MOD 4 Urology Flashcards
(146 cards)
Urinary system
begins with the kidneys. Located in the retroperitoneal space.
retroperitoneal space
a small area behind the peritoneum of the abdominal cavity
retro- behind; backward
peritone/o- peritoneum
-al…pertaining to
alternate names
urinary tract, GU (genitourinary system), urogenital system, excretory system.
genitourinary and urogenital
two systems in close proximity and with shared structures.
flank
under the lower edge of the rib cage in the flank area of the back
hilum
an area of indentation on the medial surface of the kidney
(HY-lum)
hilar
(HY-lar)
hil/o– hilum (indentation in an organ)
-ar…pertaining to
renal artery
enters the hilum. renal vein and ureter exit there.
renal cortex
layer of tissue

renal medulla
contains triangular-shaped renal pyramids

Minor calix
each tip of the renal pyramids connect to the minor calix, an area that drains urine.
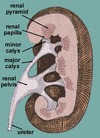
major calix
minor calices drain into a common area call the major calix

renal pelvis
major calices drain into the renal pelvils, a large funnel-shaped cavity that narrows to become the ureter

ureter
12inch tube that connects renal pelvis to the kidney to the bladder.
yoo-REE-ter
ureteral orifices
the openings into the bladder
peristalsis
propel urine into the bladder is the processs called ‘peristalsis’
peri- around
-stalsis… process of contraction
fundus
dome of the bladder
mucosa
bladder is lined with mucosa, a mucous membrane.
rugae
when bladder is empty, mucosa collapses into folds called rugae.
ROO-gee
sphincter
muscular ring that opens so that urine can flow into the urethra. opening/closing is involuntary and CANNOY be controlled consciously.
vesical
adjective form of “bladder”
vesic/o– bladder
-al– pertaining to
urethra
tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body
external urethral sphincter
muscular ring that CAN be consciously controlled to release or hold back urine.
urethral meatus
where the urethra opens to the outside of the body. (exit point of genital)


