Mack (1994) Flashcards
Describe two problems with using the normal distribution as an approximation for the true distribution of R, and identify an alternative to the normal distribution
-If the data is skewed, it is a poor approximation -The confidence interval can have negative lower limits, even if a negative reserve is not possible -Lognormal distribution
Provide 3 different variance assumptions for Cik
-Proportional to 1 -Proportional to Cik -Proportional to Cik^2
The standard error formula does not provide an estimate for a(I-1)^2. Provide 3 options for a(I-1)^2
-Set equal to 0 -Extrapolate the series using log linear regression -Set equal to min(a(I-2)^4/a(I-3)^2, min(a(I-2)^2,a(I-3)^2
List the 3 Assumptions of the Chainladder method: Using Formulas

List the 3 Assumptions of the Chainladder method: Using Words
- Expected Incremental Losses are proportional to Losses Reported to Date 2. Losses in each Accident Year are independent of losses in other Accident Years 3. Variance of incremental losses is proportional to losses reported to date

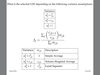
Confidence interval of reserves-normal distribution

Confidence interval of reserves-Lognormal distribution

When graphing residuals-what are we looking for and what are we testing?

For the calendar year test, what is the mean and variance of Zn?

Test for correlation of adjacent development factors

Formula for residuals



The first implicit assumption underlying the chain-ladder method states that information contained in Ci,I+1 i cannot be augmented by using other Cik. Describe a major consequence of this assumption. In addition, briefly describe a procedure for testing this assumption.
- A major consequence is the assumption that development factors are uncorrelated
- To test this, we can run a statistical test where the test statistic is Spearman’s rank correlation. If our test statistic lies within a specified confidence interval around the true correlation, we fail to reject the null hypothesis that development factors are uncorrelated
The second implicit assumption underlying the chain-ladder method states that accident years are independent. Describe a major consequence of this assumption. In addition, briefly describe a procedure for testing this assumption. The second implicit assumption underlying the chain-ladder method states that accident years are independent. Describe a major consequence of this assumption. In addition, briefly describe a procedure for testing this assumption.
- A major consequence is the assumption that CY effects do not exist
- To test this, we can run a statistical test to determine if diagonals exist where “small” development factors are prevalent (i.e. the development factors along the diagonal are smaller than usual). If our test statistic lies within a specified confidence interval around the true correlation, we fail to reject the null hypothesis that accident years are independent
Provide three options for alpha (I-3)

Briefly describe two problems with using the normal distribution as an approximation to the
true distribution of R.
⇧ If data is skewed, it is a poor approximation
⇧ The confidence interval can have negative lower limits, even if a negative reserve is not possible


