KERBOODLE SUMMARY QUESTIONS: WM Flashcards
(90 cards)
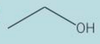
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula. Then give the sytematic name of the compound

primary alcohol
pentan-1-ol
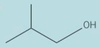
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula. Then give the systematic name of the compound

secondary alcohol
cyclohexanol
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula. Then give the systematic name of the compound

secondary alcohol
heptan-3-ol
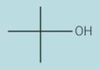
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula. Then give the systematic name of the compound

tertiary alcohol
2-methylbutan-2-ol
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula. Then give the systematic name of the compound

diol
butan-2,3-diol
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula. Then give the systematic name of the compound

primary alcohol
decan-1-ol
Give the type of function group for the skeletal formula.

ether
Why does ethanol mix with water but hexanol does not?
Hydrogen bonding between ethanol and water molecules. As the hydrocarbon chain gets longer, the importance of the -OH group relative to that of the alkyl group becomes less and hexanol is unable to mix with water.
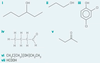
Which compound(s) is(are) alcohols?

A, B, D, E
Which compound(s) is(are) ethers?

C
Which compounds are isomers?

C and D
Which compound(s) is(are) diols?

A
Which compound do you think will be most volatile?

C
Which compound would you expect to be the most soluble in water?
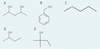
A
Which compound(s) would form carboxylic acid on refulxing with excess acidified potassium dichromate(VI)?

D
Which compound would not react on refluxing with excess acidified potassium dichromate(VI)?
E
Below are the boiling points and relative molecular masses (Mr) of a number of substances:
Use ideas about bonds between molecules to explain why ethanol has a higher boiling point than ethane

Ethanol has hydrogen bonds between molecules, ethane does not. Hydrogen bonds are the strongest intermolecular bond and so more energy is needed to break them to form gas. Therefore the boiling point is higher.
Below are the boiling points and relative molecular masses (Mr) of a number of substances:
Use ideas about bonds between molecules to explain why water has a higher boiling point than ethanol

Water forms more hydrogen bonds than ethanol so more energy is needed to break all those in water. Therefore the boiling point is higher.
Below are the boiling points and relative molecular masses (Mr) of a number of substances:
Use ideas about bonds between molecules to explain why butan-1-ol has a higher boiling point than ethanol

Both have an OH group so form hydrogen bonds. Boiling point increases down a homologous series as Mr increases. Hence butan-1-ol has a higher boiling point than ethanol
Below are the boiling points and relative molecular masses (Mr) of a number of substances:
Use ideas about bonds between molecules to explain why butan-1-ol has a higher boiling point than ethoxyethane

Butan-1-ol forms hydrogen bonds, ethoxyethane does not. Hence more energy needed to break the intermolecular bonds in butan-1-ol and so the boiling point it higher.
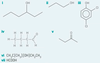
Identify a compound that would give but-1-ene on dehydration
butan-1-ol
Write an equation for a dehydration reaction that would form but-1-ene

For the compound below what would you see on addition of sodium hydroxide solution?

fizzes
For the compound below what would you see on reflux with excess potassium chromate(VII) solution?
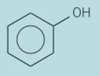
stays orange