Introduction to Antibiotics Flashcards
1
Q

A

2
Q

A

3
Q
A

4
Q

A

5
Q

A

6
Q

A

7
Q
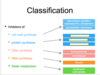
Resistance
A
- Intrinsic
- Acquired
8
Q
Ways that Antibiotics are Used
A
- Empiric therapy
- Definitive therapy
- Prophylactic therapy
9
Q
Empiric Therapy
A
- Determine that the patient is (or may be) infected
- Identify the site(s) of infection
- Formulate a list of potential pathogens
- Anticipate the susceptibilities of the presumed pathogens
- Obtain appropriate specimens for laboratory examination
10
Q
Pharmacokinetics
A
- absorption
- distribution (e.g., CSF)
- elimination
- metabolism/excretion (e.g. hepatic)
- creatinine clearance
11
Q
Pharmacodynamics
A
- antimicrobial effect
- toxicity (adverse effects)
12
Q
Pharmacodynamic Factors
A
• MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration)
- smallest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits growth
- used to define susceptibility
- this is determined based on serum concentration - may not apply to the site of infection
• Post-antibiotic effect (PAE)
- persistent suppression of growth after removal of antibiotic
13
Q
Peak conc./MIC ratio vs. Time Above MIC
A

14
Q
Host Factors
A
- Successful treatment of an infection often requires more than just the correct antibiotic
- Immunologic factors: intact innate, humoral, and/or cellular immunity
- Local factors:
- privileged compartments: CSF, bone, prostate, eye
- foreign bodies: catheters, vascular grafts, CNS shunts, prosthetic valves, prosthetic joints
- impaired diffusion: poor diffusion of antibiotics into abscess cavities
15
Q
Mechanisms of Adverse Reactions
A
- Direct effects
- aminoglycoside toxicity: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity
- bone marrow suppression
- drug-induced hepatitis
- Hypersensitivity
• e.g., anaphylaxis, serum sickness, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Alterations of the microbiota
• e.g. C. difficile-associated colitis
- Drug interactions
• e.g. warfarin, immunosuppressives
16
Q
Drug interactions: warfarin
A
- Administration of antibiotic to patient anticoagulated with warfarin may enhance anticoagulant effect
- Antibiotics can alter hepatic vitamin K metabolism or alter absorption by disrupting gut organisms
17
Q
Prevention / Prophylaxis
A
- Following exposure to a specific infectious agent with risk of serious infection
- Immunocompromised patients at high risk of infection
- post transplantation, advanced HIV, splenectomy
- Following certain surgical procedures
- Prevention of endocarditis in patients with underlying cardiac conditions following dental procedures


