Lecture 5: Hormone Signaling Pathways Flashcards
Why is only a small amount of hormone necessary to generate a signal?
The effect of hormone binding to its receptor is magnified via amplification.
Once the ligand binds to its receptor - the receptor complex can do what to cellular pathways?
- Activate or inhibit cellular pathway (s) that elicit a particular cellular response (enzyme activity, gene expression)
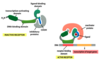
Differentiate endocrine, paracrine, autocrine, and juxtacrine signaling; give an example of a molecule that participates in each one?
Endocrine: signaling molecule released by a cell distant to target and transported via bloodstream to target. i.e., epinephrine
Paracrine: signaling molecule released by one cell type and diffused to a neighboring target cells of different cell type i.e. testosterone
Autocrine: signaling molecule acts on the same cell type as the secreting cells themselves i.e. IL-1
Juxtacrine: signaling molecule stays attached to the secreting cell and binds to a receptor on an adjacent target cell i.e. heparin-binding epidermal growth factor

Can a signaling molecule be used in more than one type of signaling?
Yes, some molecules may participate in more than one type of signaling
What are the receptor involved in hydrophilic hormone signaling; what does the signaling molecule-receptor complex initiate?
- GPCRs
- RTKs
- Initiates production of second messenger molecules inside cell
- Both found on the surface of target cells, since the signaling molecule won’t be able to diffuse throught the membrane
What are the receptor types for lipophillic hormone signaling (differentiate between the two); binding to the receptor does what?
- Cytoplasmic receptors: exist as inactive complex. Upon binding, the hormone-receptor complex translocates to nucleus where it binds to a specific DNA sequence called the hormone response element (HRE)
- Nuclear receptors: already present in nucleus bound to DNA. The hormone allows for interaction w/ additional proteins and activates the complex
- Signaling molecule-receptor complex acts as a transcription factor
Differentiate between hydrophilic and lipophilic medications?
Hydrophilic: have short 1/2-lives (seconds to mins.). Given a the time of need, like epinephrine.
Lipophilic: have long 1/2-lives (hours to days). Need to take daily, like oral contrapceptives.
What are lipophilic signaling molecules?
- Steroid hormones: progesterone, estradiol, testosterone, cortisol
- Thyroid hormone: thyroxine (T4)
- Retinoids: retinol, retinoic acid
What are some hydrophilic signaling molecules?
- AA derivatives: histamine, serotonin, melatonin, dopamine, NE, epi
- Acetylcholine
- Polypeptides: insulin, glucagon, cytokines, TSH
Explain the general mechanism for GPCR signaling
- Trimeric G-proteins contain three subunits (α, β, γ)
- Inactive G protein has GDP bound to α subunit, and to become active G protein must exchange GDP for GTP using GEF, and α-subunit separates from beta and gamma subunits
- To return to inactive state, intrinsic GTPase activity of G protein hydrolyzes bound GTP into GDP + Pi w/ help from GTPase-activating protein (GAP)
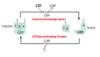
What occurs when a signaling molecule binds to a GPCR using Gs pathway?
- Stimulates adenyly cyclase, which increases cAMP that can activate PKA.
- PKA will phosphorylate target proteins to alter their activity

What occurs when a signaling molecule binds to a GPCR using Gt pathway?
- Light hits a GPCR leading to the stimulation of cGMP phosphodiesterase, which converts cGMP –> 5-GMP, halting any action being promoted by cGMP

What occurs when a signaling molecule binds to a GPCR using Gi pathway?
- Signaling molecule binds causing the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase so NO cAMP is produced, and PKA is NOT activated

What occurs when a signaling molecule binds to a GPCR using Gq pathway?
- Activates PLC, which produces the second messengers DAG and IP3
- IP3 leads to increased Ca2+
- DAG leads to the activation of PKC, which phosphorylates target proteins to alter their activities

Epinephrine, histamine, and NE bind to what type of receptors, activating which GPCR pathways?
- Epinephrine binds β-adrenergic receptor activating Gs
- Histamine binds H2-receptor activating Gs
- Epinephrine/NE bind α-adrenergic receptor activating Gi

Dopamine, ACh, and light bind to what receptors utilizing which GPCR pathway?
- Dopamine binds D2-receptor utilizing the Gi pathway
- ACh binds the M3-receptor utilizing the Gq pathway
- Light activates rhodopsin receptor utilizing Gt pathway

What is the structure of insulin?
- Two polypeptide chains referred to as the A chain (21 AA’s) and B chain (30 AA’s)
- Linked together by two disulfide bridges (S-S)

What is the secondary and tertiary structure of insulin; active vs inactive structure?
- 3-fold symmetry w/ Zinc in the center connected via histidines
- Inactive stored in body as a Hexamer
- Active form is a monomer
Describe the basic process underlying insulin synthesis and secretion
- Glucose upregulates preproinsulin mRNA
- Translated into preproinsulin protein in the ribosome
- Cleaved by a protease to form proinsulin
- Folded and transported to Golgi to be packaged into granules
- C-chain cleaved to form A-chain + B-chain insulin structure
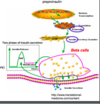
What are the 2 phases of insulin release after glucose stimulation?
1) First (rapid but transient) release comes from a limited pool of granules referred to as the readily releasabel pool (RRP)
2) Second (sustained) phase comes from a larger pool referred to as the reserve pool.
How does glucose cause the release of insulin granules from the pancreatic β-cell?
- Glucose enters the cell via GLUT 2 and will undergo glycolysis –> PDH –> TCA producing ATP/ADP
- ATP/ADP caused the closing of ATP-sensitive K+ channels, which lead to the opening of Ca2+ channels
- Opening of the Ca2+ channels stimulate the release of insulin granules into the blood

Describe the mechanism upon insulin binding the RTK that involves the RAS pathway.
- Insulin binds RTK, receptor becomes dimerized and autophosphorylates tyrosine residues.
- IRS-1 is recruited and becomes phosphorylated, attracting the scaffolding protein called GRB-2, which activates the RAS pathway
- RAS pathway phosphorylates nuclear proteins causing an increase in the transcription of Glucokinase and increased glucose uptake
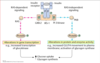
Describe the mechanism upon insulin binding the RTK that involves the RAS-independent pathway.
- Insulin binds RTK, receptors dimerizes, autophosphorylates tyrosine residues.
- IRS-1 is recruited and phosphorylated, then recruits PI 3-kinase, which activates PKB via phosphorylation
- PKB phosphorylates many nuclear proteins and trigger the translocation of GLUT4 to plasma membrane; activation of glycogen synthase
- Leads to increased glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis

How can insulin be measured in a Quantifiable manner?
Measured as amount of glucose cleared from the blood in response to a fixed dose of insulin