Lecture 7: Male Reproductive Histology Flashcards
Identify A-D

A) Tunica Albuginea
B) Epididymis
C) Rete Testis
D) Septa

The Rete Testis are channels formed within?
The CT of the mediastinum

Identify A-E

A) Leydig Cells
B) Sertoli Cells
C) Spermatogonia
D) Primary Spermatocytes
E) Spermatids

How do we identify Leydig Cells histologically?
- Contain lipid droplets (for steroid synthesis), mitochondria w/ tubular cristae, and a well-developed sER
- Close to blood vessesl and lymphatic channels
- Present in the intertubular space

The seminiferous epithelium houses which 4 structural types of nuclei; describe the characterisitcs of each?
1) Nuclei of Spermatogonia and Sertoli Cells –> close to tubular wall
2) Spermatogonia cell (primary spermatocytes): larger nuclei and clumps of chromatin
3) Early spermatids —> round, light nuclei
4) Late spermatids –> cylindrical-shaped, condensed nuclei
What is the function of Sertoli Cells?
- Support, protect, and nourish developing spermatogenic cells
- Eliminate residual bodies via phagocytosis (discared by spermatids during spermiogenesis)
- Release of mature spermatids into lumen of tubule, spermiation

What are the characterisitcs to identify the Sertoli Cells histologically?
Oval or pyramidal nuclei (potato shaped; light staining)

Identify A and B

A) Sertoli Cells
B) Peritubular Myoid Cells
At the basolateral domain of the Seminferous Epithelium, what do Sertoli cells have that is special to the testes?
- Tight junctions creating basal and adluminal compartment
- Special to the testes: typically an apical specialization
What is the function of the tight junctions in the Adluminal compartment of the Seminiferous Epithelium?
Establish the blood-testes barrier
Identify the structure labeled by A

Leydig (interstital) cells

Where are the diploid spermatogenic cells found?
- Reside in a niche of basal compartment of Sertoli cells
- Located outside the blood-testes barrier
What process do primary spermatocytes undergo and what is the product?
Undergo 1st meiotic division (reductional division) (4C) –> two secondary spermatocytes (2C)

What process do secondary spermatocytes undergo and what are the products?
- Undergo 2nd meiotic division (equational division) (2C) –> two spermatids (1C)

- Spermatids mature w/o further division
What is the ploidy of spermatids and what do they intiate?
- Spermatids are haploid
- Initiate spermiogenesis
Where are the round (early) spermatids housed vs. the elongated (late) spermatids?
Round (early): house in niches in cytoplasm of Sertoli Cells
Elongated (late): housed in crypts, deep invaginations in Sertoli apical cytoplasm
The last step of spermiogenesis is the development of what 4 characteristics?
1) The acrosome
2) The manchette
3) The tail
4) Shaping and condensation of the nucleus
What is spermiation?
Release of mature spermatids into the seminferous tubular lumen, involving the contractile forces generated by Sertoli cells
What are the 3 subdivisions of the tail of the sperm and characteristics of each?
Middle piece: helically arranged mitochondrial sheathe, Axoneme, 9 longitudinal columns, outer dense fibers, surrounding axoneme
Principal piece: is the longest segment of the tail, consists of the central axoneme surrounded by a fibrous sheath, which provides scaffold during sliding/bending of tail during forward motility
End piece: very short, only contains the axoneme
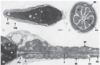
What is the sperm maturation pathway for mature spermatids (immature sperm)?
Straight tubules —> Rete Testis —> Efferent ductules —> Epididymal duct

What is A pointing to and what structure is this?

A) Columnar Sertoli Cells, which are transitioning into Cuboidal Sertoli Cells
- This is a Straight Tubule (Tubulus rectus)

What structure is this?

Rete Testis

Each Efferent Ductule is lined with what 3 cell types?
1) Columnar cells w/ microvilli/sterocilia (Principle Cells)
2) Ciliated Cells
3) Basal cells
*Also a thin inner circular layer of smooth muscle underlies epithelium and basal lamina

Identify A and B

A) Efferent Ductule
B) Smooth muscle

Histologically where is Androgen Binding Protein found?
Rete Testis

What is the function of the Prinicipal Cells with microvili in the Efferent Ductules
Absorption of NaCl and H2O to concentrate the sperm
The epididymis is lined with what?
Pseudostratified columnar w/ long and branched **stereocilia**

1) Principal cells: columnar cells
2) Basal cells
What structure is this?

The Epididymis

What strucutre is this and what are the arrows pointing to?

The Epididymis
*Arrows pointing to pseudostratified columnar epithelium w/ stereocilia

The Vas Deferns is lined with; the muscular wall consists of?
- Lined with pseudostratified columnar w/ sterocilia/stereovilli

Muscular Wall:
- Inner and outer longitudinal layers
- Middle Circular layer
What strucutre is this?

Vas Deferens/Ductus Deferens

What structure is this?

Seminal Vesicle

What is the mucosa of the Seminal Vesicle like histologically?
Highly folded mucosa lines by simple cuboidal-to-pseudostratified columnar epithelium

What structure is this?

Seminal Vesicle

The prostate gland is arranged in 3 zones what are they; what kind of glands found in each zone?
1) Central zone w/ periurethral mucosal glands
2) Transition zone w/ periurethral submucosal glands
3) Peripheral zone consisting of branched (compound) glands
Which zone does 70-80% of prostate cancer arise in; which glands are found here?
The peripheral zone w/ branched (compound) glands
What are these images of?

The prostate gland
The lumen of the prostate gland contains what?
Corpora amylacea; rich in glycoproteins and Ca2+ deposits

What is this image of?

Erectile tissue

Vascular sinuses of erectile tissue are supplied by which arteries?
Helicine arteries

Label the structures A-D

A) Tunica Albuginea
B) Corpora Cavernosa
C) Urethra
D) Corpus Spongiosum



