helices

approach to ID functional domains within a protein is to:
cleave into fragments site-specific proteases

cleaves myosin into two fragments (heavy- and light-mero-myosin)
Chymotrypsin

protease cleaves HMM (heavy-mero-myosin) into subfragment 1 (S1) and subfragment 2 (S2)
Papain
subfragment contains myosin head and neck regions
S1
these comprise the myosin tail
S2 and LMM
intrinsic ATPase activity resides in this myosin fragment
S1
actin binding ability resides in this myosin fragment
S1
S1 ATPase activity enhanced/activated by:
F-actin
these wrap around neck region and make it more rigid
light chains
type of skeletal muscle fibril can be immobilized on glass slide
myosin
end of actin that myosin “walks” to

+ end

actin is moved in direction of this charge on it

- end
using actin movement assay, these parts of myosin can move actin
HMM and S1
myosin domain determines cargo specificity
tail domain
part of myosin responsible for speed of actin filament movement
myosin neck

number of S1 myosin domains encoded in human genome
40 domains