L30 - Female reproductive cycle Flashcards
Meiosis overview
One DNA replication with two divisions
Meiosis I: separation of homologous chromosomes
Meiosis II: separation of sister chromatids
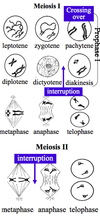
Meiosis Stages breakdown
1) Prophase I
- Preleptotene (DNA synthesis)
- Leptotene (size increases; chromosomes visible)
- Zygotene (pairing of chromosome at some points)
- Pachytene (pairing along the entire chromosomes, shortening and thickening of chromosome; crossing over)
- Diplotene (formation of chiasmata - site of crossing over)
- Dictyotene (prolonged resting phase in oogenesis)
- Diakinesis (shortening and thickening of chromosome)
2) Metaphase I (disappearance of nuclear membrane; chromosomes alignment at equator, attachement to spindel fibre)
3) Anaphase I (separation of chromosomes)
4) Telophase I (Formation of nuclear membrane)
5) Prophase II (spindle fiber formation
6) Metaphase II (disappearance of nuclear membrane; chromosomes alignment at equator, attachement to spindel fibre)
7) Anaphase II (separation of chromatids)
8) Telophase II (Formation of nuclear membrane)
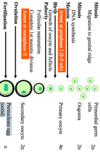
Oogenesis flow chart
1) Primordial Germ Cells (2n)
[mitosis, migration to genital ridge]
2) Oogonia (2n)
[mitosis, DNA synthesis, meiosis I (prophase I)]
3) Primary oocyte (4n, arrested at prophase I, 8-9 weeks)
[After birth: Growth of oocyte and follicle]
3) Primary oocyte (4n, larger)
[Puberty: Follicular maturation, complete meiosis I, starts meiosis II (metaphase II)]
4) Secondary oocyte (2n, arrested at metaphase II)
[ovulation]
4) Secondary oocyte (2n)
[fertilization]
5) Ootid/Pronucleate egg (n)
Characteristics of meiosis in oogenesis
– start before birth/ends after fertilization (ceiling on number of germ cells)
– arrest at prophase I and metaphase II
– Unequal cell division (polar bodies)
Ovary germ cell number with age
Decreases with age; cannot replenish
* Steep increase before birth due to mitosis
* Steep decrease after peak due to meiosis

Brief overview of follicogenesis
- primordial follicle
- > developing follicle
- > mature follicle
- > ovulated follicle
- > corpus luteum

Classification of Follicle
1) Primordial (<50 mew m; Primary oocyte, single layer of flattened granulosa cells)
2) Primary (50-100 mew m; primary oocyte, Increase size of oocyte, zona pellucida, proliferation of follicular cells)
3) Secondary (100-1000 mew m; primary oocyte, formation of antrum & cumulus)
4) Tertiary (>1000 mew m; secondary oocyte, resumption of meiosis, increase size of antrum, stigma)
Follicle structure
(from internal to external)
1) oocyte
2) microvilli
3) zona pellucida
4) basal lamina
5) granulosa
6) theca
* antrum - fluid-filled cavity adjacent to oocyte
* corona radiata, cumulus oophorus - at granulosa
Phases of follicle development
1) Preantral phase
2) Antral phase
3) Preovulatory phase
4) Ovulatory phase
5) Luteal phase


