Mosby Review Flashcards
1004 - Early somatic effects of a substantial dose of ionizing radiation include:
- Nausea
- Epilation
- Formation of solid malignant tumors
1 and 2 only
Although these two effects can occur early, it takes a high dose of radiation to cause them. Tumors are a long-term effect.
1006 - Which of the following must be increased to increase the quality of the x-ray beam?
- Filtration
- kVp
- mAs
1 and 2 only
Both kVp and filtration affect the wavelength of the beam, and consequently the quality of the beam. Because either or both is increased, beam quality increases. mAs affect the intensity of the beam, that is, the number of rays.
1008 - Which of the following are classified as controlled areas?
- Radiographic room
- Hallway
- Unattended elevators
1 only
In the radiographic room, personnel are instructed in the use of radiation and wear dosimeters. The other areas are generally populated only by the general public.
1010 - Protective shielding, which includes lead apron, curtain, and Bucky slot cover, provides:
maximum protection for the radiographer during fluoroscopy.
1011 - One of the purposes of the backup timer used with automatic exposure control (AEC) devices is to:
prevent excessive exposure to the patient
The backup timer will terminate the exposure when it goes beyond a safe level.
1012 - Two x-ray photons from the primary beam have interacted with atoms in a patient’s body. After the interaction, one of the two photons was absorbed and the other photon scattered in a direction away from the image receptor. Both of these photons may now be classified as:
attenuated photons
Attenuation is any change in the beam as it traverses the patient. Hence both of these photons have been attenuated, one by photoelectric interaction and the other by Compton interaction
1016 - The age of the radiographer in years multiplied by 10 mSv may be used to determine:
cumulative exposure for occupationally exposed individuals
This calculation is used for lifetime accumulated dose for occupationally exposed individuals. In traditional units of measurement this would be the age of the radiographer multiplied by 1 rem.
1017 - Which of the following is not effective in reducing exposure to the patient during a diagnostic examination?
Decreasing kVp
For ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) purposes, the lowest doses are high kVp, low mAs techniques.
1021 - Which of the following will not provide radiation protection for the radiographer?
OSL dosimeter
The dosimeter records the dose received, but does not contribute to Safety.
1025 - Which of the following is essential for protection of the radiographer who is performing a mobile radiographic examination?
1. Protective lead apron
- Primary protective barrier
- Six-foot exposure cord
1 and 3
A primary protective barrier is one that is struck by the primary beam. In this example, there is no need for a primary protective barrier. A lead apron should always be worn for mobile examinations. Maximum use of the 6-foot cord is essential
1027 - Which of the following devices should be used to reduce exposure to the mammary glands during a juvenile scoliosis examination?
Breast Shield
Although not used often, breast shields are very important to use for a scoliosis series.
1028 - A nonpregnant relative to a 2-year-old child volunteers to help restrain the child while AP and lateral radiographs are obtained in the upright position. This person should be provided with:
appropriate protective apparel
It is not necessary to monitor this person’s dose, but all available protective apparel must be worn, and the individual should be kept out of the primary beam.
1046 - Computed radiography may be part of an integrated system of images and text called:
PACS
Picture archival and communication systems (PACS), the computer system used for digital imaging, is a digital communication network of many systems, not an imaging method in itself.
1053 - Which of the following grid errors will result in an image that shows normal IR exposure in the middle but decreased IR exposure on the sides and may follow removal and replacement of the grid?
Upside-down grid
This describes the error that occurs when a grid is positioned upside down during replacement. Grid-focus decentering results in the same type of problem on the radiograph, but this error is caused by a violation of the grid radius, not by incorrect positioning of the grid during replacement. An off-level grid will cause image-forming rays to be absorbed all across the radiographic field, with decreased density (cutoff) visible over the entire radiograph. Lateral decentering of the grid results in visible cutoff more to one side of the radiograph. Be sure to review grid errors.
1058 - When kVp is increased, which of the following happens?
Scale of contrast lengthens
An increase in kVp results in a lengthened scale of contrast because there is more uniform penetration of the part by shorter-wavelength rays. Decreased kVp results in increased contrast and decreased density. Recorded detail is not controlled by kVp.
1060 - The lowest contrast would be produced by which of the following sets of exposure factors?
A. 60 mAs, 80 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
B. 30 mAs, 92 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
C. 120 mAs, 92 kVp, 20-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
kVp, rather than mAs or source-to-image distance (SID), is a controlling factor in the level of contrast. Higher kVp results in lower contrast; therefore, choice D, with the highest kVp, is correct.
1066 - mAs controls the:
quantity of x-rays produced at the anode
mAs controls the quantity of x-rays produced at the anode; this is proportional to the tube current. The quality of x-rays produced is controlled by kVp.
107 - This changes electric voltage and current into higher or lower values and operates on the principle of mutual induction, so it requires alternating current. This is called the:
transformer.
This describes the transformer, of which two are used in x-ray production. An autotransformer operates on the principle of self-induction. A rectifier converts AC to DC. The timer is used to regulate the duration of x-ray exposure.
1076 - kVp determines what aspect of the x-ray beam?
Penetrating ability
1079 - As the wavelength of the x-rays increases, penetrating ability
decreases
The relationship between wavelength and penetrating ability is inverse; longer-wavelength rays have decreased penetrating ability.
1080 - As the wavelength of the x-rays decreases, penetrating ability:
increases
The relationship between wavelength and penetrating ability is inverse; shorter-wavelength rays have increased penetrating ability.
1087 - The grid conversion factor for a 12:1 grid is:
5
For a 12:1 grid, multiply mAs by 5. Choice A is the grid conversion factor for a 5:1 grid; choice B, for an 8:1 grid; and choice D, for a 16:1 grid.
1093 - Differences in adjacent densities on a radiograph defines:
contrast
This is the simple definition of contrast. Density is the amount of blackness on a given area of a radiograph. Detail is the sharpness with which anatomic structures are displayed on the image receptor. Distortion is any misrepresentation that alters the size or shape of an anatomic structure on the image receptor.
1095 - An image with few gray tones, mainly black and white, is referred to as:
high contrast
A high-contrast image is mainly black and white, with few gray tones. High contrast is also known as a short-scale contrast.
1098 - An image with many gray tones is referred to as:
long-scale contrast.
An image with many gray tones is said to have long-scale contrast, also known as low, not high, contrast.
1105 - The portion of contrast represented by the anatomy and physiology is:
Subject contrast
is the portion of contrast that is inherent to the patient; that is, it already exists by nature of the patient’s anatomy, physiology, and pathology.
1108 - Spatial resolution may also be known as:
- sharpness.
- definition.
- image resolution
1, 2 and 3
Spatial resolution is also known as detail sharpness, definition, or image resolution. All of these terms refer to the same thing.
1124 - Magnification may be caused by:
short SOD
Short source-to-object distance (SOD), excessive (not short) object-to-image distance (OID), and insufficient (not long) SID can all cause magnification. Focal-spot size is a factor influencing recorded detail, not distortion. Be sure to keep all of these factors straight.
1140 - A focused grid must be used with specific ranges of:
SID
A focused grid must be used within specific ranges of source-to-image distance (SID). The distance between the source of radiation and the image receptor must be within this range so that the divergence of the beam coincides with angle of the strips.
1141 - The SID at which a focused grid must be used is called:
grid radius.
The source-to-image distance (SID) at which a focused grid must be used is called the grid radius (also called focal distance or focal range). Violating this distance will cause grid cutoff.
1149 - Using an increased OID that allows scatter to miss the IR is called:
air gap technique.
1151 - The density (mass per unit volume) of the patient or part under study can affect:
- radiographic density.
- radiographic contrast.
- differential absorption.
1, 2, and 3
1157 - One of the factors that causes magnification of the radiographic image is:
a decrease in the source-to-object distance.
Magnification may also be caused by decreased source-to-image distance (SID) or increased object-to-image distance (OID).
1161 - Which of the following equations expresses grid ratio?
r = h/d
Grid ratio is expressed as the height of the lead strips divided by the space between them.
1165 - A radiographic grid should be used when:
- the body area to be radiographed measures more than 10 cm.
- a field size larger than 10 × 12 inches is used.
- more than 60 kVp is required to penetrate a body part.
1 and 3 only
Field size is unrelated to the use of a grid. Part measurement and kVp are both directly related to the increase in scatter being produced.
1171 - Click/Touch the area on the image that represents: Photocathode

see picture
1173 - Click/Touch the area on the image that represents:
Lateral condyle

see picture

1190 - Click/Touch the area on the image that represents:
Glenoid cavity

see picture
1192 - Coracoid process
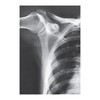
see picture

1199 - Intercondylar eminence

see picture

1216 - Click/Touch the area on the image that represents: Lamina
….

1218 - Click/Touch the area on the image that represents:
Greater sciatic notch

see picture
1219 - Click/Touch the area on the image that represents:
Ischial spine

see picture
126 - High-frequency full-wave rectification produces what percentage of ripple?
1 With high-frequency generators, voltage ripple is about 1%.
Voltage never drops to zero and is nearly constant. With three-phase, six-pulse, full-wave rectification, ripple is approximately 13%; with three-phase, 12-pulse, full-wave rectification, 4%; and with single-phase full-wave rectification, 100%
128 - The voltage actually used in three-phase, 12-pulse units is about:
96% of the kVp set on the control panel
Because three-phase, 12-pulse, full-wave rectification results in a voltage ripple of approximately 4%, the actual voltage used is about 96% of the kVp set on the control panel. High-frequency generators use about 99% of the kVp, and three-phase, six-pulse units use about 87%.
129 - The voltage actually used in high frequency is about:
A. 99% of the kVp set on the control panel.
Because high-frequency generators result in a voltage ripple of approximately 1%, the actual voltage used is about 99% of the kVp set on the control panel. Three-phase, 12-pulse units use about 96% of the kVp, and three-phase, six-pulse units use about 87%.
132 - Filaments are primarily made of ____________ because of its high melting point.
Tungsten
Because of its high melting point, tungsten, not gold, silver, or platinum, is primarily used to make filaments. A small amount of thorium may be added to reduce vaporization.
140 - Rotation of the target allows for:
greater heat dissipation.
Rotation of the target allows greater heat dissipation, which extends the life of the tube
144 - What is contained within the x-ray tube to prevent the filament’s electrons from colliding with the atoms of gas?
Vacuum
A vacuum is contained within the glass envelope of the x-ray tube so that electrons from the filament do not collide with atoms of gas. Be sure to be familiar with all parts of the x-ray tube.
146 - Inside the tube housing, what is the x-ray tube immersed in to assist with cooling and additional electrical insulation?
Oil
The tube housing contains oil, not plastic, water, or coolant. This is an often-forgotten part of the tube assembly
15 - What type of current is required for proper operation of the x-ray tube?
Direct
The x-ray tube requires a direct current (DC) to operate properly. The rectifier changes AC to DC.
156 - A device in which the x-ray tube and image intensifier are located on opposite cusps of a semicircular arch is called a:
C-ARM
The c-arm is the feature of portable (mobile) fluoroscopic units.
162 - This diagram illustrates:

Brems x-ray production
This diagram illustrates the production of Brems x-rays, in which projectile electrons are slowed near the atomic nucleus.
163 - This diagram illustrates:
characteristic x-ray production.
167 - In this diagram, D is the
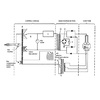
Label D is the step-up transformer, where voltage is boosted to kilovoltage levels.
Be sure to know these major parts of the x-ray circuit.
173 - Which of the following is equivalent to the speed of light in a vacuum? 1. 3 × 108 meters per second 2. 3 × 1010 cm per second 3. 186,000 miles per second
1, 2 and 3 all are ways of saying the speed of light
195 - The diagnostic useful range of x-rays is from:
0.1 to 0.5 angstrom This range is the result of the various kVp settings used for imaging
198 - The negative electrode of an x-ray tube is termed the:
cathode This is the source of the electrons, which carry a negative charge. The anode is the positive electrode.
203 - How many kilovolts equal 70,000 volts?
70 Kilo means “thousands.”
205 - X-ray photons have no: 1. energy. 2. electric charge. 3. mass.
2 and 3 only X-ray photons are bundles of energy with no mass or charge.
206 - Electron flow from negative to positive is:
electric current Like charges repel, so the electrons flow from negative to positive.
216 - Which of the following bones has nasal conchae?
Ethmoid bone
218 - Which of the following bones has a coronoid process?
Mandible The coronoid process is located on the ramus of the mandible and serves as the attachment site for the temporalis muscle.
221 - Which of the following bones has (have) no body?
Atlas The atlas, or C1 vertebra, has no body. The axis has a small body, whereas the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae have larger bodies.
242 - The part of the urinary system located between the renal pelvis and the bladder is called the:
ureter. The ureter is located between the renal pelvis and the bladder. The cortex, medulla, and nephron are all components of the kidney.
243 - The functional unit of the kidney is called the:
nephron The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. The medulla is the inner part of the kidney; the outer part is the cortex.
244 - For an AP projection of the thumb, the hand is turned in extreme:
internal rotation
247 - For the AP axial projection of the clavicle, the central ray is angled:
25 to 30 degrees cephalad The correct angle of the central ray for an axial projection of the clavicle is 25 to 30 degrees cephalad if performed anteroposteriorly. For a posteroanterior (PA) axial projection, the central ray should be angled 25 to 30 degrees caudad.
250 - For a lateral projection of the ankle, the central ray is directed perpendicular to the:
medial malleolus. For a lateral projection of the ankle, the central ray is directed vertical through the medial malleolus. Choice B would be the correct answer for an anteroposterior (AP) projection of the ankle.
271 - The talus distributes body weight from the:
tibia to the tarsals. Occupying the uppermost and central portion of the tarsus, the talus distributes body weight from the tibia above to the other tarsal bones.
273 - The trachea is located
in front of the esophagus
274 - The length of the trachea is about
12 cm The trachea is about 12 cm (not inches) long
281 - A central ray angle of 25 to 30 degrees caudad is required for what projection?
PA axial clavicle The posteroanterior (PA) axial projection of the clavicle requires that the central ray be angled 25 to 30 degrees caudad (25 to 30 degrees cephalad for anteroposterior [AP]).
282 - Directing the central ray to the base of the third metatarsal is done for what projection?
AP foot For the anteroposterior (AP) projection of the foot, the central ray is angled 10 degrees toward the heel, entering the base of the third metatarsal.
297 -The vertebral border is labeled:

III
Label III marks the vertebral border. The structure designated as label I is the axillary border. Label II is the acromion, and label IV is the scapular notch
311 - The coronoid fossa is labeled

II The structure designated as label II is the coronoid fossa. Label I marks the radial head. Label III is the lateral epicondyle, and label IV is the trochlea.
313 - The trochlea is labeled

Label IV is the trochlea. The structure designated as label I is the radial head. Label II marks the coronoid fossa, and label III is the lateral epicondyle.
316 - The triquetrum is labeled

The triquetrum is designated by label IV. The distal interphalangeal joint is marked by label I. Label II is the metacarpophalangeal joint, and the structure designated as label III is the ulna.
32 - The amount of matter in an object best defines:
Mass Mass is the amount of matter in an object—similar to, but not the same as, weight. Energy is the ability to do work. Matter is that which has form and occupies space.
320 - The capitate is labeled

The capitate is designated by label VI. Label I is the distal interphalangeal joint. The metacarpophalangeal joint is marked by label II, and label IV is the pisiform.
323 - The capitulum is labeled

label E points to the capitulum
324 - The radial head is labeled

B
329 - The zygomatic arch is labeled

E
334 - The foramen magnum is labeled

The foramen magnum is designated by label J
336 - The lesser tubercle is labeled

The lesser tubercle is designated by label D.
338 - The surgical neck is labeled

Label F marks the surgical neck
341 - The talus is labeled

I
342 - The tuberosity of the calcaneus is labeled
The tuberosity of the calcaneus is designated by label J in this radiograph.
346 - The second metacarpophalangeal joint is labeled:

Label G indicates the second metacarpophalangeal joint.
349 - The scaphoid is labeled

A
352 - The lunate is labeled

B
395 - The acetabulum is labeled

On this diagram, label E is the acetabulum
412 - The coronoid process is labeled:

C
421 - The lesser trochanter is labeled:

The lesser trochanter is designated by label D.
425 - The medial epicondyle is labeled

E
426 - The lateral epicondyle is labeled

Label I points to the lateral epicondyle.
434 - The surgical neck is labeled

The surgical neck is marked by label E
44 - Electromagnetic radiation travels:
as waves in straight lines. Electromagnetic radiation travels in waves in straight paths at the speed of light, not sound. This is true of all ionizing and nonionizing radiations.
446 - The medial epicondyle is labeled

Q
45 - The patella is labeled

B
451 - The lateral condyle is labeled

Label D points to the lateral condyle
459 - The proximal tibia is labeled

L
460 - The metatarsal bones are labeled:

A
473 - The heart is labeled:

D
477 - The manubrium is labeled

The manubrium is designated by label B.
480 - The xiphoid process is labeled

The xiphoid process is marked by label E
497 - The superior vertebral notch is labeled
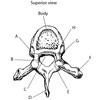
A
500 - The transverse costal facet is labeled

The transverse costal facet is marked by label F.
503 - A pathologic condition that is characterized by the collapse of lung tissue is:
Atelectasis Collapse of lung tissue is a characteristic of atelectasis. Asthma is characterized by increased mucus production in the bronchi, resulting in hyperventilation of the lungs. Emphysema involves the overinflation of the alveolar walls. Pneumonia is an acute inflammation of the lungs.
505 - A pathologic condition that is characterized by acute inflammation of the lungs is:
pneumonia Acute inflammation of the lungs is a characteristic of pneumonia. Atelectasis is characterized by collapse of lung tissue. With asthma, increased mucus production in the bronchi causes hyperventilation of the lungs. Emphysema is characterized by overinflation of alveolar walls.
51 - Current that flows in one direction only is called:
DC Direct current (DC) flows in one direction, whereas alternating current (AC) flows back and forth. A rectified current would be one that has undergone a change from AC to DC.
515 - A transverse fracture of the neck of the fifth metacarpal with palmar angulation of the distal fracture fragment is:
Boxer Boxer is a transverse fracture of the neck of the fifth metacarpal marked by palmar angulation of the distal fracture fragment. It is caused by striking a hard object with a closed fist. Colles fracture is a transverse fracture of the distal radius with posterior angulation of the lower fragment. Pott fracture is one of the medial and lateral malleoli of the ankle with ankle joint dislocation. A trimalleolar fracture is a fracture of the posterior portion of the tibia and the medial and lateral malleoli.
532 - The prefix “decub-“ means:
side
539 - The suffix “-ectomy” means
excision
551 - When a patient takes in a deep breath during chest radiography, the diaphragm:
contracts and the dome moves downward. This enables maximum visualization of the base of the lungs. A chest radiograph should always be taken on the second inspiration for maximum movement of the diaphragm and maximum inspiration.
553 - The most anterior part of a typical thoracic vertebra is the:
body Be sure to review the anatomy of each of the vertebrae.
554 - Where is the subtalar joint located?
Foot Be sure to review the anatomy of the major joints in the body and be prepared to label diagrams of them.
556 - When the foot is inverted, it is: A. dorsiflexed. B. pronated. C. turned inward at the ankle. D. turned outward at the ankle.
turned inward at the ankle
569 - With the patient properly adjusted in a 45-degree right anterior oblique position for demonstration of the cervical vertebrae, the intervertebral foramina demonstrated will be:
all those on the right side.
These are the vertebrae that are closest to the image receptor.
57 - The x-ray machine receives what type of current from the incoming line?
120-Hz AC
This current comes from the power company.
572 - With the patient properly positioned for an axiolateral projection of the hip, the central ray should be directed:
perpendicular to the long axis of the femoral neck of the side being radiographed. This provides proper visualization of the head of the femur, the acetabulum, and the neck of the femur.
579 - The primary function of the digestive system is: 1. ingestion and digestion. 2. absorption. 3. elimination.
1, 2 and 3 All of these are critical functions of the digestive system. The individual cannot survive in the absence of any of them.
586 - The abdominal structure that is not an accessory digestive organ is the: A. gallbladder. B. liver. C. pancreas. D. spleen.
The spleen is part of the lymphatic system.
599 - The semilunar notch is found on the:
ulna
605 -
Gloves must always be worn when:
- assisting patients with urinals or bedpans.
- handling needles and syringes.
- handling bandages and dressings.
- touching all patients.
1, 2 and 3
Gloves must be worn in all the situations described except touching all patients. Wearing gloves and washing your hands are the two most important things you can do to stop the spread of infectious conditions.
608 - Infectious waste must be handled according to:
CDC guidelines.
614 - Bradycardia indicates a pulse of
fewer than 60 beats per minute
616 - Shock is indicated when the diastolic pressure is: A. more than 100 beats per minute. B. fewer than 60 beats per minute. C. greater than 90. D. less than 50.
D. less than 50. Blood pressure is an important vital sign and must be measured accurately. Diastolic pressure less than 50 mm Hg gives some indication of shock, whereas diastolic pressure greater than 90 mm Hg indicates increasing level of hypertension. Blood pressure is always expressed as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure.
617 - This item contains all equipment and drugs needed during respiratory or cardiac arrest:
crash cart All the choices except choice A are pieces of equipment, so they would not contain all equipment and drugs needed for respiratory or cardiac arrest. Be sure to know the location of the crash cart and its contents.
62 - Which of the following is not a property of x-rays?
Electrically negative X-rays are electrically neutral and invisible to the human eye. They travel as bundles of energy at the speed of light.
621 - The type of shock that causes blood to pool in peripheral vessels is called:
neurogenic shock Shock occurs when blood pressure is inadequate to oxygenate tissues and remove byproducts of metabolism. Neurogenic shock originates in the nervous system. It is important for radiographers to understand the causes of various types of shock to determine whether a cause of shock is still present and untreated.
631 - This type of infection transmission occurs mainly on dust:
Airborne Transmission
You must know the various routes of transmission of infection to effectively control them.
636 - The abbreviation that stands for a stroke is:
CVA Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is a stroke. MI stands for myocardial infarction, and Hx stands for history. Bx is a medical abbreviation for biopsy.
646 - If scheduled for GI studies, patient preparation includes: 1. Low-residue diet 2. NPO for 8 to 12 hours before the procedure 3. Cathartics and enemas 4. Follow-up phone call to remind patient about preps
1, 2 and 3 A thorough cleansing of the lining of the large intestine is necessary before a gastrointestinal study and requires all of the methods listed above. Because this cleansing is a complex process, careful instructions must be provided, especially to outpatients. While a phone call reminder might be a good thing to do, it is not a routine part of preparation.
647 - Which of the following should not be asked when taking patient history?
How long have you had cancer? This question is not appropriate when taking a patient history because the patient may not know they have a particular condition. It is the prerogative of the physician only as to when a patient is informed about a disease.
651 - Unjustified restraint of the patient constitutes:
false imprisonment
Patients must consent to restraint. If restraint is not justified by the procedure, it may constitute false imprisonment. Consent must be given by the patient, ordered by the physician, or provided as implied consent if the patient is unconscious.
657 - A case in which the injured person caused some of the injury is called
Contributory negligence …is when the injured person contributes to or partially causes his or her own injuries. In such a case, the liability for the caregiver is altered because the caregiver shares liability with the injured party.
663 - The patient bill of rights provides for
informed patient consent. patient refusal of any exam. The patient bill of rights requires that the radiologic technologist or the radiologist carefully explain all aspects of a procedure, including the risks involved, and that the patient has a right to refuse any procedure or exam.
673 - Standard Precautions are stipulated by the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
679 - What includes complete sterilization of equipment and the appropriate skin preparation?
Surgical asepsis The difference between medical asepsis and surgical asepsis is one of degree. Surgical asepsis requires the removal of all microorganisms, whereas medical asepsis requires the removal of as many microorganisms as possible. Sterilization asepsis is not a term commonly used.
680 - The process used to open sterile packs is called:
sterile technique. Sterile technique is a term that applies to all radiographic procedures involving sterile packs. Asepsis is a term that means the removal of microorganisms from equipment and skin. Sterilization asepsis is not a term commonly used.
683 - The first step in pouring liquids into containers in a sterile field is to:
carefully determine the contents of the container.
688 - Do not invade the space between:
the physician and the sterile field.
694 - When mobile radiography is performed in isolation, the cassette:
is placed in a protective cover
697 - When wearing a mask in isolation:
Cover both the nose and the mouth Both the nose and mouth are routes of transmission of infection and therefore must be covered.
711 - Systolic blood pressure measures:
pumping action systolic pressure measures the pumping action of the heart, whereas diastolic pressure measures the blood pressure of the heart at rest. Blood pressure is always expressed as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. Tachycardia is when the pulse measures more than 100 beats per minute. Atrial fibrillation is a dysrhythmia that is not measured by taking blood pressure.
716 - If the radiographer is working alone and the patient requires suctioning, what is the first step to be performed?
Call for help before beginning The first thing to do is to call for help; you will need assistance if the patient’s condition worsens. Suction units are often mounted on the wall. Unwrap the suction tip and turn on the suction. Clear the patient’s mouth, pull the chin forward and down, and gently insert the suction tip.
720 - In the event of cardiac arrest, what must be done immediately?
Commence CPR After you call for help, you must begin CPR immediately. Failure to do so may result in brain damage to the patient. Starting an IV, inserting a chest tube, or taking a chest radiograph are all inappropriate responses to this emergency situation. Your first priority in an emergency is to get the heart pumping again.
73 - Electron energy is converted to light in what part of the image-intensifier tube?
Output phosphor Electron energy is converted to light by the output phosphor in amounts 50 to 75 times greater than at the photocathode. At this point, the image is brighter and smaller. The input phosphor receives exit x-rays from the patient and converts them into visible light.
730 -
What are the levels of consciousness?
- Alert and conscious or drowsy
- Unconscious but reactive to stimuli
- Comatose
1, 2, and 3
As the primary caregiver in the imaging department, the radiographer must be aware of these conditions.
732 - When may immobilization devices such as cervical collars or splints be removed?
After permission is granted by the attending physician Immobilization devices can be removed only when authorized by the attending physician. Even if other staff members appear qualified and willing to give the order, it is not in your best interest or in the best interest of the patient to have anyone other than the physician give the order.
745 - Before injecting a contrast agent, what must the radiographer do? 1. Determine whether there is a history of allergies or previous hypersensitivity to contrast media 2. Determine the extent of the patient’s medical problems 3. Review possible reactions to the contrast agent being used
1, 2 and 3 Because in many cases the radiographer administers the contrast agent, and in all cases the radiographer is providing patient care, it is the radiographer’s responsibility to assess the patient’s history of allergic reaction and the extent of the patient’s medical problems. Providing informed consent is also the radiographer’s responsibility.
745 - Before injecting a contrast agent, what must the radiographer do?
- Determine whether there is a history of allergies or previous hypersensitivity to contrast media
- Determine the extent of the patient’s medical problems
- Review possible reactions to the contrast agent being used
1, 2 and 3
Because in many cases the radiographer administers the contrast agent, and in all cases the radiographer is providing patient care, it is the radiographer’s responsibility to assess the patient’s history of allergic reaction and the extent of the patient’s medical problems. Providing informed consent is also the radiographer’s responsibility.
748 - An injection set that includes a needle with plastic wings attached is called
Butterfly needles are easier to hold during venipuncture. A butterfly needle may also be taped to the patient’s arm to free the radiographer’s hands to hold the syringe and plunger.
753 - After venipuncture, what should be done?
Observe the injection site for swelling After venipuncture, always observe the patient’s arm for swelling. Although it is unlikely to happen, swelling indicates extravasation of the contrast agent or internal bleeding. Never leave a patient unattended.
761 - The Rules of Ethics portion of the Standards of Ethics provides information on:
mandatory standards of professional conduct.
The Rules of Ethics sets mandatory minimum standards of professional behavior. Compliance with these rules is required for continued certification by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists. The Rules of Ethics are enforceable and violations may result in sanctions.
762 - Which of the following is a violation of the ARRT Rules of Ethics?
Discussing specific questions from the Registry examination with classmates or instructors after completion of the test.
Content of any of the Registry’s exams may not be passed on to others in any way, using any form of communication. This includes post test discussions, writing down questions that may be remembered, or any verbal or written summary of specific test content. It is also a violation of the Rules of Ethics to encourage others to do the same.
772 - The AIDS virus is not transmitted by: 1. airborne germs. 2. sexual contact. 3. casual contact such as touching a patient who has the disease
1 and 3 only Notice that the question asks “not transmitted.” In this case, casual contact or airborne germs do not transmit the virus.
777 - Which of the following statements regarding precautions for body substances are true? 1. Used needles should be recapped before placing them in an appropriate disposable container 2. Latex gloves need not be worn when wiping up all blood spills 3. Protective mask and/or eye shields should be worn whenever the eyes and/or mucous membranes could be splashed with body substances
3 Used needles must never be recapped because of the possibility of a needle puncture occurring during the recapping. Gloves must always be worn.
779 - When taken orally, the normal body temperature is:
98.6°F.
78 - Three-phase, 12-pulse equipment produces how much higher average photon energy?
41%
Three-phase, 12-pulse equipment produces x-rays with 41% higher average photon energy. Therefore, when heat units are calculated, the constant of 1.41 is used (kVp × mAs × 1.41). The calculation of heat units three-phase, six-pulse equipment is kVp × mAs × 1.35, producing x-ray photons with 35% higher average photon energy.
786 - A code signaling cardiac arrest should be initiated when a:
carotid pulse cannot be detected Absence of a pulse would indicate cessation of cardiac activity. A code must be called immediately. In the other three examples, the patient’s vital signs are still present.
788 - A patient is to undergo an invasive procedure in the radiology department. Before starting the procedure, the radiographer should first:
check the patient’s chart to see if the informed consent form has been signed Informed consent must be on file before any part of the procedure begins.
790 - Which of the following personnel practices will help control the spread of infection in the radiology department? 1. Wash hands between patients 2. Wash hands after handling a bedpan or emesis basin 3. Wash hands after using the toilet
1, 2, and 3
800 - Which of the following are patients’ rights?
- To be able to examine her own medical records on request
- To take possession of and permanently keep her radiographs
- To have the opportunity to review and receive an itemized copy of her hospital bill
1 and 3 ONLY
Patients may, however, request copies of radiographic images.
803 - If a patient is suspected of having a perforated viscus, the contrast medium of choice should be:
water soluble. A water-soluble contrast agent is sterile, thus eliminating the possibility of infection. Other agents could cause infection and would be considered surgical contaminants.
808 - Attenuation may be defined as:
changes in the x-ray beam as it travels through the patient. These changes may include absorption and scatter radiation. Radiation that emerges from the patient is called exit radiation.
814 - Which of the following is attributed to linear energy transfer?
It varies for different types of radiation
Linear energy transfer varies based on the different levels of ionization. It occurs with high-ionization radiations such as neutrons and alpha particles, as well as during x-ray and gamma-ray procedures.
815 - What imaging modality uses the unit of measurement known as the Bq?
Nuclear Medicine The Becquerel (Bq) measures the quantity of radioactive material
818 - What dose-response curve best illustrates cataractogenesis, which does not occur at low levels of radiation exposure?
Threshold There is a definite safe, or threshold, dose at which cataractogenesis does not occur. Choice C does not make logical sense because the question states that cataractogenesis does not occur at low levels of radiation exposure. Occupational dose is the amount of radiation to which radiographers are exposed.
82 - A compound’s smallest component is the:
molecule The smallest component of a compound is the molecule, which still has the characteristics of the compound. An electron is an elementary particle with one negative charge. An atom is the smallest particle of an element capable of entering into a reaction. An element is a substance made up of atoms with the same atomic number and the same chemical properties; it cannot be broken down further without changing its chemical properties.
821 - What is the annual effective absorbed dose equivalent limit for the general public (frequent exposure)?
1 mSv
83 - A device used for most quality control testing is the: A. sensitometer. B. densitometer. C. ionization chamber. D. digital dosimeter.
digital dosimeter. The digital dosimeter allows for several quality control tests to be done with one device. A sensitometer is an optical step wedge that is used to produce a characteristic curve. A densitometer measures optical density of exposed film. The ionization chamber detects and measures radiation intensity in areas outside of protective barriers.
830 - What is the cell’s master molecule?
DNA According to target theory, there is substantial research indicating that DNA, contained in the cellular nucleus, is the master molecule. Hydrogen peroxide is a poison that can damage the cell. A free radical is a highly reactive ion with unpaired electrons in the outer shell. RNA transmits genetic instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm of the cell.
833 - Where does most radiation-induced damage to cells occur?
At doses of radiation much higher than that used in radiography
836 - Which of these describes somatic effects of radiation?
They are caused when a large dose of high-LET radiation is received by a large area of the body. These take large doses to manifest themselves.
839 - What are possible results of ionization? 1. Unstable atoms 2. Production of low-energy x-rays 3. Formation of new molecules harmful to the cell
1, 2 and 3 Ionization is multifaceted
844 - According to NCRP Report #160, what percentage of human exposure is natural background radiation?
50% Natural background radiation, which has been present since the formation of the universe, accounts for approximately 50% of human exposure. The greatest single source is radon.
862 - The photon–tissue interaction that does not cause ionization is
coherent Ionization does not occur during coherent scattering because electrons are not removed—they only vibrate. Compton and photoelectric interactions both result in ionization.
87 - A change in wavelength will always correspond to a change in:
frequency.
871 - The radiation weighting factor (WR) for x-ray is:
1 X-rays are a low-energy, low-LET radiation; therefore, a WR higher than 1 is not necessary because there is no increased damage to account for (as there would be with higher LET radiations). Therefore, 1 rad equals 1 rem.
872 - A concept of radiologic practice that encourages radiation users to adopt measures that keep the dose to the patient and themselves at minimum levels is called: A. LET. B. RBE. C. MPD. D. ALARA.
ALARA ALARA stands for “as low as reasonably achievable” and is a guiding principle for radiation users, who strive to produce a quality image with the lowest possible dose to the patient. MPD is an outdated term, replaced by absorbed dose equivalent limit. Relative biologic effectiveness (RBE) and LET are factors in biologic damage caused by ionizing radiation, but they do not directly encourage the use of minimum-level doses.
874 - This dose-response curve demonstrates:

linear-nonthreshold
This curve shows a response that is directly proportional to the dose; therefore, it represents a linear dose-response relationship. The curve intersects the dose axis at 0, so it demonstrates a nonthreshold dose-response relationship. Be sure to review dose-response curves.
878 - The annual effective absorbed dose equivalent limit for occupational exposure is:
50 mSv
88 - Wavelength and frequency are:
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional. As wavelength increases, frequency decreases; the converse is also true.
881 - The effective absorbed dose equivalent limit for the unborn during gestation is:
5 mSv The total fetus-embryo effective dose limit for gestation is 5 mSv. Be sure to review all of the dose equivalent limits.
885 - Which of the following is not an organelle?
Nucleus
The nucleus, which contains DNA, is one of the three main parts of the cell, along with the cell membrane and the cytoplasm. It is a separate component of the cell, not a smaller body within the cytoplasm.
891 - Germ cell division is called:
meiosis Germ cell division, or meiosis, is essential for reproduction. Mitosis is the division of somatic cells. Interphase is the stage between divisions.
900 - X-ray photons depositing their energy in the water of the cytoplasm may cause:
Radiolysis Radiolysis occurs as radiation energy is deposited in the water of the cell, leading to the creation of free radicals. Electrolysis is destruction by a galvanic electric current, used to disintegrate chemical compounds or to remove excess body hair. In pair production, the incident x-ray interacts with the nucleus of the atom, not the cytoplasm. Radioactivity is used to measure the quantity of radioactive material.
901 - Radiolysis creates ion pairs called:
free radicals. Radiolysis may result in free radicals, highly reactive particles that have an unpaired electron in the outer shell.
906 - Each cell has a master molecule that directs cell activities. If this master molecule is damaged by radiation and is inactivated, the cell will die. This summarizes:
Target Theory Target theory states that each cell has a master molecule. If this molecule is the target of radiation and is inactivated, the cell will die. This may occur as a result of direct or indirect effect. Meiosis is the division of germ cells. Relative biologic effectiveness is the ability to produce biologic damage.
911 - Which of the following is most radiosensitive? A. Immature sperm cells and ova B. Adult nerve tissue C. Muscle cells D. All are very radiosensitive
Immature sperm cells and ova According to the law of Bergonié and Tribondeau, the most radiosensitive of these choices would be immature sperm cells and ova; hence the need for gonadal shielding. Muscle cells, because they are highly specialized and lack cell division, are relatively insensitive to radiation.
914 - Genetic effects follow what type of dose-response curve?
Linear-nonthreshold
Because the degree of genetic effects is proportional to the amount of radiation dose received and because there is no safe gonadal dose, the dose-response curve is linear-nonthreshold. Any dose may cause damage.
915 - The amount of radiation that causes the number of mutations in a population to double is called:
doubling dose.
917 - Collimators that automatically restrict the beam to the size of the cassette have a feature called automatic collimation or:
positive beam limitation.
919 - Cylinder cones work by:
restricting the beam to a small area. Cylinder cones restrict the beam to a small area. They do not work by focusing the x-ray beam down the cone; x-rays cannot be focused.
923 - How often is aluminum added filtration adjusted by the radiographer?
NEVER Filtration is adjusted by a medical radiation physicist, not by the radiographer.
924 - Gonadal shielding may reduce female gonad dose by up to:
50% Gonadal shielding may reduce female gonad dose by up to 50%, a very significant decrease. It is even more effective in men, reducing the male gonad dose by up to 95%.
927 - For optimal Safety, what type of exposure technique should be used?
High kVp, low mAs Low mAs reduces the amount of radiation striking the patient. Choosing the highest kVp optimum for the part being radiographed increases the quality of the x-ray beam, thus reducing the need for repeat exposures. Low kVp, high mAs would result in the opposite. An all-manual technique may be high or low mAs. Small focal spot may result in a longer exposure time, which can increase motion blur and result in the need for repeat exposures.
93 - The law of conservation of energy states:
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only in changed in form The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; this is a basic law of the universe. Choice A is the law of conservation of matter.
942 - Walls that may be struck by scatter or leakage radiation require:
secondary protective barriers. Secondary protective barriers made of lead equivalent, not necessarily lead, are located wherever leakage or scatter radiation may strike. Walls that may be struck by the primary beam require primary protective barriers.
943 - How thick are secondary protective barriers?
1/32-inch lead equivalent Secondary protective barriers consist of 1/32-inch lead equivalent, not concrete. Primary protective barriers consist of 1/16-inch lead equivalent.
944 - To what height must in-wall secondary protective barriers extend?
The ceiling The secondary protective barrier extends from where the primary protective barrier ends to the ceiling, with a ½-inch overlap
946 - For shielding purposes, what is the x-ray control booth considered?
Secondary protective barrier The primary beam is never aimed at the control booth. The exposure switch in the x-ray control booth must have a cord that is short enough that the radiographer must be behind the secondary protective barrier to operate the switch.
957 - The Bucky slot cover must be at least:
0.25-mm lead equivalent
959 - Film badges measure doses as low as:
100 μGya
Film badges measure doses as low as 100 μGya. Readings below 100 μGya are reported as minimal
969 - The energy stored in an OSL dosimeter is released by exposing it to:
laser The energy stored in an OSL dosimeter is released by exposing it to a laser. The energy is then released as visible light. The energy stored in a TLD is released by heat.
974 - When adjacent mA stations are employed and exposure time is adjusted so as to achieve constant mAs, the resultant output radiation intensity must remain
constant. There must not be variations in radiation output to keep the dose to the patient as low as possible.
981 - Which of the following is the target responsible for radiation-induced leukemia?
Bone Marrow
This is where blood cells are produced; therefore, overexposure of the bone marrow can lead to leukemia.
983 - Cleaved or broken chromosomes are a consequence of ionizing radiation striking and breaking:
Two opposite areas of the sugar-phosphate molecular chain of a DNA macromolecule that lie within the same rung Such an exposure “breaks” the chromosome in half.
989 - Which of the following processes of interaction between x-ray and matter are responsible for most of the radiation received by members of the medical radiography team?
Compton scattering Compton interaction produces scatter, which is the source of occupational exposure
991 - Without medical justification, which of the following radiologic examinations are considered to be nonessential? 1. PA chest radiograph upon scheduled admission to the hospital 2. PA and lateral chest radiographs accompanying a preemployment physical 3. PA and lateral chest radiographs accompanying an annual physical examination
1, 2, and 3
992 - In image-intensified fluoroscopy, no matter what the distance is between x-ray source and image receptor, the radiologist must ensure that the primary beam:
is confined to the limits of the image receptor. Collimation is an essential practice in radiation safety. There is nothing to be gained by overlapping image receptor borders.
994 - If ionizing radiation interacts with a human cell, causing it to die after one or more divisions, it is classified as:
mitotic death. The cell is no longer able to divide (mitosis).
995 - If the radiation weighting factor of ionizing radiation is higher, relative biologic effectiveness:
is also higher.
Radiation weighting factor and RBE are directly proportional.
998 - The photoelectric interaction most likely occurs between an incident photon and a(n):
inner shell electron.


