ERM Ch.3 Flashcards
(17 cards)
1
Q
IRM Components
A
- Startup: Staffing & Scope
- Parameter Development
- Implementation
- Integration & Maintenance
2
Q
Startup: Staffing & Score Components
A

3
Q
Parameter Development Components
A
- Modeling software – Assess the capabilities of the modeling software available, and make sure it matches capabilities of the IRM team
- Parameter Development – include expertise from Underwriting, Planning, Claims and Actuarial. Develop a systematic way to capture expert opinion
- Correlation – have the IRM team recommend correlations. This needs to be owned at a high level (CEO,CRO,CUO), since it crosses lines of business, and has a significant impact on the allocated capital.
- Validation‐ Validate and test over an extended period. Provide training, so that interested parties all have a basic understanding of the statistics
4
Q
Implementation Components
A
- Priority Setting – have top management set the priority for implementation
- Communications – Regular communication and to a broad audience
- Pilot Testing – allows effective preparation of the company for the magnitude of the change
- Education – training so leadership has a similar base level of understanding
5
Q
Integration & Maintenance Components
A
- Cycle – Integrate into planning calendar
- Updating – Major input review should be no more than twice a year; minor updates can be handled by modifying the scale of the impacted portfolio segments
- Controls – Maintain centralized control of inputs, outputs and even application templates
6
Q
Coefficient of Variation of the total losses
A
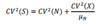
7
Q
Two ways to estimate Projection Risk
A
- Simple Trend Model
- Trend as a Time Series
8
Q
Estimation Risk
A
- Parameters are often estimated using the MLE
- Lowest estimation error of unbiased estimators
- Work with the negative of the second derivative of the log likelihook (information matrix - inverse of the covariance matrix)
- Slope is steep near the MLE - high confidence
9
Q
Why Joint LogNormal? (Small dataset problems)
A
- Standard deviations may be large ->Significant probability of having parameters w/ negative values
- For heavy tail distributions,, the parameters themselves are heavy tailed
10
Q
Model Risk - Selecting the best distribution
A
- Use the Hannan-Quinn Information Criterion (HQIC)
- It is a compromise of other information criteria which add larger or smaller penalties
11
Q
Select paramters for model risk
A
- Randomly select a mean for alpha and beta, and a covariance matrix from a pool of disributions you have selected
- Now that you’ve selected a distribution for alpha and beta, randomly draw an alpha0 and beta0
- For each claim that is simulated, draw from the distribution with parameters (alpha0,beta0)
12
Q
Kendall’s t
Concordant
Discordant
A
- t = (C-D)/# of pairs
- Concordant:
- x1>x2 and y1>y2 or vice versa
- Discordant:
- Mixed
- Focuses on rank of each data point not on its value
13
Q
Frank’s Copula
A
- Small tail dependencies

14
Q
Gumbel’s Compula
A
- More probability in the tails
- More density in the right tail
- t(a) = 1- (1/a)

15
Q
Heavy Right Tail (HRT) Copula
A
- Less correlation in the left tail, but high correlation in the right tail
- t(a) = 1/(2a+1)
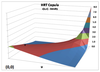
16
Q
Normal Copula
A
- Joins two distributions using the correlations from the bivariate normal
- More dependencies in the tail
- Symmetrical
- t(a) = 2arcsin(a)/pie
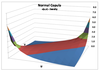
17
Q
Tail Concentration Function - L & R
A
- L(z) = c(z,z)/z
- R(z) = (1 - 2z + C(z,z))/(1-z)


