Lab Quiz 2: Labs 4, 5, 6 Flashcards
(136 cards)
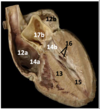
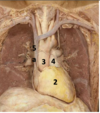
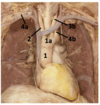
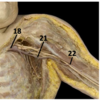
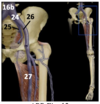
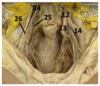
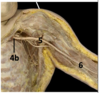
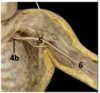
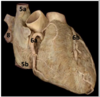
Identify the arteries

Blood oxygen saturation level (SpO2)
- Describe
- What is used to measure it?
- Amount of oxygen present in blood compared to the maximum amount of oxygen the blood could contain
- Measured using a pulse oximeter
Blood pressure
- Describe
- Where is it commonly measured?
- Normal range
- Amount of pressure exerted by the blood as it pushes against blood vessel walls
- Rises and falls as the heart contracts and relaxes
- Commonly measured in the brachial artery
- Normal range: 110-130 / 75-85 mm Hg




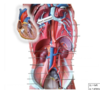

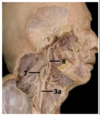
Identify the veins




Cardiac output formula
Stroke Volume (ml) * Heart Rate (beats/min) = Cardiac Output
Which artery is used to measure the carotid pulse rate?
Common carotid artery
Deoxyhemoglobin
- Describe
- Hemoglobin that is not bound to oxygen
- Less oxygenated blood appears dark red in color
Describe how the pulse is generated
- As blood is forced out of the left ventricle, it expands the elastic arteries
- Blood moves through the arterial system
Diastolic blood pressure
- Describe
The pressure measured when the ventricles relax
Dubb sound
- Describe
- What creates the sound
- Second sound of the heart beat (S2)
- Sound is shorter and sharper than S1
- Associated with the closure of the semilunar valves
What is used to listen (auscultate) for the S1 and S2 sounds?
Stethoscope
What SpO2 level is considered to be that of hypoxemia?
- < 90% SpO2
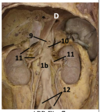
Identify #1

Pericardium
Identify #1

Atrioventricular mitral valve
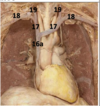
Identify #1

Brachiocephalic trunk
Identify #1

P-wave
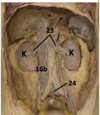
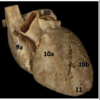
Identify #10

Superior mesenteric artery
Identify #10

Interventricular septum
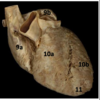
Identify #10a
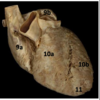
Right venticle
Identify #10b

Left ventricle