Anatomy of the Thorax Flashcards
How do you call the inferior and superior ends of the thorax?
Superior thoracic aperture (open, allows continuity with neck)
Inferior thoracic aperture (closed by diaphragm)
Which three structures are involved in breathing movement?
Diaphragm
Thoracic wall (muscles)
Ribs (Bucket handle, pump mechanism)
How many times does a rib articulate with vertebral collum?
Most (II-IX) 3 times: (three facets)
Own vertebra
Vertebra above
transverse process of own vertebra

How many ribs are there and how are they classified?
Ture ribs 1-7
False Ribs (8-10)
Free /Floating Ribs (11+12)
–> Total: 12
What are the borders of the superior thoracic aperture?
Which major structures pass through it?
Posterior: T1 vertebra
Superior Rib 1
Anteror: Superior border of manubrium

How do you call the joint between the transverse process of a vertebra and its related rib? How is the other joint (between the vertebral body) and rib called?
- Costotransverse joint
- Costovertebra joint

How is a costotransverse joint stabilised?
By three ligaments:
Costotransverse ligament (medial to joint)
lateral costotransverse ligament (lateral to joint)
Superior costotransverse ligament (superior surface of the rib to the transverse process above)

How are the connections between Sternum and ribs I-VII called?
What is different between joint Rib I and others?
Sternocostal joints
I: Not synovial but fibrocartilaginous connection
II - VII: Synovial
How are the connections between costal cartilages of adjacent ribs called?
Interchondral joints

Synovial joint
Glenk mit gelenkflüssigkeit und Kapsel
What is the endothoracic fascia?
Connective tissue posterior to ribs+ intercostal spaces
Sepparates structures (muscles, ribs, spaces etc.) from pleura

Where and in what order are intercostal vein, artery and nerve located?
Are located in the costal groove (comma-shaped ribs)
Colateral bonds often also superior to inferior rib below
Superior to inferior:
Vein
Artery
Nerve (often not protected by groove anymore)

What are the three layers of intercostal muscles?
How are they innervated?
- External intercostal muscles
- Internal intercostal muscles
- Inntermost intercostal muscles
Innervated by Intercostal nerves T1-T11

External intercostal muscles (orientation, function)
Inferior margin of the rib above to superior margin of rib below
Orientation: Inferior medially
Inspiration, superior movement of ribs

Internal intercostal muscles (orientation, function)
Lateral edge of costal grove rib above to sperior margin of tib below
Orientation: Inferior laterally
Function: Expiration, inferior movement of ribs

Innermost intercostal muscles
Medial edge of superior costal grove to internal superior margin of rib below
Orientation (like internal) Inferiorlaterally
Function: Supports internal

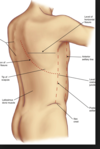
What are the borders of the safe tiangle?
Superior border of rib
4th or 5th intercostal space, between anterior axillary and mid-axillary line (pec and latissimus dorsi)

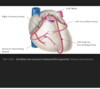
Which structures pass the diaphragm at which levels?
VIII: Inferior vena cava
X: Oesophagus
XII: Aorta
Which nerves innervate the diaphragm?
Innervated by phrenic nerve (C3,4,5)
What are the medial, superior and inferior borders of the pleural cavities?
Superior: above rib 1 into the root of neck
inferior: just above the costal margin
medial: mediastinum
How are the two sides of the pleura called?
Visceral pleura: attached to the lung surface
Parietal pleura: wall of pleural cavity
What shows the purple and blue colour?

Purple: marking of the lungs (visceral pleura)
Blue: Pleural cavity( parietal pleura)
–> a lot of space to extend
What happens to the pleura at the hilum of the lung?
It deflects and visceral + parietal pleura are continous