Cardiovascular System Flashcards
Outline the external structure (different layers) of the heart
Pericardium: Sack with pericardial fluid between visceral and parietal periacardium

Cardiac anatomy: demonstrate the basic anatomy of the heart, inculding the four chambers and the valves w. its simmilarities and differences

Explain different layers of blood vessels and explain their function
Tunica externa: collagen, protection and holding blood vessel in place
Tunica media: elastic smooth muscle, collagen and elastin
Tunica intima: vascular endothelium + support

Other name for arteries
conduit vessel
carry blood to destination
Ateriole
resistance vessel
control flow into capillaries
Other Name for Vein
Capacitance vessel
–> store most blood in human body
Explain coronary aterial circulation (3(4)) main arteries

Main vein(s) in coronary circulation
all blood comes together in coronary sinus

Major arteries in human body

Major veins in human ciculation
Everything ends in vena cava inferior + superior
Exitation-Contraction Coupling in Heart muscle

Length tension relatin in cardiac muscle
The more cardia muscle is stretched the higher passive + active force (til a limit)
–> more resistant to stretch and less compliant (nachgiebig) than skeletal muscle
–> due to ECM and cytoskeleton
Explain the two forms of muscle contraciton
Isometric: Same lenght, more tension
Isotonic contraction: Same tenstion, length changes
–> both important in cardia muscle contraction
Preload
load that stretches muscle in resting state
–> filling of the heart (more blood= more stretched
–> venous return of blood to the heart

Afterload
weight that is nor papparent in resting state but after start of contraction
–> load against left ventricle has to pust: Blood pressure
–> more afterload = less isotonic + more isometric contraciton
Frank-Starling-Relationship
Increased diastolic fiber length increases ventricular contraction (More preload = more stroke volume)
–> allows input = output
Because
- number of myofilament cross-bridges (too short = overlap)
- Ca2+ sensitivity increases –> conformational change in Troponin C (theory) increases affinity for Ca2+
Less Ca2+ for same force is needed
Stroke work

Law of LaPlace
Effect: Left ventricle smaller radius –> more pressure with similar wall stress
–> in failing hearts often hearts get dialated which increases wall stress
Vascular example –> aneurism –> higher radius, higher wall stress

Stroke volume (calculation and normal values)
End diastolic volume - End systolic Volume = Stroke Volume
108mL - 36mL = 72 mL
Ejection fraction (definition, calculation, normal ranges)
Shows, how much blood is ejected in relation to filling
Normal ; 60 - 70%
Ejection fraction = 100x Stroke Volume / End diastolic volume
67% = 100x 72ml / 108 ml
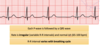
Cardiac cycle (phases, better overview in written notes)
Atrial systole
Isovolumetric contraction (1st heart sound)
Rapid ejection
Reduced ejection
Isovolumetric filling
Rapid passive filling
Reduced passive filling

Expain volume pressure loop and effects of pre and afterload
Box-like appearance with top left corner at end-systolic pressure volume relation (ESPVR)
- Preload: Determines stretching /volume at beginning of stroke –> more preload, shifted to the right
–> increased preload –> increased stroke volume
- Afterload: Determines pressure –> more after load = hight BP = higher pressure + higher curve
–> increased after load –> decreased stroke volume (less isotonic contraction

cardiac output
Blood pumped per minute
Heart rate x stroke volume
Peusoilles equasion
Small changes in radius have big effects on flow