CGP EXAM QUESTIONS: WM Flashcards
(30 cards)
Which homologous series does the molecule below belong to?
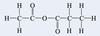
A) ketones
B) acid anhydrides
C) alcohols
D) ethers
B) acid anhydrides
Draw the full structural formula of an aldehyde with the molecular formula C5H10O

Draw the full structural formula of an ether with the molecular formula C3H8O
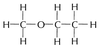
Circle the functional group in CH3CH2COOCH3 and name the homologous series to which it belongs

Class the alcohol as primary, secondary or tertiary

primary
Class the alcohol as primary, secondary or tertiary

tertiary
Class the alcohol as primary, secondary or tertiary

secondary
A student wants to produce a carboxylic acid from the molecule below.
Draw the two products which could be formed by oxidising the alcohol.


A student wants to produce a carboxylic acid from the molecule below.
Give the reagents and conditions needed to produce a carboxylic acid

Oxidising agent (e.g. acidified potassium dichromate(VI) This then needs to be heated under reflux
Write the shortened structural formulae for the products of ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) + ethanol (CH3CH2OH)
CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
Write the shortened structural formulae for the products of butan-2-ol (CH3CHOHCH2CH3) + hydrogen bromide (HBr)
CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + H2O
Write the shortened structural formulae for the products of ethanoic anhydride (CH3CO)2O + methanol (CH3OH)
CH3COOCH3 + CH3COOH
Write the shortened structural formulae for the products of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) refluxed with concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
CH2CH2 + H2O
A student carried out an experiment to make hex-1-ene from hexan-1-ol using the following procedure
1) Mix 1 cm3 hexan-1-ol with concentrated phosphoric acid in reflux apparatus, and reflux for 30 minutes
2) Once the mixture has cooled, pour it into a separating funnel, add 5 cm3 water. Stopper the separating funnel, shake it and then allow the layers to separate. Remove the aqueous layer. Dry the organic layer.
What is meant by reflux and why is it a technique sometimes used in organic chemistry?

Reflux is continuous boiling/evaporation and condensation
It’s done to prevent loss of volatile liquids while heating
A student carried out an experiment to make hex-1-ene from hexan-1-ol using the following procedure
1) Mix 1 cm3 hexan-1-ol with concentrated phosphoric acid in reflux apparatus, and reflux for 30 minutes
2) Once the mixture has cooled, pour it into a separating funnel, add 5 cm3 water. Stopper the separating funnel, shake it and then allow the layers to separate. Remove the aqueous layer. Dry the organic layer.
Explain why step 2) would give pure hex-1-ene

The unreacted hexan-1-ol is water-soluble, hex-1-ene is insoluble in water. So the hexan-1-ol dissolves in the aqueous layer and is removed when it is run off.
Drying the organic layer removes water from the product, giving pure hex-1-ene
A scientist refluxes ethyl ethanoate with dilute sodium hydroxide, and obtains impure solid sodium ethanoate
Describe how she could purify this solid by recrystallisation from an appropriate solvent.
Dissolve the solid product in a minimal amount of hot solvent
Leave the saturated solution to cool slowly and filter to remove crystals of pure product
Wash the crystals in cold solvent, then dry them
A scientist refluxes ethyl ethanoate with dilute sodium hydroxide, and obtains impure solid sodium ethanoate
What would make a solvent appropriate for the recrystallisation process in order to purify the solid?
An appropriate solvent would be one which sodium ethanoate is very soluble in when it’s hot and nearly insoluble in when it’s cold
A scientist refluxes ethyl ethanoate with dilute sodium hydroxide, and obtains impure solid sodium ethanoate
Describe the melting point range of the impure sodium ethanoate compared to the pure product
The melting point range of the impure product is lower and broader than that of the pure product
The diagram below shows a chromatogram of four unknown substances (1 to 4) and two unknowns labelled X and Y
One of the unknowns is pure and the other is a mixture
State whether each of the different substances is pure or impure.

Substances 1, 2, 3, 4, and X are pure
Substance Y is impure
The diagram below shows a chromatogram of four unknown substances (1 to 4) and two unknowns labelled X and Y
One of the unknowns is pure and the other is a mixture
Suggest which of the known substances (1 to 4) are present in the unknown that is a mixture. Explain your answer

1 and 2 since the spots present in mixture Y are at the same height (and would have the same Rf values) as 1 and 2
The diagram below shows a chromatogram of four unknown substances (1 to 4) and two unknowns labelled X and Y
One of the unknowns is pure and the other is a mixture
The solvent front on the chromatogram was measured at 8cm from the baseline, and substance 1 travelled 5.6cm. Calculate the Rf value of substance 1.

Rf = spot distance/solvent distance 5.6/8 = 0.7 (no units - because its a ratio)
The diagram below shows a chromatogram of four unknown substances (1 to 4) and two unknowns labelled X and Y
One of the unknowns is pure and the other is a mixture
All the substances on the chromatogram above are colourless. Suggest two methods that could have been used to make these colourless chemicals visible

A fluorescent dye could have been added to the TLC plate and then a UV light shone on it to reveal the spots
Or the spots could have been exposed to iodine vapour
A molecule with a molecular mass of 74 produces the IR spectrum shown below
Which bonds are responsible for peaks A and B?

A: O-H bond in carboxylic acid
B: C=O bond in aldehyde, ketone, acid or ester
A molecule with a molecular mass of 74 produces the IR spectrum shown below
Give the molecular formula and name of this molecule. Explain your answer

The spectrum suggests it’s a carboxylic acid - it’s got a COOH group
This group has a mass of 45, so the rest of the molecule has a mass of 29 (79 - 45), which is likely to be C2H5
So the molecule could be C2H5COOH - propanoic acid








