Less toe deformity Flashcards
Claw toe hammer toe mallet toe synovitis 2nd MT Bunionette Freiberg's disease
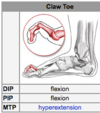
What is a claw deformity characterised by?
- MTPJ HYPEREXTENSION —> PIPJ AND DIPJ FLEXION similar to intrinsic deformity of the hand
- combination of hammer and mallet toe
What is claw’s toes epidemiology?
- Bilateral
- Typically involves multiple toes
What is the pathophysiology of claw toes?
- PRIMARY MCPJ HYPEREXTENSION
- –> UNOPPOSED FLEXION PIPJ and DIPJ BY FDL
- MTP PLANTAR PLATE becomes insufficient
- _Base of _PROX PHALANX TRANSLATES DORSALLY
- INTEROSSEI AND LUMBRICALS move DORSALLY
- shift rotation dorsally
What is the result of the pathophysiology?
- Shifts flexion moment to WRONG SIDE OF CENTRE OF ROATION -> FLEXION
Describe the Aetiology of claw toe?
- SYNOVITIS- most common
- TRAUMA
- DELAYED COMPARTMENT SYNDROME- DEEP POST COMPARTMENT
What other conditions are associated with Claw toes?
- Pes CAVUS
- NEUROMUSCULAR disease- effects intrinsics
- INFLAMMATORY ARTHROPATHIES- leads to soft tissue attenuation and MTPJ instability
What do patients with Claw toe present with?
Symptoms
- METATARSALGIA
- PAIN AT LEVEL OF UNSTABLE MTCP
Signs
- Claw like deformity of toe
- Depressed metatarsal head with callus formation adn tenderness
- Flexed IPJ with callosities and tenderness

Describe non operative tx of claw toes?
Non operative
-
Taping / Shoe modificaiton
- first line of treatment
- adequate plantar padding using MT and or crest pads or orthotics to off load plantarly sublused MT heads
- sling to hold proximal phalanx parallel to the ground
Describe operative tx of claw toes?
-
Extensor Digitorium brevis tenotomy, Extensor Digitorium Longus lengthening, FDL flexor to extensor transfer ( girdelstone)
- for painful , flexible deformities without contractures
- ulcerations caused by shoe wear
- Girdlestone, MTP capsulectomy, and proximal phalanx and head resection = fixed contracture
-
Girdelstone and MT shortening osteotomy = Weils
- clawing of all 4 lesser toes
- oblique shortening osteotomy
- translated MT heads PROXIMAL & PLANTAR

What are the complications of surgical correction of claw toes?
- Floating toe
- most common complx of Weils osteotomy
- caused by _intrinsics migrating dorsall_y to the joint and acting as MTP extensors
- avoid by osteotomy parallel to plantar surface if foot or a wafer of bone resected to ensure that joint is not depressed as the mT is shortened- see pic
-
Reoccurance
- __Persistent plantar plate dysfunction

decribe the anatomy of extensor digitorium brevis and extensor hallucis?
Extensor digitorium brevus
- orgin- lateral portion of calcaneus
- inserts- Base prox phlanax 2-4 toes
Extensor hallucis brevis
- origin- dorsal lateral side of calcaneus
- inserts- base of prox phalanx great toe

What is this?

- Hammer toe
- Flexion at PIPJ and extension at DIPJ
What is the epidemiology of hammer toes?
- Most common deformity of lesser toes
- more common in older women
- second toe most commonly affected

What is the pathanatomy of hammer toe?
- Overpull of Extensor Digitorium Longus
- Imbalance of Intrinsics
Describe any associated conditions of hammer toes?
- Painful corns at PIPJ
What are the signs and symptoms of hammer toes?
Symptoms
- Pain on dorsal surface of shoe wear
- deformity
Signs
- Flexion deformity of PIPJ of lesser toes with extension of DIPJ
- PUSH UP TEST- flexible deformity is correctable with dorsal directed pressure on plantar aspect of involved metatarsals

what is the tx for hammer toe deformities?
Non operative
- Shoe with high toe box, foam or silicone gel sleeves
- pain or corns on dorsal PIP
Operative
-
Flexor tendon (FDL) to extensor Tendon transfer
- Flexible deformity that failed non op
-
Resection arthroplasty +/- tenotomy and tendon transfers
- Rigid deformity that has failed non op mx
-
Girdlestone procedure with flexor to extensor transfer
- MTP involvement
- Similar to claw toe tx
-
Arthrodesis
- rigid deformity
- high non union rate
Describe resection arthroplasty and tenotomy & tendon transfer?
-
Resection of head and neck or proximal phalanx to create a fibrous joint
- +/- FDL to EDL transfer
- hold in place with K wires 2-3 wks
- post op additional 3 weeks w taping of PIPj in extension
Describe the girdlestone procedure for hammer toes?
- (flexor to extensor transfer)
- Extensor tendon lengthening Z plasty
- Preform MTP capsule release
- +/- Metatarsal shortening with oblique osteotomy
- FDL to EDL transfer
What is this?

- Mallet deformity
- Hyperflexion of the DIPJ
- normal PIPJ and MTPJ
Deformity may be fixed or flexible
What is the pathoanatomy of mallet toe?
- Contracture/ of FDL
- **>70% of patient have a longer **
What is the congential mallet toe associated with?
- Flexion and lateral deviation of DIPJ
What is seen on examination of a mallet toe?
-
Callosities on toe
- dorsum of DIPJ
- Tip of toe
- Pain results from impacting the ground with gait
What is the TX of mallet toes?
Non operative
- Shoes with hogh toe boxes, silicone/foam toe sleeves
- first line
Operative
-
Percutaneous FDL tenotomy
- flexible deformity that have failed non op
-
Middle phalangeal distal condylectomy (excision arthroplasty of DIP)
- Rigid deformities that have failed non op mx
- repair attenuated extensor tendons
- K wire placement used to hold affected digit in extension













