L4.2+4.3 Ab viscera Flashcards
1
Q
How is the abdominal quadrants divided?
A
- Horizontal line through umbilicus
- Vert line from sternum to pubic symphysis
2
Q
Esophagus
A
- Muscular tube, 25cm
- Conduct food from pharynx to stomhac via peristalsis
- Enters stomach from the L of side, into R side of somtach

3
Q
Esophogastric junction (Z-line)
A
- Changes from esophageal mucosa to gastric mucosa
- Stratified squamous epithelium → simple columnar epithelium)

4
Q
Esophageal narrowings
A
- Cervical: Upper esophageal sphincter
- Thoracic: Aortic arch & LMB
- Abdomen: Diaphragmatic orifice
5
Q
BS of the esophagus (ab part only)
A
- L gastric branch from aorta
6
Q
Venous drainage of the esophagus (ab part only)
A
- L gastric portal
7
Q
Herniation of the stomach
A
- Sliding hiatal hernia: Through esophagus
- Paraesophageal hernia: Next to esophagus

8
Q
Stomach
A
- LUQ, intraperitoneal
- J-shaped → have greater & lesser curvature
- Cardiac orifice (Prox opening of R border)
- Pyloric orifice (distal opening)
- Fundus (part that projects upwards above the cardio orifice - usually full of gas)
- Body
- Angular notch (on lesser surface where body ends - begins to funnel down)
- Pyloric antrum (funnel bit)
- Pylorus (converges on the most tubular & distal part)
- Has a pyloric sphincter - controls gastric outflow into duodenum
- Rugae (gastric folds in stomach - more predominant twd pylorus)

9
Q
Mesentery of the stomach
A
- Lesser omentum: Connected to under surface of liver on the lesser curvature of stomach
- Greater omentum: connects stomach to POS wall

10
Q
BS to the stomach
A
- Gastroepiploic vessels running along curvatures
11
Q
Duodenum
A
- Retroperitoneal (but 1st inch is intraperitoneal → hasn’t made it back to POS wall), 25cm
- C-shaped loop surrounding head of pancreas
- Site of digestion & absorption of digestive products
- Villi → ↑SA → ↑Abs

12
Q
Duodenum 1) Duodenal cap
A
- 5cm
- Upwards & backwards (adjacent to R.crus, overlying hilum of R. kidney)
- Ulcers tend to form (due to imbalance of gastric contents & acid)

13
Q
Duodenum 2) Descending vertical part
A
- 7.5cm
- Vertical descent on R.psoas next to head of pancreas
- Has transverse mesocolon (surrounds the transverse colon)
- Have pailla

14
Q
Duodenum 3) Horizontal part
A
- 10cm
- Has root of mesentery of SI
- R to L.psoas in front of IVC & aorta, at level of L3

15
Q
Duodenum 4) Ascending part
A
- DJ flexure
- Curves forward

16
Q
Duodenal papilla
A
- On P-M wall 1/2 down of 2nd part of duodenum
- Major: where common bile duct & pancreatic duct enters
- Minor: position is higher than maj, where accessory pancreatic duct enters

17
Q
Jejunum + Ileum
A
- 4-6m
- Starts at DJ flexure
- 2/5 jejenum, 3/5 ileum
18
Q
Differences b/w jejunum & ileum
A
- Jejunum has ↑abs
- ∴↑mucosal folds, thicker walls…
- Jejunum (LUQ), Ileum (RLQ)
- Jejunum has long vasa recta, few arcades
- Ileum has short vasa recta, lots of arcades
19
Q
BS to SI
A
- Arcades: Mesenteric A arranged in loops
- Vasa recta: long projections twd intestines

20
Q
LI
A
- Frames the central coils of the SI
- Muscle coats:
- Inner circular coats
- Outer longitudinal muscle coats
- Forms 3 discrete muscle bands → Teniae Coli
- Bands are shorter than mucosal tubes → creates Haustra (sacs of LI)
- Epiploic appendices (fat tags) → unique to LI

21
Q
Caecum
A
- Retroperitoneal
- Begins with ileum ends
- Blind pouch behind ileocaecal valves
22
Q
Ileocecal junction
A
- Has ileocaecal valve (mucosa covering anatomical sphincter)
23
Q
Appendix
A
- Hangs off base of caecum, where 3 teniae coli meet (fixed)
- Variable length
- Contains modules of lymphoids
- Tips of appendix is variable
- Pelvic appendix (~25%) → hangs twd pelvis
- Retrocaecal appendix (~65%) → tucked up behind A.colon

24
Q
Rectum
A
- No teniae along rectum
- Longitudinal fibres becomes continuous
25
Liver
* RUQ, Intraperitoneum
* 2 surfaces: diaphragmatic (smooth) & visceral (has adjacent structure impressions)
26
Liver: Diaphragmatic surface
* Has sharp INF edge of liver
* Falciform ligament → divides into 2 functionally equal lobe (but R anatomically larger than L)

27
Falciform ligament
* Double fold mesentery
* Connects to ANT wall
* Down to level of umbilicus → becomes the ligamentum teres (round ligament) → obliterated after birth → Remnant umbilical V in fetus

28
Liver: Visceral surface
* Hilum of liver (creates H-shape fissure → creates 2 more lobes)
* Quadrate (INF)
* Caudate (SUP)
* Quadrate + Caudate + L lobe → functional L lobe
* Gallbladder b/w R lobe & quadrate lobe
* IVC embedded into V surface b/w R lobe & caudate lobe

29
Ligamentum venosum
* Remnant of ductus venosus
* Connects portal V & directly drains into IVC
* Used by bypassing liver in fetus
30
Hilum (porta hepatis)
* Structures all divide into R/L
* Left of hilum: Proper hepatic A
* Right of hilum: Hepatic duct → brings bile out (R+L = common hepatic duct)
* Back of hilum: Portal V → venous drainage from GI tract (all the products from GI presented to liver)

31
Venous drainage of the liver
* IVC embedded in visceral surface (doesn't come out of hilum)
* Hepativ veins drain directly into IVC
32
Epiploic foramen
* Able to see hilum structures

33
Gallbladder
* Stores & concentrate bile prod. From liver
* Sits in groove of visceral surface of liver
* Fundus of gallbladder hangs below INF margin of liver, corresponding with R.costal margin & with R. Rectus abdominus
* Able to palpate if gallbladder is infected (i.e. from gallstones etc…)
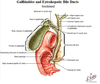
34
Pathway of the gallbladder
* Fundus → Body (narrows) → Neck (narrowed further) → Cystic duct → joins common hepatic duct → becomes common bile duct → along edge of L.omentum → behind 1st of part duodenum → groove b/w head of pancreas of 2nd part of duodenum → maj papilla

35
Hepatopancreatic sphincter
* At the terminal portion of pancreatic & bile duct
* Closed in resting state, relaxes only in the presence of fatty meals

36
How is bile stored in the gallbladder
* Bile comes from liver → sphincter closed → bile moves back into cystic duct → gallbladder
37
How is bile released from the gallbladder
* Fatty meal → gallbladder contracts → bile out
38
Pancreas
* Has exocrine functions (using ducts) & Endocrine functions (released into bloodstream ∴ rich BS)
* Head:
* Within C-shaped duodenum
* Uncinate process (landmark to identifying SUP mesenteric vessels)
* Neck
* Deep to pylorus of stomach
* Body
* Above DJ flexure
* Tail
* Leads directly to hilum of spleen

39
Ducts of pancreas
* Begins at tails → joins common bile duct → maj duodenal papilla
* Accessory pancreatic duct:
* Drains uncinate process

40
Spleen
* Oval shaped, variation in size
* Atrophy with age
41
Spleen: Diaphragmatic surface
* Smooth & characterised by notches

42
Spleen: Visceral surface
* Colic (colon impressions), Gastric, Renal surfaces
* Hilum → splenic A & V (VERY VASCULAR)
* A travels along SUP border of pancreas into hilum

43
Position of the spleen
* LUQ, above L. splenic flexure
* Beneath diaphragm

44
Relationship of the spleen with the ribs
* Directly related to ribs 9-11
* Axis along shaft of 10th rib
* Fractured ribs → pierces spleen


