Living anatomy Abdomen and Pelvis Flashcards
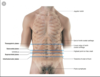
In which nine regions can you separate the anterior abdominal wall?
Which planes would you use to separate these regions?
Horizontal planes
- Sub-costal plane (horizontal line joining the right and left costal margin at mid-axillary line
- Transtubercular plane (line joining the right and left iliac tubercles)
Vertical Planes
- Right and left from mid clavicular to mid-inguinal points

Reference : Spinal levels of important structures


What are the superior borders of the liver?
Closely follows diaphragm
Line over
- Right 5th rib and costal cartilage
- Extends over lowe end of sternum
- to the left 5th intercostal space, midclarvicular line

Describe the surface markings of the oblique (lower) border of the liver
- Follows right costal margin
- To the tip of right 9th costal cartilage
- Left 8th costal cartilage
- 5th intercostal space on the left

What is the right border of the liver (surface marking)?
Right mid-axillary line costal margin
to
plane of 5th rib/costal cartilage on mid-axillary line

What is the surface marking of the gall bladder?
Tranypylroric plane at the right mid-clavicular line (Tip of 9th CC)

What are the surface markings of the spleen?
9,10,11 rib on right back
Lateral borders: Erector spinae and mid-axillary line

What do you have to expose to be able to perform an abdominal examination?
Everything from the nipple to the pubic symphysis
Which 4 steps are important in a physical examination
What is different in an abdominal examination?
- Inspection
- Palpation
- Percussion
- Ausculation
„However, in abdominal examination, auscultation is done before palpation or percussion in order to prevent the bowel sounds being disturbed by deep palpation“
How do you feel the pulse of the abdominal aorta in a physical examination of the abdomen?

How should you palpate the spleen in an abdominal physical examination?

Identify the ASIS


Identify the PSIS






Identify the iliac crest


What is the sub-pubic arch?

Different in male and female pelvis

What is the sacral promontery?

Top part of sacrum
What are the greater and lesser sciatic notches?
Form greater and lesse sciatic foramina with ligaments in place

Where is the pubic symphesis?
Joining of the pubis
–>

What is the sacroiliac joint?
Joining of the sacrum and ileum

What are the differences between male and female bony pelvis?
- Pelvic inlet
- Male = heart spaped, small
- Female, oval/round, big
- Sub-pubic angle
- male: steep (V shaped), <90°
- Female wider (>100°)

What is the The pelvic girdle?
The pelvic girdle is composed of the appendicular hip bones (ilium, ischium, and pubis) oriented in a ring, and connects the pelvic region of the spine to the lower limbs

What can you find at vertebra level L2/L3?
Sub-costal plane (Rib 10)